The Role of Smart Technology in Biophilic Cities.
In an increasingly urbanized world, the concept of biophilic cities emerges as a promising solution, integrating nature with urban living to enhance human well-being and environmental health through sustainable urban design and nature integration.
This article delves into the principles that define biophilic cities, emphasizing their significance and the numerous benefits they provide for both individuals and the planet through urban ecology, smart urbanism, and ecological diversity.
We analyze the role of smart technology within these urban environments, highlighting innovative solutions such as green roofs, smart waste management systems, and vertical gardens that are transforming our interactions with the surroundings and promoting urban biodiversity.
This exploration addresses the challenges and future prospects of integrating technology into biophilic design, thereby paving the way for more sustainable and harmonious urban environments that prioritize climate resilience and ecological restoration.
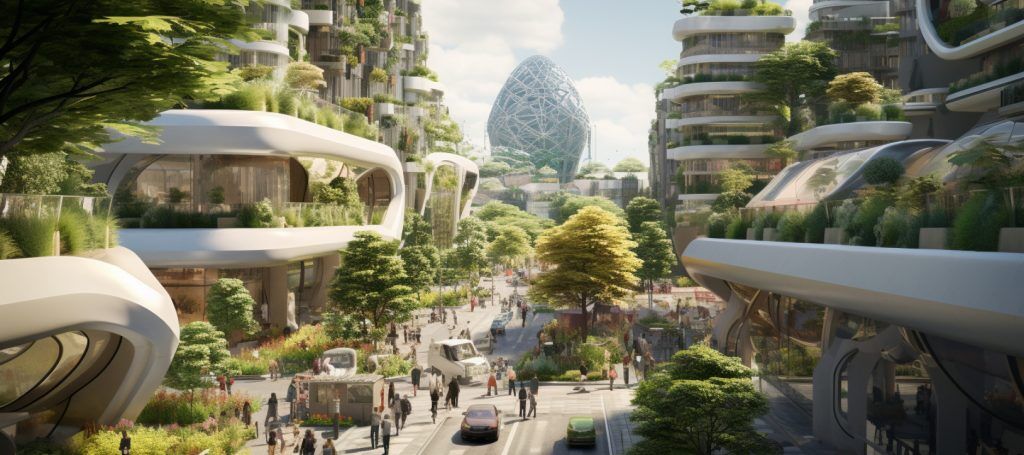
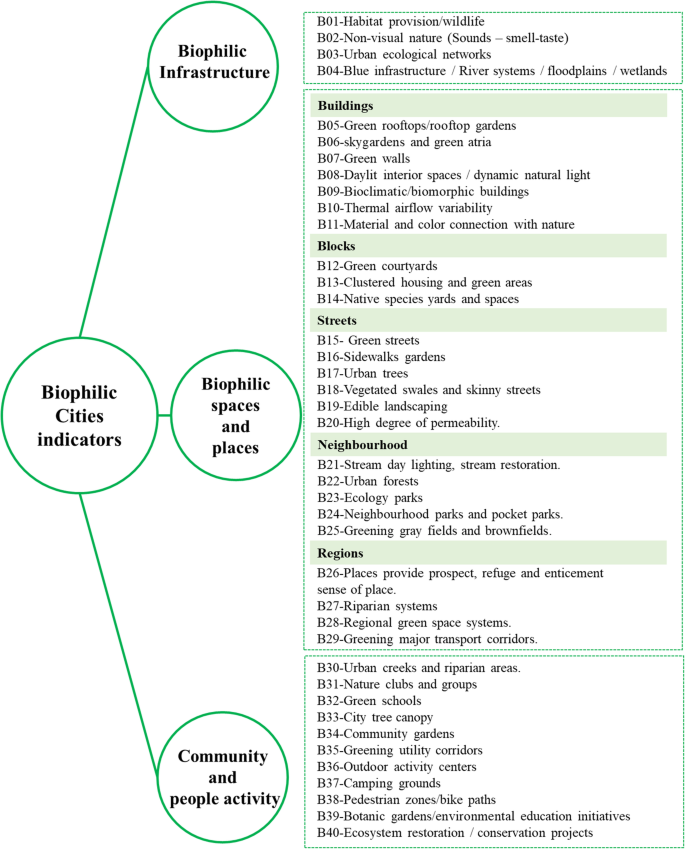
What Are Biophilic Cities?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
Biophilic cities refer to urban environments that incorporate natural elements into their design, promoting a harmonious relationship between the built and natural environments and fostering urban resilience.
This approach underscores the significance of green spaces, biodiversity, and ecological restoration, thereby enhancing community well-being and public health in urban settings while also supporting ecosystem services and nature connectivity.
By employing nature-based solutions, biophilic cities strive to improve air quality and support sustainable development, rendering urban areas more livable and resilient in the face of climate change.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies, including smart sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT), is vital for optimizing these urban spaces, facilitating effective environmental monitoring, enhancing energy efficiency, and supporting sustainable materials to reduce ecological footprints.
What Are the Principles of Biophilic Cities?
The principles of biophilic cities focus on strengthening the relationship between urban residents and nature through deliberate urban planning and design. These principles advocate for the integration of green architecture, sustainable practices, and nature-based solutions, which are fundamental in creating a harmonious living environment.
Features such as green roofs, vertical gardens, and urban forests contribute not only to the aesthetic appeal of the city but also to the enhancement of urban biodiversity and the promotion of environmental stewardship and landscape connectivity among citizens.
By adopting these principles, urban planners can develop spaces that promote well-being and facilitate community interaction, ultimately fostering a stronger sense of place. The integration of nature into urban settings—an essential aspect of biophilic design—encourages residents to actively engage with their environment, thereby cultivating a culture of sustainability.
For instance, community gardens and local parks act as crucial social hubs while simultaneously reducing the ecological footprint associated with urbanization. Citizen engagement plays a vital role in this process; it enables individuals to participate in ecological initiatives, thereby enhancing the resilience of urban ecosystems and ensuring that cities not only operate efficiently but also thrive in harmony with their natural surroundings, promoting environmental justice and participatory design.
Why Are Biophilic Cities Important?
Biophilic cities play a vital role in promoting community well-being, enhancing public health, and fostering urban resilience in response to climate challenges, with significant health benefits derived from nature-based solutions and pedestrian-friendly design.
By incorporating biodiversity into urban landscapes, these cities create environments that support mental health, encourage physical activity, and facilitate social interaction among residents, also contributing to noise reduction and the cultural heritage of the area.
Access to nature not only improves air quality and mitigates the urban heat island effect but also contributes to the sustainability of local ecosystems, supports urban wildlife and wildlife corridors, and ensures a healthier living experience for urban dwellers.
How Do Biophilic Cities Benefit People and the Environment?
Biophilic cities provide numerous advantages for both individuals and the environment by promoting psychological well-being, enhancing community interaction, and contributing to ecosystem health and landscape architecture. The incorporation of green spaces and accessibility to nature not only improves the aesthetic appeal of urban areas but also encourages outdoor activities, thereby fostering a stronger sense of community.
This connection to nature contributes to reduced stress levels, improved air quality, and a smaller ecological footprint, underscoring the significant environmental benefits of integrating biophilic principles into urban planning and climate adaptation strategies.
For example, in Singapore, the integration of vertical gardens and parks has resulted in a notable reduction in urban heat, enhancing residents’ comfort and encouraging outdoor socialization. Similarly, in New York City, the transformation of an unused railway into the High Line park has created a vibrant public space, illustrating how facilitating community interaction can positively influence mental health outcomes and increase local business revenue.
These examples demonstrate that biophilic cities not only enhance individual well-being but also foster a sense of belonging, encouraging residents to engage more meaningfully with their environment and one another through community gardens, interactive public art, and green mobility initiatives.
What Is Smart Technology?
Smart technology encompasses the integration of advanced digital connectivity and the Internet of Things (IoT) into everyday systems, facilitating real-time data collection and analysis to enhance efficiency and sustainability, supporting smart city initiatives and digital twin technology.
This category of technology includes smart sensors that monitor environmental conditions, as well as smart grids that optimize energy consumption across urban areas.
The implementation of smart technology in urban design not only fosters improved energy efficiency but also equips cities to adapt to evolving environmental conditions while promoting sustainable development.
What Are the Types of Smart Technology Used in Biophilic Cities?
Various forms of smart technology are employed in biophilic cities to enhance environmental monitoring and resource management. These technologies encompass:
- Smart irrigation systems designed to optimize water usage for urban agriculture and green spaces,
- Smart waste management solutions that streamline waste collection processes, and
- Smart lighting systems that adjust according to pedestrian activity, thereby promoting safety and energy conservation.
The integration of these technologies ensures that urban environments are both functional and sustainable, promoting smart mobility and technological innovation.
Sensor-driven air quality monitors play a vital role by providing real-time data on pollution levels, which enables cities to implement more effective regulations and health initiatives, supporting environmental education and energy-efficient urban systems. Additionally, smart transportation systems that promote the use of electric vehicles and optimize traffic flows contribute to a cleaner urban atmosphere. Integrated HVAC systems within buildings further enhance energy efficiency and comfort for occupants.
By adopting these advanced technologies, urban planners address ecological challenges while simultaneously fostering greater community well-being. This ultimately leads to healthier and more connected urban living environments.
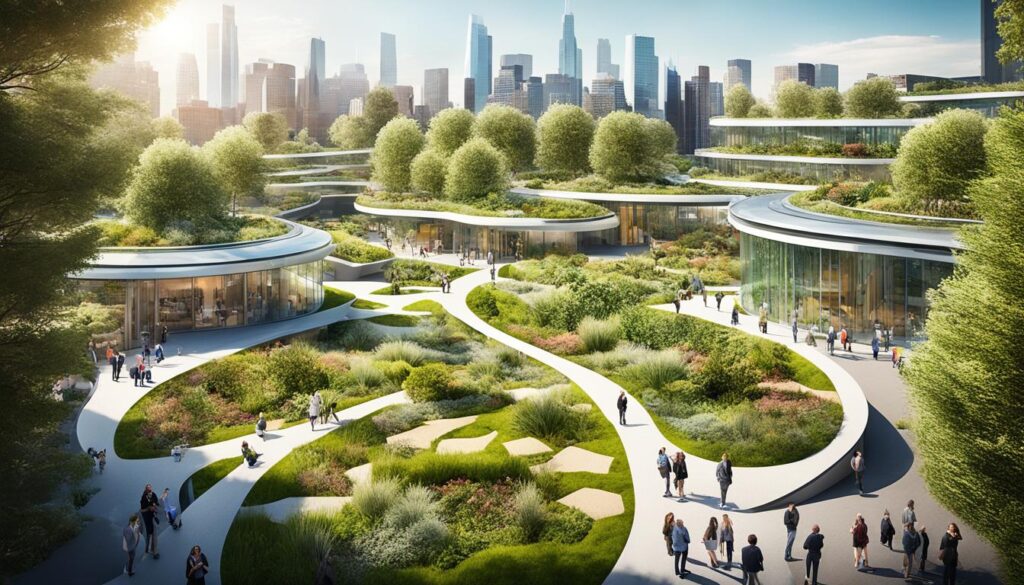
How Does Smart Technology Contribute to Biophilic Cities?
.jpg_01.jpeg)
Smart technology plays a crucial role in advancing the sustainability of biophilic cities by supplying real-time data that informs urban planning and climate adaptation strategies.
By utilizing smart sensors and digital connectivity, cities can effectively monitor environmental conditions, manage resources with greater efficiency, and actively involve citizens in sustainability initiatives.
This integration of technology not only optimizes urban processes but also promotes community engagement and stewardship among residents.
What Are the Advantages of Using Smart Technology in Biophilic Cities?
The advantages of incorporating smart technology within biophilic cities are numerous, significantly improving environmental impact, energy efficiency, and social sustainability in urban areas. By utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart sensors, cities can optimize resource management, minimize waste, and enhance air quality, resulting in healthier environments for their residents.
These technologies contribute to urban resilience, enabling cities to adapt to changing climate conditions, adopt sustainable development practices, and enhance landscape restoration efforts.
For example, smart irrigation systems can modify watering schedules based on real-time weather data, thereby conserving water resources while preserving verdant green spaces. Additionally, energy-efficient buildings equipped with smart energy management systems can substantially reduce their carbon footprint by automating heating and cooling according to occupancy levels.
These innovations not only aid in mitigating urban heat islands but also promote biodiversity, ecological diversity, and urban farming, thereby making cities more vibrant and livable with home automation and energy-efficient solutions. By highlighting these practical applications, it is evident that the integration of smart technology is not simply an enhancement; it is a necessity for fostering sustainable and resilient urban ecosystems.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing Smart Technology in Biophilic Cities?
The integration of smart technology in biophilic cities poses several challenges, including urban planning considerations, the digital divide, and privacy concerns among residents.
The rapid advancement of technology often surpasses the development of regulatory frameworks, resulting in gaps in effective governance. Additionally, unequal access to digital resources can exacerbate social inequities within communities.
It is imperative to address these challenges to ensure that the benefits of smart technology are equitably distributed among all citizens, supporting energy efficiency, environmental justice, and community participation in sustainability goals.
How Can These Challenges Be Overcome?
Overcoming the challenges associated with the implementation of smart technology in biophilic cities necessitates collaborative efforts among various stakeholders, including government entities, the private sector, and local communities. By fostering partnerships and developing inclusive public policies, municipalities can ensure equitable access to technology while effectively addressing privacy concerns and promoting environmental justice.
Engaging citizens in both the planning and implementation processes enables communities and enhances the overall effectiveness of smart solutions. This participatory design approach strengthens community engagement and ensures that the urban design is responsive to local needs.
This collaborative approach not only builds trust but also encourages innovation by incorporating diverse perspectives into the process of technological adaptation. Case studies, such as Barcelona’s Smart City initiative, demonstrate how integrating citizen feedback can result in more user-friendly systems and energy-efficient solutions.
Additionally, partnerships between local governments and technology firms in cities like Amsterdam have illustrated the potential of real-time data analytics to enhance urban services, such as smart grids and smart transportation, while respecting community privacy.
As cities work toward sustainability, enableing residents through outreach programs and educational workshops can further bolster community engagement, ensuring that smart technologies are embraced and effectively utilized to meet the needs of all citizens.
Examples of Smart Technology in Biophilic Cities
Numerous examples demonstrate the effective integration of smart technology into biophilic cities, highlighting innovations that enhance urban living and promote sustainability.
Noteworthy implementations include:
- Green roofs, which mitigate urban heat;
- Smart waste management systems that optimize waste collection processes;
- Sensor-based lighting systems that adjust to pedestrian activity, thereby enhancing safety and reducing energy consumption.
These examples exemplify the potential of smart technology to foster more livable and resilient urban environments.
1. Green Roofs and Vertical Gardens
Green roofs and walls represent significant components of biophilic cities, offering essential benefits such as enhanced biodiversity and improved environmental outcomes. These structures play a crucial role in managing stormwater and mitigating urban heat while also providing habitats for wildlife and supporting urban agriculture.
The incorporation of green roofs not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also fosters a deeper connection to nature for residents.
The presence of vegetation on rooftops and walls promotes a more vibrant urban ecosystem, attracting pollinators and other species that may otherwise be absent in densely populated areas. Cities such as Toronto and Singapore serve as exemplary models of successful implementation, where extensive green roof initiatives not only enhance air quality but also facilitate local food production through urban farms.
These innovative designs can result in reduced energy costs and contribute to climate change mitigation, demonstrating how prioritizing green infrastructure can address both ecological and social needs in increasingly urbanized environments. Such initiatives also promote urban biodiversity and the inclusion of wildlife corridors to support ecological diversity.
2. Smart Irrigation Systems
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Smart irrigation systems are essential for enhancing resource management and water efficiency in biophilic cities. By employing advanced technology, such as soil moisture sensors and weather data analysis, these systems optimize water usage for green spaces, ensuring that plants receive the appropriate amount of water while conserving this vital resource.
The integration of smart irrigation contributes to urban sustainability by minimizing water waste and promoting responsible landscaping practices.
These innovative systems not only prevent overwatering but also adapt to changing weather patterns, making them highly effective in diverse urban environments. Cities like San Francisco and Melbourne have adopted these technologies and demonstrated significant reductions in water usage while preserving vibrant green areas.
In San Francisco, the implementation of smart irrigation systems across public parks led to a 20% decrease in water consumption over a two-year period, illustrating the potential for responsible management of natural resources. Such success stories emphasize the effectiveness of smart irrigation as a foundational element for sustainable urban development.
3. Sensor-based Lighting Systems
Sensor-based lighting systems represent an innovative application of smart technology within biophilic cities, significantly enhancing energy efficiency and urban safety. These systems automatically adjust lighting levels in response to real-time pedestrian activity, ensuring that public spaces are well-lit while simultaneously minimizing energy consumption.
By fostering a more pedestrian-friendly environment, sensor-based lighting encourages greater community interaction and promotes outdoor activities.
This adaptive approach effectively reduces unnecessary illumination during off-peak hours, resulting in considerable savings on energy expenditures and a reduction in the carbon footprint of urban areas.
Cities such as Los Angeles and Barcelona have already commenced the implementation of these systems, yielding improved safety metrics and a decrease in crime rates attributable to enhanced visibility in public spaces.
The integration of sensor technology not only advances sustainability initiatives but also cultivates a sense of security among residents, enabling them to feel more at ease while exploring their neighborhoods during nighttime hours.
4. Smart Waste Management Systems
Smart waste management systems play a crucial role in optimizing the collection and processing of waste within biophilic cities, thereby significantly enhancing operational efficiency and reducing environmental impact. By utilizing technologies such as IoT sensors in waste bins, these systems offer real-time data on waste levels, facilitating more effective collection routes and schedules. This approach not only minimizes the carbon footprint associated with waste collection but also cultivates a culture of sustainability among residents.
For example, cities like San Francisco have adopted smart waste technologies, achieving notable diversion rates from landfills through targeted recycling and composting initiatives. Additionally, these systems foster community engagement by providing citizens with insights into their waste disposal habits, which encourages more responsible behaviors.
Moreover, cities such as Barcelona have implemented smart bins that automatically compact waste, thereby increasing storage capacity and reducing collection frequency, which further diminishes vehicle emissions. These implementations underscore the potential of smart waste management in advancing urban sustainability, promoting both efficiency and favorable environmental outcomes.
Future of Smart Technology in Biophilic Cities
The future of smart technology in biophilic cities presents significant potential, with ongoing developments aimed at enhancing urban sustainability and resilience.
As technological innovation progresses, it is anticipated that advanced solutions, including AI-driven environmental monitoring, augmented reality for urban planning, and improved citizen engagement platforms, will be integrated into urban frameworks.
These advancements are expected to enhance the quality of life in urban areas while simultaneously fostering a stronger relationship between residents and their natural environments through increased nature connectivity and the creation of public spaces that promote human well-being.
What Are the Potential Developments and Innovations in This Field?
The potential developments and innovations in the realm of smart technology for biophilic cities are extensive and diverse, with a primary focus on enhancing environmental monitoring and improving citizen engagement.
Innovations such as real-time air quality monitoring systems, intelligent public transportation solutions, and interactive technology designed for community participation are anticipated to significantly influence the future landscape of urban living. These advancements seek to establish more responsive and adaptive urban environments that prioritize sustainability and quality of life.
By incorporating sensors that can deliver real-time data on urban heat islands and water quality, city planners are better equipped to make informed decisions that address the needs of citizens and environmental challenges.
Citizen engagement is further strengthened through mobile applications that enable residents to report environmental issues, thereby fostering a sense of community involvement. This proactive participation promotes a collaborative approach to urban planning, ensuring that developments meet not only aesthetic considerations but also ecological stability and public health.
Ultimately, these innovations hold the potential to nurture healthier urban ecosystems in which both nature and residents can thrive in harmony.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of smart technology in biophilic cities?
.jpg_11.jpeg)
The role of smart technology in biophilic cities is to enhance the connection between humans and nature through the use of advanced technology, such as IoT and smart sensors. It aims to improve sustainability, livability, and overall well-being of urban areas by incorporating aspects of nature into city design and infrastructure, promoting the integration of nature-based solutions and green technology.
How does smart technology contribute to the biophilic approach in cities?
Smart technology contributes to the biophilic approach in cities by providing innovative solutions that promote nature-based design, green infrastructure, and sustainable practices. It also allows for the monitoring and management of urban systems through smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) to ensure a harmonious coexistence between humans and nature.
What are some examples of smart technology being used in biophilic cities and urban design?
Some examples of smart technology being used in biophilic cities include green roofs and walls, smart irrigation systems, and urban farming technology. These technologies help to integrate natural elements into the urban environment while also improving resource efficiency, public spaces, and reducing the carbon footprint of cities through sustainable urban design.
How can smart technology improve the livability and sustainability of biophilic cities?
Smart technology can improve the livability of biophilic cities by creating a more sustainable and eco-friendly environment. This can lead to improved air and water quality, reduced noise pollution, and increased access to green spaces, all of which contribute to a higher quality of life, human well-being, and health benefits for city dwellers.
What challenges may arise in implementing smart technology and sustainable practices in biophilic cities?
Challenges in implementing smart technology in biophilic cities may include high costs, lack of technological infrastructure, and resistance to change. There may also be concerns about privacy and security with the collection and use of data in smart systems. However, these challenges can be overcome with proper planning, community engagement, and collaboration between city officials, technology experts, and community members, promoting urban resilience.
How can individuals play a role in promoting the use of smart technology and urban resilience in biophilic cities?
Individuals can play a role in promoting the use of smart technology in biophilic cities by educating themselves about the benefits of these technologies and advocating for their implementation in their communities. They can also support local initiatives and businesses that prioritize sustainability and biophilic design, and make environmentally conscious choices in their daily lives, contributing to urban ecology and environmental justice.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário