Future Directions for Urban Environmental Policies.
Urban environmental policies serve as essential frameworks aimed at enhancing sustainability and resilience within urban areas. As cities continue to expand, the necessity for effective policies that address environmental challenges becomes increasingly imperative.
This article examines the importance of these policies, the challenges they encounter, and their key components, such as sustainable development and community engagement. It will also highlight successful examples from around the globe and discuss future directions, including technological innovation and environmental justice, while underscoring the critical role that individuals can play in this initiative.
The exploration will reveal how urban environmental policies can contribute to shaping a greener and healthier future for urban environments.
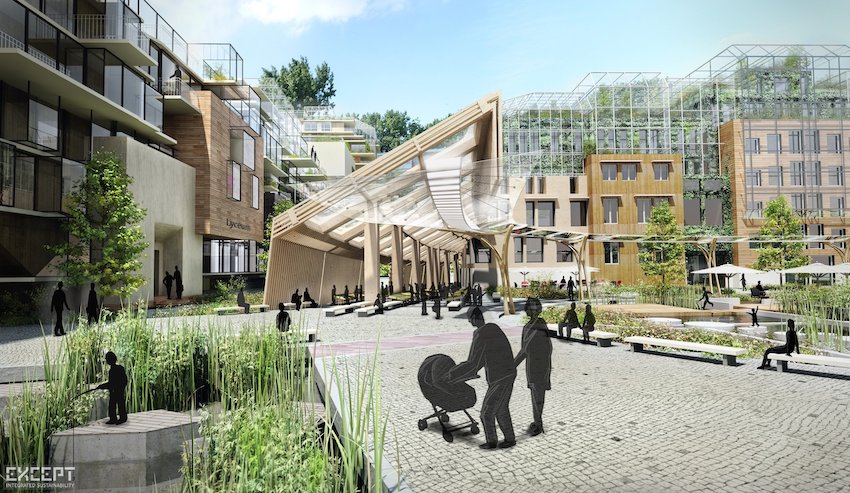
What Are Urban Environmental Policies?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
Urban environmental policies serve as essential frameworks established by city governments and organizations to tackle the numerous challenges associated with urban sustainability and climate change resilience.
These policies incorporate a range of strategies aimed at reducing the urban ecological footprint, promoting green infrastructure, enhancing public health, and ensuring the effective management of resources, like water management and waste management, to support sustainable development objectives and sustainable transportation.
Through innovative policy frameworks and collaboration among stakeholders, urban environmental policies aim to mitigate the impacts of climate change, improve air quality management, enhance urban resilience, and promote biodiversity conservation.
As urban areas continue to expand, the necessity for comprehensive policies that prioritize climate adaptation, social equity, and biodiversity conservation becomes increasingly critical, especially in the context of urban planning and urban ecology.
Why Are Urban Environmental Policies Important?
Urban environmental policies are crucial in the development of sustainable cities, as they have a direct influence on public health, environmental quality, climate resilience, and urban socio-ecological systems.
These policies are essential for addressing the challenges associated with urbanization, including pollution reduction, waste management, and the optimization of transportation systems, all of which significantly impact the quality of life for residents, while supporting urban renewal and disaster preparedness.
Additionally, well-designed urban environmental policies promote social equity by ensuring equitable access to green spaces and sustainable resources, while fostering civic engagement, policy coherence, and participation in decision-making processes.
Given the increasing threats posed by climate change, the significance of these policies in creating adaptive, resilient, and livable urban environments is paramount, emphasizing the need for climate mitigation and smart cities.
What Are the Current Challenges Facing Urban Environmental Policies?
Urban environmental policies hold significant importance; however, cities encounter numerous challenges that impede their effectiveness in promoting sustainability and resilience.
Key obstacles include insufficient stakeholder collaboration, inadequate funding for green infrastructure projects, and ongoing issues such as pollution control and waste reduction. The structures of urban governance often create barriers to the implementation of comprehensive policies that address the multifaceted nature of urban challenges, including climate adaptation, environmental justice, and policy effectiveness.
The increasing frequency of urban flooding, the prevalence of urban heat island effect, and the deterioration of air quality further complicate these issues, necessitating innovative approaches, policy advancements, and urban infrastructure improvements.
For instance, a lack of coordination among various government agencies may lead to fragmented efforts that dilute the impact of proposed initiatives. Cities frequently grapple with competing priorities, where economic growth can overshadow critical environmental concerns. A pertinent example is the fight against air pollution, which necessitates stringent regulations and green regulatory measures that may conflict with business interests. This ongoing struggle not only hinders effective governance but also erodes public trust in the authorities responsible for ensuring a sustainable urban future through sustainable finance and policy integration.
Ultimately, addressing these challenges requires a more integrated framework that fosters active participation from local communities, allocates sound financial investments for sustainable community design, and commits to adapting policies in response to evolving environmental conditions through smart growth and green technology.
What Are the Key Components of Effective Urban Environmental Policies?
Effective urban environmental policies are founded upon several essential components that collectively promote urban sustainability and resilience.
These components include:
- sustainable development strategies,
- community engagement initiatives,
- the integration of green infrastructure within urban planning frameworks.
By prioritizing climate adaptation and resilience planning, cities can proficiently address environmental challenges and enhance their capacity to withstand climate-related disruptions through policy innovation and resource management.
Additionally, these policies should encourage participatory planning and stakeholder collaboration to ensure the inclusion of diverse community voices in decision-making processes, ultimately fostering social equity, climate equity, and improving the overall quality of life.
1. Sustainable Development
Sustainable development serves as a foundational element of urban environmental policies, aimed at achieving a balance between economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity within urban areas. It emphasizes the efficient utilization of resources, the adoption of renewable energy, and the integration of green building standards, ultimately contributing to the establishment of a low-carbon city framework through sustainable city initiatives and green economy practices.
Policies that support urban sustainability, centered on sustainable development, encourage climate action and promote community resilience by enhancing ecosystem services and preserving habitats. Initiatives in urban agriculture and the development of local food systems are critical components that contribute to reducing carbon footprints and transportation emissions while fostering economic sustainability and local governance.
Through the promotion of collaboration among local governments, community stakeholders, and businesses, sustainable development initiatives frequently yield innovative solutions to pressing urban challenges. For example, cities such as Amsterdam and Copenhagen have successfully implemented comprehensive cycling infrastructures, significantly decreasing reliance on automobiles and thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing air pollution efforts.
The incorporation of green spaces within urban settings not only improves air quality but also enhances social cohesion by providing public spaces for recreation and community engagement, contributing to urban community development and greenways.
These examples demonstrate that an integrated approach to urban environmental policies can effectively mitigate climate impacts while fostering vibrant and resilient communities capable of adapting to future challenges, including the need for environmental education and participatory planning.
2. Community Engagement
Community engagement is vital for the success of urban environmental policies, as it enables citizens to actively participate in shaping their urban environments. Effective policies emphasize citizen engagement initiatives that facilitate collaboration among local authorities, stakeholders, and residents, ensuring that diverse perspectives inform decision-making processes.
This participatory approach not only enhances transparency and accountability in urban governance but also promotes environmental justice by addressing the needs of marginalized communities disproportionately affected by urban pollution, urban sprawl, and environmental degradation.
Community participation in initiatives such as urban forestry and green space development can significantly strengthen urban resilience and encourage eco-friendly practices. By actively involving community members, these programs create a platform for residents to express their concerns and propose solutions tailored to their specific circumstances, enhancing stakeholder engagement.
For example, the establishment of community gardens in low-income neighborhoods serves two key purposes: it improves local food security while also creating green spaces that contribute to health, urban health, and well-being.
Successful initiatives, such as the ‘Green Hearts’ program in Detroit, demonstrate how collective action can transform vacant lots into vibrant community spaces, fostering both environmental restoration, habitat restoration, and social cohesion.
Therefore, integrating community engagement into urban environmental policies not only mitigates existing inequities but also cultivates a sense of ownership among residents, ultimately leading to more sustainable and equitable urban ecosystems through civic engagement and environmental governance.
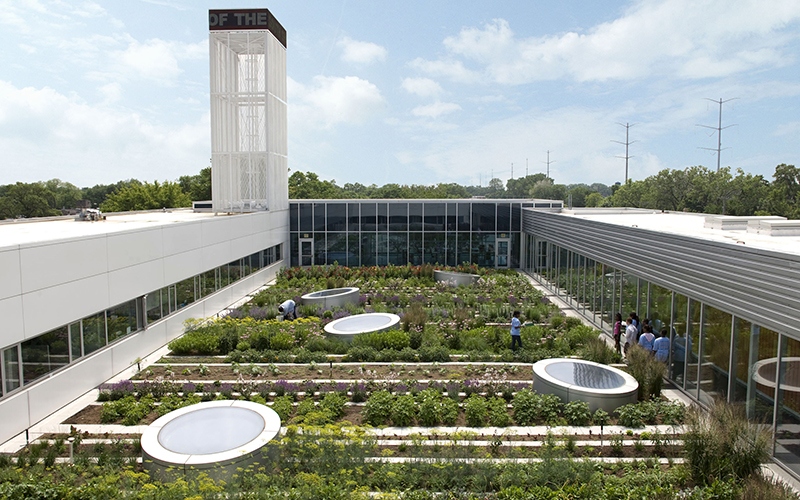
3. Green Infrastructure
.jpg_01.jpeg)
Green infrastructure refers to a network of natural and semi-natural systems that deliver essential services while enhancing urban landscapes and improving overall environmental health. By incorporating elements such as green roofs, urban forests, and permeable pavements, green infrastructure plays a vital role in pollution reduction, stormwater management, urban heat mitigation, and land use planning.
This approach not only addresses immediate environmental challenges but also promotes long-term sustainability. For example, cities such as Philadelphia have successfully implemented green stormwater infrastructure to manage rainfall, thereby reducing runoff and enhancing water quality. Similarly, the creation of urban green spaces can significantly diminish heat islands, resulting in cooler environments for residents and supporting environmental monitoring initiatives.
Additionally, enhancing urban biodiversity through these initiatives has proven invaluable in supporting local wildlife and promoting nature-based solutions and circular economy practices.
Cities that adopt green infrastructure are better positioned to confront climate-related challenges, ultimately fostering healthier and more resilient communities through sustainable materials and climate policies.
4. Climate Adaptation and Resilience and Urban Heat Island Effect
Climate adaptation and resilience constitute essential elements of urban environmental policies, aimed at equipping cities to address the impacts of climate change and resilience while minimizing vulnerabilities. These strategies are focused on enhancing urban resilience through the implementation of disaster risk reduction measures, the advancement of urban infrastructure development, and the promotion of adaptive reuse of existing structures.
By prioritizing climate adaptation, cities can alleviate the effects of urban flooding, heat waves, and other climate-induced challenges that pose risks to public health and safety. The incorporation of climate resilience and environmental policies into urban planning processes ensures a proactive approach that fosters sustainable resource management and bolsters community resilience in the face of adversity.
The integration of these principles is crucial for the creation of urban environments capable of withstanding the increasing frequency and severity of climate-related disasters, thereby promoting urban ecology and sustainable city initiatives.
For example, cities such as Copenhagen have adopted innovative stormwater management and water management practices, including green roofs and permeable pavements, which not only mitigate flooding risks but also enhance urban aesthetics. Similarly, in New York City, following the impact of Superstorm Sandy, there has been a shift in focus towards resilient infrastructure, which involves elevating critical facilities and implementing comprehensive emergency management plans.
These examples illustrate how adaptive strategies can lead to more robust urban systems, fostering a sense of security and stability for residents while promoting inclusive community participation and civic engagement in resilience planning.
What Are Some Successful Examples of Urban Environmental Policies?
Numerous cities across the globe have successfully implemented urban environmental policies that exemplify innovative approaches to sustainability and resilience. These case studies demonstrate how effective urban governance and policy innovation can address challenges related to air quality, waste management, and the integration of renewable energy.
Notable examples include:
- Curitiba, Brazil, which is recognized for its efficient public transportation system and urban planning strategies that prioritize biodiversity conservation.
- Copenhagen, Denmark, has established itself as a leader in climate action through its ambitious goals for carbon neutrality and commitment to smart city initiatives.
- Additionally, Portland, Oregon, serves as a model for successful community engagement in urban planning, leading to enhanced quality of life and improved environmental health.
1. Curitiba, Brazil
Curitiba, Brazil, is frequently recognized as a model for effective urban environmental policy and governance, particularly due to its innovative public transportation system that has significantly transformed urban mobility. The city’s bus rapid transit (BRT) system not only provides efficient transportation but also fosters sustainable resource management by reducing dependence on private vehicles.
Through meticulous urban planning and policy innovation, Curitiba has successfully integrated green spaces into its urban environment, thereby enhancing the quality of life and supporting biodiversity conservation, while also addressing the urban heat island effect and minimizing pollution. This comprehensive approach exemplifies the capacity of urban areas to confront environmental challenges through effective governance.
The strategic placement of dedicated bus lanes facilitates swift transit across the city, considerably reducing travel times and creating a more commuter-friendly environment. The establishment of interchange stations promotes seamless transitions between various modes of transportation, thereby encouraging a culture of public transit usage and sustainable transportation.
Such initiatives not only alleviate traffic congestion but also contribute to a reduction in carbon emissions, reflecting a strong commitment to more sustainable urban living and emission reduction.
In conjunction with transportation reforms, urban zoning regulations in Curitiba have emphasized mixed-use developments, which enhance walkability and diminish the necessity for long commutes, further aligning with principles of sustainability, environmental stewardship, and smart growth.
2. Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen has established itself as a global leader in climate action, with ambitious objectives aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2025. The city has implemented a comprehensive array of urban environmental policies that prioritize renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and green infrastructure, thereby significantly reducing its carbon footprint and enhancing urban resilience.
Copenhagen’s commitment to smart city initiatives and stakeholder collaboration has enhanced community engagement and environmental literacy, empowering residents to actively participate in the city’s sustainability efforts. The incorporation of green roofs and urban agriculture initiatives contributes to urban resilience and biodiversity conservation, demonstrating the effectiveness of well-structured environmental policies.
As part of its strategic approach, the city has made substantial investments in wind energy, which constitutes a significant portion of its electricity supply, thereby fostering a robust renewable energy economy and supporting the energy transition.
Additionally, Copenhagen has developed extensive cycling infrastructure that promotes cycling as a viable alternative to car travel, thus decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Innovative waste management systems further illustrate the city’s commitment to sustainability by promoting recycling, pollution control, and minimizing contributions to landfills.
By adopting a holistic approach to urban planning, Copenhagen not only prioritizes climate action but also aspires to create a vibrant and healthy environment for all its inhabitants, thereby setting an inspiring benchmark for cities around the globe and supporting climate mitigation.
3. Portland, Oregon
Portland, Oregon, is distinguished for its strong community engagement and innovative strategies in sustainable urban transportation. The city has enacted policies that prioritize public transportation systems, cycling infrastructure, and pedestrian-friendly urban spaces, resulting in significant reductions in pollution, enhancements in air quality, and improvements in urban health.
Through participatory planning processes and stakeholder collaboration, Portland has effectively integrated environmental justice into its urban governance framework, ensuring that all community members have a voice in shaping their environment. This comprehensive approach has led to successful urban regeneration projects, an enhanced quality of life, and a steadfast commitment to social equity within environmental policies.
Along with emphasizing cycling and walking, Portland’s initiatives include the development of the TriMet transit system, which connects various neighborhoods and facilitates ease of access throughout the city. The commitment to decreasing car dependency is further exemplified by the implementation of the 20-minute neighborhoods concept, which encourages residents to reside within a short distance of essential services, supporting sustainable community design.
By fostering partnerships between local government, businesses, and community organizations, Portland serves as a model where sustainable mobility aligns with community well-being, establishing itself as a leader in urban sustainability, social sustainability, and a prototype for other cities aspiring to achieve similar objectives.
What Are Some Future Directions for Urban Environmental Policies?
.jpg_10.jpeg)
As cities continue to evolve, future directions for urban environmental policies must prioritize technological innovation, environmental justice, and interdisciplinary collaboration while addressing the challenges of urban sprawl and climate justice.
Embracing technology can significantly enhance data collection and monitoring practices, thereby facilitating more effective urban governance, environmental monitoring, and climate policy frameworks.
Addressing environmental justice and equity is essential to ensure that all residents benefit from sustainable development initiatives, green infrastructure, and urban renewal projects.
By fostering collaboration among stakeholders across various sectors, cities can develop integrated approaches that effectively address complex urban challenges while promoting community resilience, urban renewal, and climate adaptation strategies.
1. Embracing Technology and Innovation
Embracing technology and innovation is essential for the formulation of effective urban environmental policies that address contemporary challenges. Smart cities utilize data-driven solutions to optimize resource management, enhance public transportation systems, and improve air quality monitoring.
For example, cities such as Barcelona and Singapore are implementing Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to manage water usage and monitor waste disposal efficiently. These data-driven initiatives not only streamline municipal operations but also promote a culture of sustainability among residents.
The application of artificial intelligence algorithms in traffic management can significantly reduce congestion and emissions, thereby contributing to enhanced urban air quality.
Moreover, by granting stakeholders access to real-time environmental data through mobile applications, citizens are give the power toed to actively engage in sustainability efforts. This technological integration helps bridge gaps between government agencies and the community, ensuring that urban development aligns with ecological preservation and social equity.
2. Addressing Environmental Justice and Equity
Addressing environmental justice and equity is essential in shaping the future of urban environmental policies, ensuring that all community members have equitable access to resources and opportunities. Policymakers must prioritize inclusive approaches that consider the needs of marginalized populations disproportionately affected by pollution, urban degradation, and the urban heat island effect.
By integrating social equity into urban governance frameworks, cities can enhance community resilience and foster civic engagement, ultimately leading to more effective climate adaptation and mitigation strategies. This commitment to environmental justice should be explicitly reflected in policies concerning land use planning, waste management, air quality management, and access to green spaces.
For example, cities such as San Francisco have implemented participatory budgeting initiatives, enabling residents to directly influence the allocation of public funds to environmental projects. This not only gives power to community voices but also ensures that investments are directed toward areas that require them most, such as parks in underserved neighborhoods. Additionally, urban agriculture projects and green infrastructure developments are prioritized to promote sustainable community design.
Additionally, Portland’s commitment to equitable development through initiatives that support affordable housing near green spaces addresses the housing crisis while simultaneously enhancing environmental amenities. These approaches illustrate that centering environmental justice within urban policies is not merely a moral imperative but also a strategic necessity for the creation of sustainable and inclusive cities. Portland also integrates climate change resilience and ecosystem services into its urban planning efforts.
3. Collaborating with Other Sectors in Urban Environmental Policies
Collaboration among various sectors is crucial for the development of comprehensive urban environmental policies that effectively address complex urban challenges. Cross-sector partnerships involving government entities, private organizations, and non-profit institutions can leverage collective resources and expertise to create innovative solutions for urban sustainability, including green building standards and smart growth initiatives.
Such collaborations enhance stakeholder engagement and foster consensus on key policy initiatives, ultimately leading to improved outcomes in areas such as air quality, transportation systems, and waste management. By cultivating a collaborative environment, cities can successfully implement strategies that promote social equity, environmental health, and community resilience.
These partnerships not only maximize impact but also facilitate knowledge sharing among diverse stakeholders, fostering climate action and each contributing their unique strengths.
For example, successful initiatives like the Los Angeles Cleantech Incubator illustrate how public and private sectors can collaborate to drive clean technology innovations that significantly reduce urban emissions. Similarly, the partnership between local governments and neighborhood associations in urban reforestation projects exemplifies how community-driven efforts can restore green spaces, enhance biodiversity, and facilitate habitat restoration.
By actively engaging stakeholders—including residents, businesses, and researchers—cities can develop tailored solutions that effectively address the environmental challenges they encounter, including pollution control and ecological footprint reduction, ensuring long-term sustainability and engagement at all societal levels.
4. Incorporating Public Health and Well-being into Urban Environmental Policies
Incorporating health and well-being into urban environmental policies is essential for enhancing the quality of life for urban residents. Policies that prioritize public health can effectively address issues such as air quality, noise pollution, and access to green spaces, thereby promoting healthier lifestyles and community well-being. Sustainable transportation systems and green regulatory measures can contribute significantly to these goals.
By integrating health considerations into urban planning processes, cities can create environments that foster active living, mental health, and social cohesion. These policies can mitigate environmental stressors, ensuring that urban areas remain resilient and adaptable to the evolving challenges posed by climate change. Urban resilience through sustainable land use and water management can further support these objectives.
This comprehensive approach encourages the development of pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, supports local food systems, promotes active transportation options such as cycling and walking, and incorporates nature-based solutions to enhance urban socio-ecological systems.
Cities like Copenhagen and Amsterdam have successfully implemented initiatives that emphasize cycling and pedestrian pathways, resulting in significant reductions in pollution-related health issues. Furthermore, the integration of urban gardens and community parks not only enhances aesthetic value but also fosters community engagement and overall well-being. These initiatives are supported by robust environmental monitoring and climate policies.
By prioritizing these factors, urban environmental policies can transform neighborhoods into vibrant ecosystems that nurture both the physical and mental health of residents, ultimately contributing to a more harmonious urban experience. Policies focusing on renewable energy and sustainable materials further support these transformations.
What Role Can Individuals Play in Supporting Urban Environmental Policies and Sustainable City Initiatives?
Individuals play a crucial role in supporting urban environmental policies and sustainable city initiatives through active community participation and sustainable initiatives. By engaging in local governance, residents can articulate their concerns and contribute to the formulation of policies that address the challenges of urban sustainability and promote urban renewal.
This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, thereby encouraging greater participation from residents in initiatives aimed at creating greener cities that adhere to green building standards and emphasize urban health.
For example, involvement in community gardening projects not only enhances neighborhood aesthetics but also supports local biodiversity, reduces dependence on imported foods, and promotes urban agriculture as a key factor in urban ecology.
Furthermore, individuals can advocate for sustainable transportation options, such as cycling and public transit, by organizing awareness campaigns that emphasize the benefits of decreased car usage and the importance of reducing their carbon footprint.
Social media platforms serve as valuable tools for amplifying their voices, sharing success stories, and inspiring others to take concrete actions. These platforms can also facilitate environmental education and awareness on issues like climate justice and sustainable development goals.
By recognizing their individual contributions, urban residents can collectively champion vibrant, sustainable communities that prioritize long-term ecological health and effective climate adaptation strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
.jpg_11.jpeg)
What are some current challenges facing urban environmental policies?
Some current challenges include rapid urbanization, climate change, pollution, urban sprawl, and resource depletion.
What is the goal of future directions for urban environmental policies?
The goal is to develop sustainable and equitable solutions to urban environmental issues.
How can technology play a role in future urban environmental policies?
Technology can be used to improve monitoring and data collection, develop more efficient and renewable energy sources, and promote sustainable transportation options. Additionally, smart cities initiatives can integrate technology for better environmental risk assessment and disaster preparedness.
What is the importance of community involvement in future urban environmental policies?
Community involvement is crucial in addressing environmental issues as it allows for a more comprehensive understanding of local needs and concerns, and promotes ownership and accountability for implementing sustainable solutions.
How can urban environmental policies be integrated with economic development goals?
By incorporating environmentally-friendly practices into economic development plans, urban areas can promote sustainable growth and attract businesses and investments that align with environmental goals, such as green jobs and the green economy.
What are some potential future directions for urban environmental policies?
Some potential directions include increasing green spaces, promoting biodiversity, implementing green infrastructure, reducing waste and promoting recycling, developing sustainable transportation systems, and enhancing urban infrastructure through policy innovation.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário