Green Roofs Legislation: Case Studies from Around the World.
As urbanization continues to increase, cities around the world are actively seeking innovative solutions to address environmental challenges and promote urban sustainability.
One effective solution is the implementation of green roofs, which not only enhance the urban landscape but also contribute to biodiversity, energy efficiency, stormwater management, and urban ecology.
This article examines the legislation pertaining to green roofs across various countries, including Germany, France, Canada, the United States, and Australia, highlighting how environmental policy and government regulations support their adoption.
Successful case studies from cities such as Toronto, Portland, Sydney, Paris, and Hamburg illustrate the transformative impact of these eco-friendly initiatives on urban development.
These global examples provide valuable insights that can inspire sustainable urban development, promoting community engagement and ecological benefits within local communities.
Green Roofs Legislation Around the World
.jpg_00.jpeg)
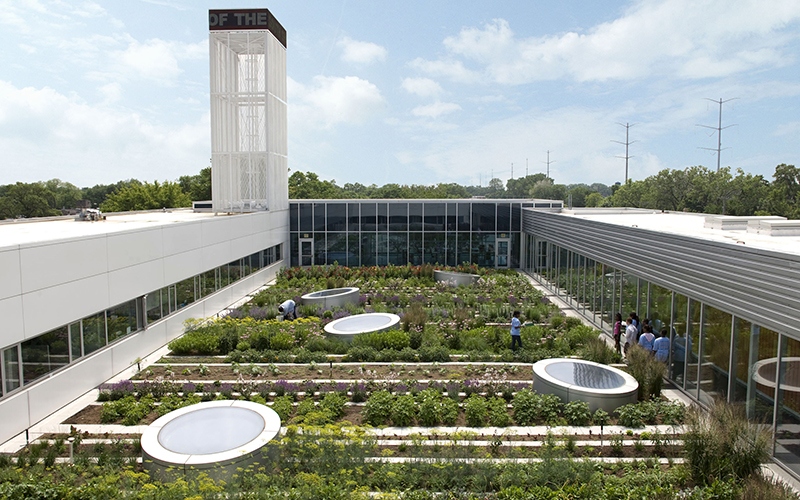
Green roofs, also known as living roofs, are a vital component of urban sustainability and environmental policy on a global scale, with numerous countries enacting legislation to foster their development and integration within urban landscapes as part of comprehensive policy frameworks.
These initiatives effectively tackle stormwater management, energy efficiency, and climate adaptation while also promoting biodiversity and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
Through the establishment of building codes and zoning regulations that support green infrastructure, governments strive to create resilient urban environments that not only contribute to climate change mitigation, disaster resilience, and infrastructure resilience but also provide economic benefits to taxpayers and enhance property values through increased green space.
1. Germany
Germany is at the forefront of green roofs legislation, having established comprehensive policies that promote the integration of green infrastructure within urban planning frameworks. The country has enacted a variety of laws and incentive programs designed to enhance biodiversity, improve energy efficiency, and effectively manage stormwater runoff.
These initiatives not only contribute to climate change mitigation but also bolster urban resilience. For example, cities such as Berlin and Hamburg have implemented specific regulations that mandate the installation of green roofs on new buildings, thereby significantly increasing green space in densely populated areas.
Research conducted by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment has demonstrated that green roofs can reduce temperatures in urban settings, resulting in improved air quality and better public health outcomes.
The successful implementation of these measures has fostered social cohesion by creating accessible green spaces that encourage community interaction and recreation, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable urban ecosystem.
2. France
In France, green roofs have emerged as a recognized solution to address the urban heat island effect and support climate action initiatives through local environmental regulations. The French government has introduced various incentives to promote the construction of rooftop gardens and other forms of green infrastructure in urban settings.
These regulations are part of a comprehensive initiative aimed at enhancing urban sustainability and environmental sustainability, as green roofs not only mitigate heat but also manage stormwater, improve air quality, and promote biodiversity within densely populated cities. Local municipalities frequently mandate the incorporation of green roofs in new developments, particularly in metropolitan areas such as Paris, where architectural design harmoniously integrates with natural elements.
Case studies, including the successful implementation of green roofs at the Cité du Refuge, demonstrate how these eco-friendly spaces contribute to communal well-being.
Furthermore, cities like Singapore and Toronto have experienced measurable benefits from similar policies, underscoring how a commitment to green infrastructure encourages community engagement and fosters a shared responsibility for environmental stewardship.
3. Canada
Canada has enacted a range of legislative measures designed to promote green roofs as a strategy for enhancing urban ecology and fostering citizen engagement in environmental stewardship. Municipal guidelines and government incentives have facilitated the implementation of innovative green infrastructure and retrofit projects across major cities.
As urban centers confront the challenges posed by urban sprawl and climate change, initiatives at both the provincial and federal levels have been established to support the development of green roofs. Funding opportunities through programs such as the Green Municipal Fund enable municipalities to invest in these sustainable practices, thereby reducing the ecological footprint of urban environments.
Local governments play a pivotal role in this process by frequently introducing zoning laws that encourage or mandate the inclusion of green roofs in new developments. This collaborative effort not only contributes to urban renewal but also enhances biodiversity and improves air quality, thereby making urban spaces more livable and environmentally sustainable.
4. United States
.jpg_01.jpeg)
In the United States, the development of green roofs is primarily driven by policy analysis, stakeholder collaboration, and the establishment of supportive building codes that facilitate the adoption of green infrastructure. Public-private partnerships, educational campaigns, and environmental education initiatives are instrumental in raising awareness and promoting implementation.
Local governments, acknowledging the economic advantages of sustainable development, are introducing incentives for businesses and homeowners to adopt green roofing solutions. These incentives frequently take the form of tax breaks, grants, or low-interest loans, which alleviate the financial burden associated with installation and maintenance practices.
Additionally, private entities are increasingly adopting renewable energy technologies and recognizing the aesthetic appeal of green roofs, positioning these solutions as advantageous for both environmental sustainability and economic performance.
As communities emphasize climate resilience, collaboration between the public and private sectors becomes essential, establishing a sustainable framework that not only enhances urban landscapes but also promotes economic growth.
5. Australia
Australia’s approach to green roofs emphasizes climate adaptation and urban sustainability, with various initiatives designed to promote the integration of green spaces within urban environments. These initiatives encompass the establishment of community gardens and the enhancement of local biodiversity through targeted legislation.
One significant initiative is the Green Roofs and Walls Policy in Sydney, which encourages developers to incorporate green installations into their buildings. This policy addresses not only temperature regulation and stormwater management but also promotes community engagement and social equity by creating spaces for residents to connect with nature.
Research conducted by the University of Melbourne demonstrates that these green innovations considerably improve air quality and mitigate urban heat island effects. Case studies, such as the rooftop gardens at One Central Park in Chippendale, illustrate how these efforts cultivate more livable environments while promoting biodiversity, enhancing local ecosystems, and providing ecosystem services, ultimately contributing to a more resilient urban landscape.
Case Studies of Successful Green Roofs Legislation
An examination of case studies concerning successful green roofs legislation offers valuable insights into the effectiveness of various policies and initiatives designed to promote urban sustainability and environmental stewardship.
These examples underscore best practices that can be replicated in other regions to attain comparable ecological benefits, improve public spaces, and promote habitat creation.
1. City of Toronto, Canada
The City of Toronto has emerged as a leader in green roofs legislation in Canada, implementing comprehensive municipal guidelines that encourage the installation of green roofs across a range of building types. This initiative not only enhances urban agriculture but also contributes to effective stormwater management and biodiversity.
By mandating the inclusion of green roofs in new developments, Toronto is addressing the urban heat island effect while simultaneously promoting urban agriculture and the cultivation of food crops. This approach fosters local food production, encourages community engagement, and supports sustainable practices.
For example, a recent study estimated that these green roofs have the capacity to capture up to 60% of stormwater runoff, significantly alleviating the burden on the city’s drainage systems.
Projects such as the green roof atop Toronto’s City Hall serve as successful case studies, showcasing the introduction of over 200 species of native plants. This not only enhances local biodiversity but also provides habitats for various urban wildlife, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and resilient urban ecosystem.
2. City of Portland, United States
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Portland, Oregon, serves as a prime example of the successful integration of green roofs within its urban planning framework, bolstered by robust environmental policies and community awareness initiatives. The city has established a comprehensive system of incentives and guidelines that promote the installation of green roofs throughout the metropolitan area.
These initiatives not only advance sustainable building practices but also encourage collaboration among residents, architects, and environmental organizations. By involving the community in the design and maintenance processes, the city enhances awareness of the ecological benefits associated with green roofs and supports the goals of landscape architecture.
Consequently, air quality improves due to decreased urban heat island effects and the filtration of pollutants, while natural vegetation helps mitigate noise pollution, resulting in a more tranquil urban environment. The integration of green roofs and green infrastructure plays a significant role in urban development by promoting urban ecology and enhancing environmental sustainability.
Furthermore, these green spaces contribute to public health outcomes by providing recreational areas that promote physical activity and mental well-being, underscoring Portland’s dedication to a livable and resilient urban future. These efforts reflect broader environmental policy initiatives that emphasize the importance of sustainability and climate resilience.
3. City of Sydney, Australia
Sydney has established itself as a leader in the promotion of green roofs through innovative legislation that enhances urban ecology and fosters climate resilience in response to environmental challenges. The city’s initiatives are designed to create green spaces that contribute to biodiversity, sustainable development, and the reduction of carbon footprints. These efforts are also in line with government regulations and policy frameworks aimed at addressing climate change.
This proactive approach addresses the urban heat island effect while also mitigating stormwater runoff, improving air quality, and promoting energy efficiency. By incorporating living architecture and rooftop gardens, Sydney is advancing urban sustainability and ecological benefits.
Numerous case studies highlight the success of these initiatives, including the City of Sydney’s Green Roof Policy, which has played a crucial role in guiding developers to incorporate vegetation into their buildings. These policy analyses offer valuable insights into effective building codes and incentive programs that encourage the adoption of green infrastructure.
International collaborations, such as partnerships with cities like Singapore and Berlin, provide valuable insights into best practices and innovative techniques. Collectively, these legislative measures and collaborative efforts lay the foundation for a greener, more sustainable urban landscape that benefits both residents and the environment.
4. City of Paris, France
Paris has implemented policies aimed at promoting green roofs as an essential element of its urban sustainability strategy, with a focus on reducing air pollution and enhancing biodiversity. The city actively encourages the development of rooftop gardens and green spaces to improve public health and enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban environments.
These initiatives not only introduce vibrant greenery atop buildings but also facilitate the absorption of carbon dioxide, resulting in a significant reduction in harmful emissions. According to a study conducted by the Paris Institute for Research and Development, green roofs have the potential to lower ambient temperatures by up to 4 degrees Celsius and substantially improve air quality by filtering particulate matter and absorbing toxic pollutants.
The integration of vegetation into urban architecture has been demonstrated to increase biodiversity, attracting various species of birds and insects back into urban areas. This multifaceted approach not only enhances the visual appeal of the city but also promotes a healthier, more sustainable environment for its residents.
5. City of Hamburg, Germany
Hamburg has positioned itself as a leading model for green roofs legislation, enacting policies that effectively address the urban heat island effect while promoting ecological restoration. The city’s initiatives are focused on integrating green infrastructure into urban planning, thereby enhancing the quality of life for its residents.
This comprehensive strategy not only alleviates temperature fluctuations but also fosters biodiversity within urban landscapes. For example, the implementation of the “Green Roofs Law” has provided incentives for building owners to install vegetation on rooftops, resulting in the transformation of previously underutilized spaces into thriving ecosystems.
Case studies, such as the renowned Hofgarten Hamburg, demonstrate how these projects contribute to efficient stormwater management and improved air quality. By supporting local flora and fauna, these green roofs serve as essential habitats, enhancing the overall ecological restoration of the city while simultaneously creating visually appealing environments for the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
.jpg_11.jpeg)
What is green roof legislation?
Green roof legislation refers to laws, regulations, or policies that promote or require the installation of green roofs in a particular area. These laws aim to increase the number of green roofs in a city or country for environmental, economic, and social benefits.
Which countries have implemented green roof legislation?
Several countries around the world have implemented green roof legislation, including Germany, France, Canada, and the United States. Each country has its own specific laws and regulations, but they all share the goal of promoting and supporting the use of green roofs.
What are some examples of successful green roof legislation?
One example of successful green roof legislation is the City of Toronto’s Green Roof Bylaw, which requires all new residential, commercial, and institutional buildings to have a green roof. Another example is the German city of Berlin, which has a policy that provides financial incentives for building owners who install green roofs.
How do green roof legislation and case studies tie together?
Case studies of successful green roof projects can be used as evidence to support the implementation of green roof legislation. They can demonstrate the benefits and effectiveness of green roofs in a particular city or country, and provide guidance for future projects.
What are some common benefits of green roof legislation?
Green roof legislation can bring numerous benefits, including reducing urban heat island effect, improving air and water quality, providing habitat for wildlife, and increasing energy efficiency in buildings. It can also create green jobs and promote sustainable development.
How can I learn more about green roof legislation around the world?
There are many resources available to learn more about green roof legislation, such as government websites, academic papers, and industry associations. You can also attend conferences or workshops focused on green roofs and network with experts in the field.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário