The Impact of Zoning Laws on Urban Green Spaces.
Zoning laws play a pivotal role in determining land use in urban areas, regulating aspects ranging from residential developments to commercial centers. These laws also significantly influence urban green spaces, which offer numerous benefits and contribute to the overall livability and environmental health of cities.
This article examines the relationship between zoning laws and urban green spaces, addressing their various types, significance, challenges, and potential improvements to zoning practices that can promote greener, more sustainable urban environments.
This exploration highlights how strategic zoning can enhance urban living by preserving and developing green spaces.
What Are Zoning Laws?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
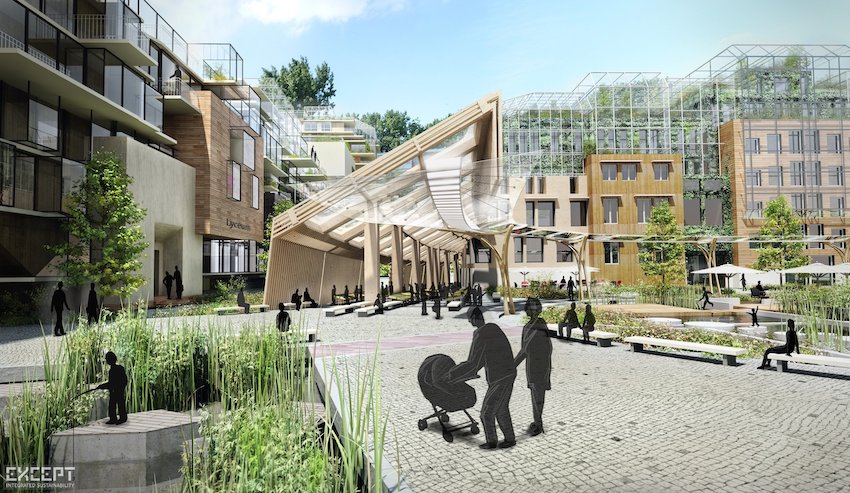
Zoning laws are regulations instituted by local governments to govern the utilization of land within designated areas, with the objective of balancing diverse land use requirements such as residential, commercial, and public facilities. These regulations are a core aspect of urban planning and have substantial impacts on land development and property rights.
These regulations not only affect property values but also play a crucial role in shaping urban landscapes and influencing the overall quality of life for residents, thus representing a fundamental component of urban planning and community development. Furthermore, zoning codes and zoning classifications established by the planning commission ensure orderly land use and infrastructure development.
Additionally, zoning regulations have significant implications for environmental considerations, including the preservation of urban green spaces and biodiversity, as they dictate the permitted types of developments within various zoning districts.
How Do Zoning Laws Affect Land Use and Environmental Impact?
Zoning laws are instrumental in determining land use by establishing regulations that govern housing density, permissible building types, and the allocation of open space within urban environments. These regulations significantly influence the development and preservation of urban landscapes by dictating the locations of residential areas, commercial entities, and recreational spaces. By considering factors like urban sprawl and urban aesthetics, these laws aim to create a balanced and sustainable urban environment.
This structured approach to city planning takes into account environmental considerations, such as climate adaptation and habitat preservation, and the well-being of the community.
By specifying the parameters for the number of homes that can be constructed on a given parcel of land, zoning laws directly impact housing density, thereby influencing the character of neighborhoods and the availability of affordable housing. This also addresses land use conflict and proactively manages urban sprawl.
Furthermore, zoning plays a critical role in commercial development by designating specific areas for businesses, which in turn affects job availability and the vitality of local economies.
A thoughtful allocation of green spaces not only enhances the aesthetic quality of urban areas but also promotes biodiversity and mitigates the urban heat island effect. This underscores the necessity of balancing development needs with environmental sustainability and maintaining ecological balance.
As cities continue to evolve, the relationship between zoning laws and land use patterns remains essential for achieving a sustainable future.
What Are Urban Green Spaces?
Urban green spaces are defined as areas within urban environments that are designated for vegetation and open space, including public parks, community gardens, green rooftops, green corridors, and urban forestry.
These areas serve multiple ecological, social, and health-related functions. They not only enhance the aesthetic appeal and recreational opportunities available to residents but also play a crucial role in promoting biodiversity, improving air quality, enhancing urban resilience, and mitigating the effects of urban heat islands. These functions contribute to the overall urban ecology and sustainability.
Consequently, urban green spaces significantly contribute to the overall sustainability and livability of cities.
Types of Urban Green Spaces
Urban green spaces can be classified into several categories, including public parks, community gardens, green roofs, greenways, and green corridors, each serving distinct functions that enhance urban ecology and improve the quality of life for residents.
For example, public parks provide recreational areas for leisure activities, greenbelt areas protect large stretches of natural landscapes, while community gardens promote urban agriculture and encourage citizen participation. Urban agriculture, in particular, fosters community well-being and environmental stewardship.
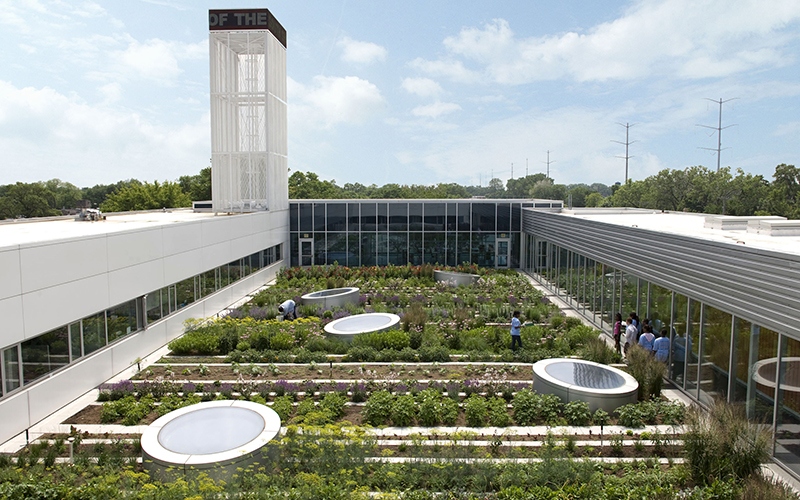
Green roofs, typically located atop commercial buildings, are instrumental in reducing energy costs, managing stormwater, and providing habitats for urban wildlife, thus contributing to biodiversity within predominantly concrete environments.
Similarly, green corridors play a vital role in facilitating wildlife movement and ensuring ecological connectivity, enabling species to navigate urban barriers safely.
These green spaces not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also promote community engagement by offering venues for social activities and events. Each type of urban green space is essential for enriching urban life, fostering connections between individuals and nature, and ultimately contributing to a healthier urban ecosystem. This also aligns with goals of social equity and public engagement in urban development.
Why Are Urban Green Spaces Important?
Urban green spaces are essential for promoting ecological balance and enhancing urban environments, offering a wide array of benefits that include improving public health and supporting biodiversity conservation.
These areas function as critical habitats for urban wildlife, contribute to climate adaptation, environmental justice, and provide recreational opportunities that foster community well-being.
Consequently, they play a fundamental role in the advancement of sustainable urban development, land conservation, and ecological footprint reduction.
Benefits of Urban Green Spaces
The advantages of urban green spaces are extensive and multifaceted, significantly contributing to public health, environmental sustainability, and social equity within communities. These spaces help mitigate noise pollution and enhance air quality, provide recreational opportunities, and improve mental well-being, thereby fostering a sense of community and belonging among residents.
Research indicates that access to greenery can reduce stress levels by as much as 30%, underscoring the psychological benefits associated with spending time in well-maintained parks and gardens. Moreover, public health is significantly improved through regular interaction with urban green spaces.
Furthermore, these green spaces play a vital role in addressing urban heat islands, which can elevate temperatures in cities by 5 to 7 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature reduction not only benefits the environment but also supports public health by decreasing the incidence of heat-related illnesses.
Urban vegetation is essential for supporting biodiversity, offering habitats for various species, which is critical for maintaining ecological balance and addressing habitat fragmentation. As communities prioritize the development of accessible green areas, they also promote social equity, ensuring that all residents, regardless of their background, can reap the benefits of a healthier and more sustainable environment. This is crucial for enhancing urban resilience and overall community development.
How Do Zoning Laws Impact Urban Green Spaces?
.jpg_01.jpeg)
Zoning laws significantly influence urban green spaces by governing their preservation, development, and integration within the larger urban environment. Effective zoning ordinances and land use policies are essential for safeguarding these green spaces.
By implementing carefully structured zoning regulations, local governments can effectively safeguard and maintain these vital areas, thereby promoting environmental justice and supporting community development initiatives. This ensures that public amenities and recreational areas are equitably distributed across different neighborhoods.
1. Zoning for Green Space Preservation
Zoning for green space preservation entails the implementation of regulations designed to protect existing urban green areas from encroachment and development, thereby ensuring their availability for future generations. This approach not only maintains ecological balance but also promotes community well-being by providing accessible recreational spaces and minimizing the ecological footprint of urban areas.
Cities such as New York and San Francisco have successfully incorporated these zoning measures into their land use planning frameworks. For example, New York’s zoning laws include specific regulations focused on the preservation of parks and greenbelts, while also incentivizing developers to create green roofs and open spaces.
San Francisco, on the other hand, has enacted policies that protect its cherished parks, ensuring they remain accessible to the public in the face of urban expansion.
These examples demonstrate how effective zoning regulations can mitigate environmental impacts, enhance biodiversity, and promote healthy lifestyles, underscoring the significance of comprehensive land use planning and environmental regulations in preserving green spaces.
2. Zoning for Green Space Development
Zoning for green space development is centered on the creation of new urban green spaces through zoning regulations that promote the establishment of parks, community gardens, and other green infrastructure projects. This proactive strategy not only enhances urban ecology but also encourages social inclusivity and active citizen participation in community initiatives, thereby fostering community resilience and urban renewal.
The process involves collaborative efforts with local organizations and stakeholders to maximize the positive impact of these green spaces on the community. By engaging with neighborhood groups and non-profit organizations, municipalities can co-develop plans that accurately reflect the needs and aspirations of residents. This collaboration also supports nature-based solutions and environmental stewardship initiatives within urban settings.
Strategies such as establishing joint-use agreements for schoolyards or transforming vacant lots into community gardens effectively utilize underused spaces while promoting environmental stewardship and local ecology. These initiatives are part of broader urban regeneration efforts aimed at improving city sustainability.
These partnerships can yield innovative solutions that prioritize equitable access to public parks and green infrastructure, ensuring that all community members benefit from an enriched urban landscape, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life.
3. Zoning for Mixed-Use Development
Zoning for mixed-use development effectively integrates residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within urban environments, facilitating the inclusion of green spaces in diverse neighborhoods. This approach not only promotes walkability and community resilience but also enhances property values by creating vibrant and appealing city ecosystems. Furthermore, the integration of green infrastructure within mixed-use developments supports urban sustainability and quality of life improvements.
By strategically planning for higher housing density in conjunction with commercial hubs, urban areas can foster a sense of community while reducing reliance on automobiles, thereby minimizing environmental impact. When individuals reside, work, and engage in leisure activities in close proximity, it fosters social connections, strengthens local economies, and supports urban sustainability. Additionally, such planning contributes to reducing the urban heat island effect and improving walkability.
The incorporation of green spaces contributes significantly to mental well-being, biodiversity, and provides residents with opportunities for leisure and recreation, ultimately enhancing their overall quality of life. As cities continue to expand, the implementation of such zoning practices becomes essential for sustainable development, environmental stewardship, and for creating inclusive spaces that cater to diverse populations.
Challenges of Implementing Zoning Laws for Urban Green Spaces
The implementation of zoning laws for urban green spaces presents various challenges, including conflicts related to land use, limited availability of space, and the necessity for effective enforcement and monitoring of regulations.
These obstacles may impede the establishment and maintenance of urban green spaces, thereby affecting community well-being and environmental sustainability.
1. Limited Space, High Land Costs, and Land Use Conflict
Limited space, high land costs, and land use conflicts present significant challenges to the creation and preservation of urban green spaces, especially in densely populated cities where the demand for real estate and property rights issues are substantial.
Zoning laws and land use regulations must effectively address these constraints to ensure that adequate community spaces are available without compromising property development and urban planning goals.
As urban areas continue to expand, urban planners and policymakers are tasked with the complex responsibility of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. This challenge encompasses not only the creation of new parks, public amenities, and recreational areas but also the protection of existing green spaces from encroachment by commercial and residential developments.
Innovative strategies, such as vertical gardens, green roofs, and rooftop parks, can optimize the use of limited land while enhancing biodiversity and improving the quality of life for residents.
Additionally, incentivizing developers to incorporate green spaces, community gardening, and green infrastructure into their projects through tax incentives or density bonuses may promote a more harmonious relationship between urban development and environmental stewardship.
2. Conflicting Interests and Priorities
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Conflicting interests and priorities among stakeholders can significantly complicate the implementation of zoning laws for urban green spaces, as various communities may prioritize development, housing, or preservation differently. Effective engagement with stakeholders is essential for balancing these interests and ensuring that green spaces are maintained and valued within the context of urban planning and city planning initiatives.
In many instances, community development efforts are most successful when local residents, businesses, and governmental agencies collaborate to create inclusive plans that address diverse needs. For example, in a neighborhood undergoing revitalization, a series of public forums and opportunities for public participation may effectively engage local voices, allowing them to articulate concerns regarding potential housing developments that could encroach upon critical park areas and open spaces.
As a result, a consensus can emerge, leading to innovative solutions such as mixed-use developments that incorporate green spaces, which are vital for enhancing the overall quality of life and urban aesthetics. This collaborative approach not only builds trust among stakeholders but also fosters a sense of ownership and pride within the community.
3. Lack of Enforcement and Monitoring
The inadequate enforcement and monitoring of zoning laws present a significant challenge to the efficacy of regulations aimed at protecting urban green spaces. In the absence of proper oversight, violations may occur, resulting in the degradation of these essential areas and undermining community initiatives for sustainable urban development and urban resilience.
This situation poses a dual threat: it not only jeopardizes biodiversity but also adversely affects the quality of life for residents who depend on these green spaces for recreation and relaxation.
Local governments can enhance compliance by instituting regular inspections and establishing clear penalties for violations, thereby reinforcing the importance of adherence to zoning regulations.
Moreover, community engagement and public engagement play a crucial role; fostering a sense of ownership among residents can encourage them to report infractions and actively participate in monitoring efforts.
Establishing accessible channels for communication between local agencies and the public can further strengthen collaborative efforts, ensuring that zoning laws and zoning codes effectively fulfill their intended purpose of preserving vital urban landscapes, urban habitats, and local ecosystems.
How Can Zoning Laws Be Improved to Better Support Urban Green Spaces?
Enhancing zoning laws to more effectively support urban green spaces necessitates a comprehensive approach that incorporates improved community engagement, revised zoning regulations, and a steadfast commitment to sustainable development initiatives and environmental regulations.
By integrating the insights of community stakeholders and prioritizing green infrastructure, local governments, and planning commissions can achieve a more harmonious balance between urban development and environmental preservation.
1. Incorporating Green Space Requirements in Zoning Regulations
Incorporating green space requirements into zoning regulations represents a proactive strategy that ensures urban development includes essential allocations for parks and green areas, thereby promoting environmental justice, community well-being, and enhancing community resilience. This approach not only improves livability but also reduces the ecological footprint associated with urbanization.
By mandating a specific percentage of land to be designated for green spaces, zoning regulations can effectively transform neighborhoods into more sustainable environments.
For example, cities such as Portland and New York have successfully integrated such mandates into their master plans, resulting in vibrant community parks that function as essential recreational areas and habitats for biodiversity.
These developments not only enhance air quality but also ensure equitable access to nature for all residents, effectively addressing the disparities often observed in underserved communities.
Along with promoting sound land use planning, these regulations serve as a fundamental component for fostering community engagement and enhancing urban resilience.
2. Collaborating with Community Stakeholders
Collaboration with community stakeholders is essential for the development of effective zoning laws that support urban green spaces. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and ensures that diverse perspectives are integrated into the planning process.
Involving residents, businesses, and local organizations can lead to more equitable and sustainable outcomes.
Such collaboration enhances the decision-making process while building trust among community members, thus encouraging their active participation in ongoing discussions regarding land use and development. By incorporating local knowledge and preferences, the formulation of zoning laws can more accurately reflect the actual needs and desires of the community.
Engaging various stakeholders during the implementation phase is critical for identifying potential obstacles and opportunities, facilitating a smoother transition towards greener urban environments and ensuring the integration of nature-based solutions.
Consequently, community engagement plays a pivotal role in cultivating not only green spaces but also a vibrant community spirit that values shared resources and promotes inclusive growth.
3. Regular Review and Updates of Zoning Laws
Regular review and updates of zoning laws are essential to ensure their continued effectiveness in promoting urban green spaces amidst the evolving challenges of urban landscapes. By adapting regulations to align with current environmental needs and community aspirations, municipalities can strengthen their commitment to sustainable urbanism.
Such evaluations not only identify deficiencies in existing codes but also create opportunities to incorporate innovative design concepts that prioritize ecological health, social equity, and urban biodiversity. The process typically involves engaging a variety of stakeholders, including community members, urban planners, and environmental experts, to gather a wide range of perspectives.
As cities confront issues such as overcrowding and climate change, these periodic assessments become critical in effectively redistributing land use. This approach facilitates the introduction of increased greenery, wildlife corridors, and recreational spaces, thereby enhancing residents’ quality of life and fostering a sense of community.
Furthermore, updating zoning laws can enable the integration of emerging technologies that contribute to environmentally-friendly urban developments.
Frequently Asked Questions
.jpg_11.jpeg)
What are zoning laws and how do they impact urban green spaces and urban ecology?
Zoning laws are regulations set by local governments to control the use of land and buildings in specific areas. They can impact urban green spaces and urban ecology by designating areas for recreational, conservation, or development purposes.
Are zoning laws and zoning classifications the same in all cities?
No, zoning laws and zoning classifications vary from city to city depending on their unique needs and priorities. Some cities may have stricter zoning laws to protect green spaces and greenbelts, while others may have more lenient laws to allow for more development.
Do zoning laws only affect public green spaces and open space preservation?
No, zoning laws also impact private green spaces such as backyards and gardens. These laws can dictate the size and type of greenery allowed in residential areas, as well as regulations for commercial and industrial properties. Moreover, zoning classifications and zoning codes often influence urban planning and land use, affecting the overall urban landscape.
Can zoning laws be changed to benefit urban green spaces and public parks?
Yes, zoning laws can be changed by local governments through a public process, often involving public participation and community engagement. This can include rezoning certain areas to promote the preservation or creation of green spaces, or implementing incentives for developers to include green spaces and public amenities in their mixed-use developments.
Do zoning laws have any negative impacts on urban green spaces and urban biodiversity?
Yes, zoning laws can have negative impacts on urban green spaces by allowing for excessive land development or prohibiting the use of certain areas for green spaces. They can also contribute to urban sprawl, gentrification, and displacement of low-income communities, which may decrease access to green spaces and affect environmental justice. Such issues can further affect urban ecology, ecological balance, and social equity.
How can I get involved in advocating for green spaces and ecological sustainability in my city’s zoning laws?
You can get involved in urban renewal efforts by attending local government meetings, joining community groups focused on promoting green spaces, and contacting your representatives to voice your concerns about land use policies. You can also educate yourself and others about the importance of green spaces, urban forestry, and their benefits for urban areas, including improving air quality and mitigating the urban heat island effect. Engaging in community gardening and supporting green infrastructure initiatives can enhance community resilience and quality of life.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário