Vertical Gardens: Transforming Urban Buildings from the Inside Out.
Vertical gardens are transforming the perception of urban spaces by converting uninspired buildings into vibrant green environments, promoting urban greening and eco-friendly design.
This article examines various types of vertical gardens, including green walls, tower gardens, and pocket gardens, each possessing distinct characteristics and functionalities.
It emphasizes the numerous advantages these gardens present, such as improving air quality, increasing biodiversity, and enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Furthermore, a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to establish your own vertical garden, including plant selection and maintenance requirements, will be included.
Explore the possibilities of reintroducing nature into our concrete landscapes, promoting climate resilience and urban ecology.
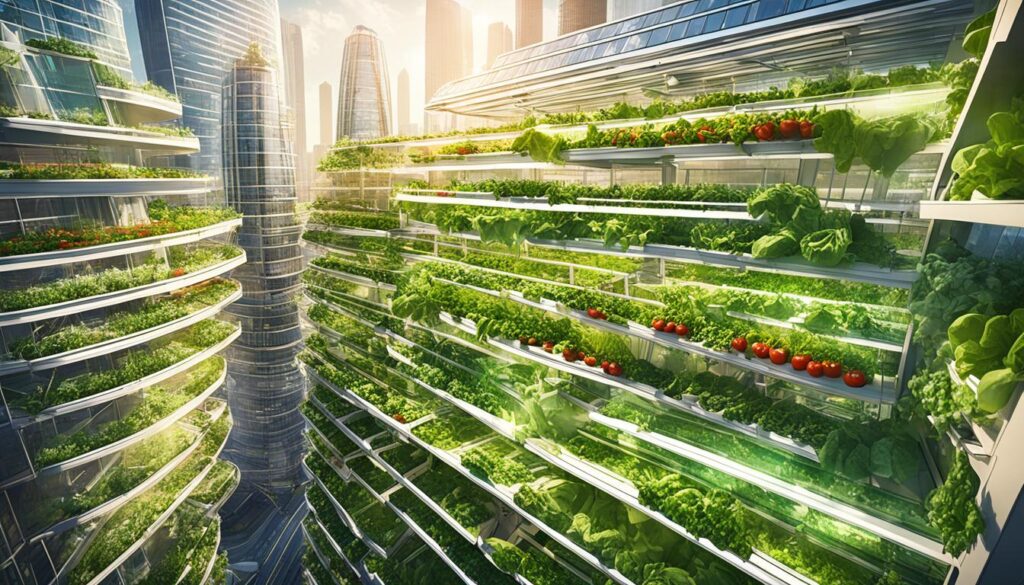
Types of Vertical Gardens
.jpg_00.jpeg)
Vertical gardens, commonly referred to as living walls, represent an innovative approach to urban greening that encompasses a variety of installations on urban buildings and residential landscapes, contributing to urban revitalization and environmental restoration.
These green architectural solutions not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban environments but also provide significant environmental benefits, including improved air quality, increased biodiversity, and noise reduction.
By incorporating indoor plants and sustainable design principles, vertical gardens offer practical applications in both commercial and public spaces, enhancing indoor ecosystems and promoting wellness design.
The various types of vertical gardens, such as:
- green walls
- pocket gardens
- trellis gardens
- tower gardens
facilitate creative gardening while maximizing space efficiency, making them an optimal choice for urban residents aiming to enhance their surroundings through space-saving solutions and urban agriculture.
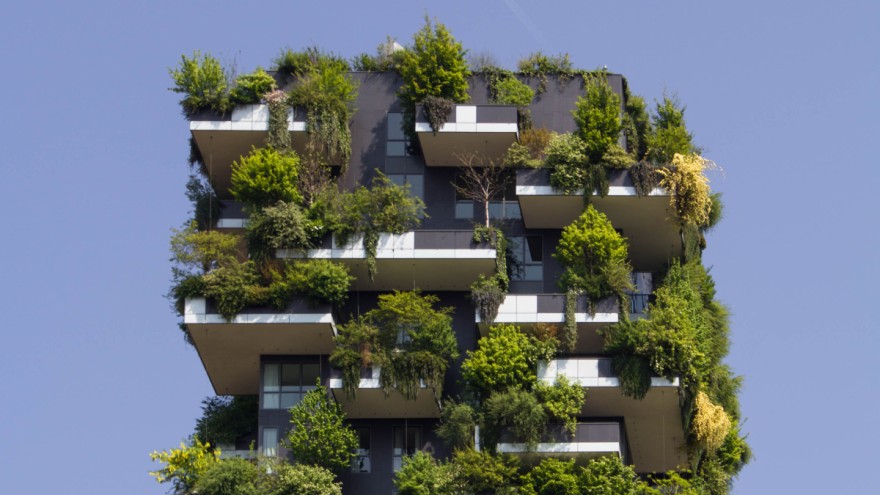
1. Green Walls
Green walls represent a sophisticated form of vertical gardening that employs a structured framework to support a diverse array of plants, thereby enhancing air quality, promoting air purification, and contributing to the aesthetic value of urban settings.
These innovative installations serve as striking focal points within any landscape, while simultaneously promoting biodiversity by providing habitats for various species. The careful selection of plant species is essential, as it necessitates choosing varieties that thrive under specific light and climatic conditions, all while ensuring year-round visual interest and seasonal planting.
Maintenance is generally straightforward, typically involving periodic watering and pruning, which facilitates easy upkeep. Furthermore, the incorporation of eco-friendly materials in their construction, such as recycled plastics and sustainably sourced wood, underscores a commitment to environmental responsibility, thereby reinforcing their status as a sustainable architectural feature.
2. Living Walls
Living walls represent an innovative aspect of green architecture, incorporating a diverse range of plants into vertical structures, promoting biophilic design and plant care. This approach not only promotes biophilic design but also enhances the overall urban landscape.
These vertical gardens serve to beautify spaces while providing numerous environmental benefits, including improved air quality, reduced noise pollution, and an increase in urban biodiversity. By integrating living walls into community settings, individuals can cultivate greater engagement and awareness regarding environmental sustainability and urban living.
Installation techniques for living walls may vary, often employing modular systems that facilitate easier maintenance, adaptability to various surfaces, and structural support. It is essential to select the appropriate plants; careful consideration of light conditions is necessary to ensure the greenery thrives.
This fosters a vibrant and sustainable ecosystem that benefits both the community and the surrounding environment.
3. Pocket Gardens
Pocket gardens are compact vertical gardens specifically designed to optimize small spaces, providing a unique solution for urban residents to engage in urban agriculture, promote biodiversity, and enhance urban greening.
These gardens can be seamlessly integrated into both residential balconies and commercial building facades, creating a vibrant contrast against concrete surroundings and promoting nature connection. By incorporating such green spaces, urban environments can enhance their ecological footprint, thereby improving air quality and supporting a diverse range of plant and animal life, including natural habitats and urban biodiversity.
Additionally, these gardens serve as a source of fresh produce, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with food transportation.
For successful growth, it is imperative to follow comprehensive horticulture practices:
- Select appropriate plants that thrive in vertical configurations,
- Utilize high-quality soil enriched with organic matter,
- Maintain proper hydration while ensuring effective drainage.
Regular monitoring of the garden’s health will facilitate robust plant development and contribute to a thriving pocket ecosystem.
4. Trellis Gardens
Trellis gardens employ vertical structures to support climbing plants, thereby creating a dynamic vertical ecosystem that enhances functional planting, contributes to climate control, and promotes green infrastructure.
This innovative approach not only optimizes limited space in urban environments but also facilitates passive cooling and evapotranspiration, as the plants provide shade and reduce the reliance on air conditioning. The layers of foliage function as a natural sound barrier, attenuating urban noise and fostering a more tranquil environment.
Incorporating trellis gardens into comprehensive urban design strategies can enhance overall air quality while promoting biodiversity. Additionally, they frequently serve as a vital component of community gardens, encouraging collaboration among residents and cultivating a shared sense of stewardship for green spaces. This communal engagement ultimately strengthens social ties and supports sustainable living practices.
5. Tower Gardens
Tower gardens represent a contemporary approach to vertical farming, facilitating efficient space utilization and the establishment of self-sustaining systems that contribute to urban food systems.
These innovative structures allow individuals to cultivate a diverse array of plants, including vegetables and herbs, in a compact format, making them well-suited for both small backyards and urban environments, thus promoting urban agriculture and horticulture.
The unique irrigation systems utilized in tower gardens ensure even distribution of water through a recirculating method, which minimizes waste while promoting healthy root development and efficient water use.
Maintenance is relatively straightforward, requiring regular monitoring of nutrient levels and periodic pruning to ensure optimal growth.
By promoting local food production, tower gardens not only reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting food over long distances but also enhance community well-being by increasing access to fresh produce.
Benefits of Vertical Gardens
.jpg_01.jpeg)
Vertical gardens provide numerous advantages, transforming urban environments into vibrant green landscapes that substantially enhance air quality, mitigate the urban heat island effect, and improve overall aesthetics through innovative design and urban greening.
These innovative green infrastructures not only benefit the well-being of urban residents but also promote biodiversity, offer insulation for buildings within metropolitan areas, and contribute to energy efficiency.
By incorporating nature into architectural designs, vertical gardens advance environmental sustainability, create opportunities for urban agriculture, and enhance community involvement, thereby fostering community engagement and promoting wellness.
The functional benefits of vertical gardens extend well beyond mere aesthetics, positioning them as a vital component of sustainable urbanism, effective city planning, and productive urban ecology.
1. Improves Air Quality
One of the most significant advantages of vertical gardens is their capacity to enhance air quality through natural air purification processes and stress reduction, thereby creating healthier urban environments for residents.
These innovative green structures function as natural filters, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen while concurrently capturing harmful pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter. Research indicates that plants can eliminate up to 87% of air toxins within a 24-hour period, offering a remarkable solution to address urban air pollution.
The implementation of vertical gardens in densely populated areas not only contributes to improved air quality but also mitigates the urban heat island effect, resulting in enhanced overall environmental benefits and contributing to climate adaptation strategies.
As cities increasingly invest in these green spaces, the positive impact on air quality becomes increasingly apparent, fostering healthier communities and promoting biodiversity within urban landscapes.
2. Reduces Urban Heat Island Effect
Vertical gardens play a vital role in mitigating the urban heat island effect by providing natural shade and cooling through the process of evapotranspiration, thereby supporting climate adaptation strategies and fostering urban resilience.
These innovative green structures enhance air quality while simultaneously attracting biodiversity, which contributes to the improvement of local ecosystems.
By incorporating vertical gardens into urban design, cities can achieve substantial energy efficiency gains, as these structures help reduce reliance on air conditioning systems during warmer months and contribute to passive design strategies.
The process of evapotranspiration not only cools the ambient air but also enhances the overall thermal performance of buildings, providing insulation against extreme temperatures and contributing to climate resilience.
Consequently, the passive cooling techniques offered by vertical gardens highlight the significance of sustainable practices in architecture and urban planning, fostering a healthier and more resilient environment for communities.
3. Increases Biodiversity
The incorporation of diverse plant species in vertical gardens significantly contributes to urban biodiversity, facilitates ecological restoration in densely populated areas, and supports habitat creation for various species.
These innovative structures not only create aesthetically pleasing green spaces but also serve as crucial habitats for a variety of wildlife, including birds, insects, and other small organisms. For example, successful initiatives in cities such as Sydney and Singapore have implemented vertical gardens that attract pollinators and provide refuge for native species, thereby promoting the resurgence of local fauna and enhancing urban biodiversity.
The diverse plant selections within these gardens help cultivate ecosystems that enhance air quality, manage stormwater, and reduce the urban heat island effect in urban environments, ultimately improving the resilience of cities to climate change. Furthermore, the integration of such greenery plays an essential role in connecting fragmented habitats, allowing wildlife to thrive within urban landscapes.
4. Aesthetically Pleasing
The aesthetics of vertical gardens are undeniably impressive, presenting a visually striking integration of nature within urban architecture that significantly enhances the overall appeal of both residential and commercial spaces, thereby contributing to green architecture.
These living walls not only offer a vibrant palette that evolves with the seasons but also introduce a diverse range of textures, creating a dynamic and engaging visual experience. The use of seasonal planting and various vegetation types promotes a sensory experience. As various plants coexist harmoniously, the resulting tapestry fosters a profound connection between residents and their environment.
This design versatility enables communities to incorporate greenery in innovative ways, transforming uninspiring surfaces into captivating displays that encourage social interaction.
Such visually compelling spaces are essential for urban renewal, as they can foster community pride and facilitate social engagement, thereby amplifying the effectiveness of neighborhood revitalization efforts and promoting community gardens.
5. Provides Insulation
Vertical gardens serve as an effective means of insulation for buildings, thereby enhancing energy efficiency by regulating indoor temperatures and lowering heating and cooling costs.
These installations function as a natural barrier against external temperature fluctuations, enabling occupants to enjoy more comfortable indoor environments without an excessive reliance on mechanical systems. Moreover, their capacity to absorb sunlight contributes to a reduction in solar heat gain, further decreasing the dependence on air conditioning during warmer months and enhancing energy efficiency.
As architects and designers increasingly acknowledge the importance of integrating sustainable elements into construction, the incorporation of vertical gardens has emerged as a hallmark of environmentally responsible building practices. Plus their immediate thermal benefits, these living walls enhance urban aesthetics, promote biodiversity, and capture carbon, thereby reinforcing the overall sustainability of contemporary architecture.
How to Create a Vertical Garden
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Establishing a vertical garden requires meticulous planning and thoughtful consideration of several factors, including installation techniques, plant selection, and maintenance requirements, to foster a thriving ecosystem within urban environments. Incorporating green infrastructure and design elements can significantly impact the success of your vertical garden.
By adhering to sustainable practices and utilizing green technology, individuals can transform walls into vibrant displays of indoor plants, thereby contributing to urban greening initiatives, improving air quality, and enhancing indoor ecosystems.
Whether applied in residential buildings or commercial spaces, the implementation of a vertical garden can have a profound impact on urban ecology, urban agriculture, and the overall well-being of the community.
1. Choose the Right Location
Selecting the appropriate location for a vertical garden is essential, as it significantly impacts plant growth, light conditions, and the overall success of the installation. Light exposure, microclimates, and the availability of structural support are key factors to consider.
Several factors must be considered when determining the ideal site.
- Sunlight exposure is critical; the orientation of the wall can influence the amount of light the plants receive throughout the day. Light requirements vary among plant species.
- It is also important to analyze the microclimate in the vicinity, as nearby structures and trees may cast shadows that could impede growth.
- Additionally, assessing wind exposure is crucial, as strong gusts have the potential to damage fragile plants and lead to rapid soil desiccation.
Furthermore, evaluating the availability of support structures, such as trellises or wall mounts, is necessary to ensure that the garden is both visually appealing and sufficiently robust to accommodate the diverse growth of the selected plants, facilitating vertical structures.
2. Determine the Type of Vertical Garden
Determining the appropriate type of vertical garden to establish requires a comprehensive understanding of specific objectives and the resources available. This foundation facilitates the implementation of vertical ecosystems and biophilic design that effectively address functional planting needs.
With a wide range of options, including wall-mounted planters, freestanding structures, and hydroponic systems, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their spatial constraints and intended applications, utilizing modular systems and space-saving solutions.
For those interested in urban agriculture, vertical gardens can be designed to serve not only decorative purposes but also practical functions, such as the cultivation of fresh produce in limited spaces. Integrating vertical farming techniques can maximize yield in small areas.
Incorporating sustainable practices during the planning phase can significantly reduce water usage and enhance biodiversity, thereby creating an optimal environment for successful cultivation in one’s backyard or balcony. Utilizing soil-less growing methods such as hydroponics can contribute to efficient water use.
3. Select Suitable Plants
Selecting appropriate plants is crucial for the success of a vertical garden, as it ensures optimal growth, health, and sustainability within the gardening ecosystem.
When undertaking this endeavor, it is essential to consider critical factors such as soil health, light conditions, and moisture retention.
Soil health significantly influences nutrient availability and microbial activity, both of which are vital for robust plant development. Understanding light conditions is important for selecting species that will thrive in specific environments, whether they are exposed to bright sunlight or situated in shaded areas. Assessing soil composition and plant health are crucial steps in this process.
Moreover, attention to moisture retention is of utmost importance; certain plants require consistently damp soil while others thrive in drier conditions. By meticulously evaluating these factors, gardeners can establish a flourishing vertical space that promotes both biodiversity and aesthetic appeal.
4. Install Irrigation System
The installation of an efficient irrigation system is a crucial step in the maintenance of a vertical garden, as it ensures adequate moisture retention and promotes healthy plant growth.
By exploring options such as drip irrigation and automatic timers, one can establish a sustainable watering regimen that minimizes water waste while providing the necessary hydration for a diverse range of plants. Effective irrigation systems are key to maintaining a healthy garden.
Drip irrigation systems are particularly advantageous as they deliver water directly to the root zone, thereby reducing evaporation and runoff, making them an environmentally friendly option. These systems also support sustainable practices in garden maintenance.
Additionally, automatic timers can enhance the watering process by ensuring that plants receive consistent moisture without the need for constant supervision. Collectively, these methods not only reduce the maintenance burden but also contribute to a flourishing vertical garden that demonstrates a commitment to sustainable practices and environmental benefits.
5. Maintain and Care for the Vertical Garden
Regular maintenance and care are essential for the longevity and health of a vertical garden, ensuring that plants thrive and continue to provide significant environmental benefits. Adhering to proper plant care routines is crucial for success.
To cultivate a flourishing vertical garden, it is imperative to prioritize essential tasks such as strategic pruning, appropriate fertilization, and effective pest management. These elements are integral to successful horticulture practices.
Pruning plays a critical role in promoting healthy growth by removing dead or overgrown sections, which enhances air circulation and can significantly reduce the risk of disease. Proper fertilization increases nutrient availability, thereby fostering vigorous plant development and supporting plant health.
Equally important is pest management; diligent monitoring and prompt action against infestations are necessary to protect the integrity of the garden and ensure optimal plant growth.
By consistently attending to these maintenance tasks, garden enthusiasts not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of their vertical gardens but also promote sustainability, making a positive contribution to the urban ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
.jpg_11.jpeg)
What is a vertical garden?
A vertical garden, also known as a living wall or green wall, is a type of garden where plants are grown vertically on a structure attached to a building or wall. It can be either indoors or outdoors and is a popular method of urban gardening and interior landscaping.
How do vertical gardens transform urban buildings?
Vertical gardens can transform urban buildings in multiple ways. They can improve air quality, reduce energy consumption, provide insulation, and add aesthetic value to a building. These gardens also contribute to sustainable practices and reduce the ecological footprint of urban spaces.
What are the benefits of vertical gardens?
The benefits of vertical gardens include improving air quality, reducing energy consumption, providing insulation, adding aesthetic value, and promoting biodiversity in urban areas. They also create a sense of well-being, contribute to stress reduction and productivity enhancement, and can increase property value.
What types of plants are suitable for vertical gardens?
There are many types of plants that are suitable for vertical gardens, including succulents, ferns, herbs, vegetables, and even small fruit trees. Selecting ornamental plants and those suited to vertical plant systems is key. It is important to choose plants that can thrive in the specific conditions of the vertical garden, such as lighting and watering.
Do vertical gardens require a lot of maintenance?
The maintenance required for a vertical garden depends on the type of plants used, plant care, and the specific conditions of the garden. Generally, vertical gardens, including living walls and green walls, require regular watering, pruning, and fertilizing, but there are low-maintenance options available. Factors like air purification, soil-less growing, and vertical plant systems can influence the maintenance requirements. Hydroponics and efficient irrigation systems can also be employed to reduce plant care efforts.
Can anyone install a vertical garden on their building or urban spaces?
While anyone can install a vertical garden or participate in urban agriculture, it is recommended to consult with a professional to ensure proper installation and maintenance. Considerations such as structural support, light requirements, and modular systems are crucial. Some buildings may not be suitable for a vertical garden due to structural limitations, space optimization issues, or lack of proper lighting and ventilation for indoor plants. However, with proper planning and using eco-friendly design principles, urban biodiversity, and sustainable practices, installation can be successful. Additionally, such gardens contribute to environmental benefits like air quality improvement, stormwater management, and reducing the urban heat island effect.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário