How Cities Can Incentivize Biophilic Design in Private Developments.
Biophilic design represents more than merely a trend; it is a critical approach that facilitates a reconnection with nature within urban environments.
As urban areas continue to expand and evolve, the integration of natural elements and green infrastructure into private developments becomes essential for enhancing well-being, promoting sustainability, and improving overall quality of life by ensuring effective water management and climate resilience.
This article examines the fundamental principles of biophilic design, its significance, and its numerous benefits, including its impact on environmental psychology and urban biodiversity. Additionally, it discusses practical strategies, such as public policy incentives and regulatory frameworks, that cities can implement to encourage developers to adopt this innovative design philosophy, highlights prominent examples, and addresses potential challenges that may arise in the process.
This exploration reveals how biophilic design can significantly transform urban landscapes for the better.
What is Biophilic Design?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
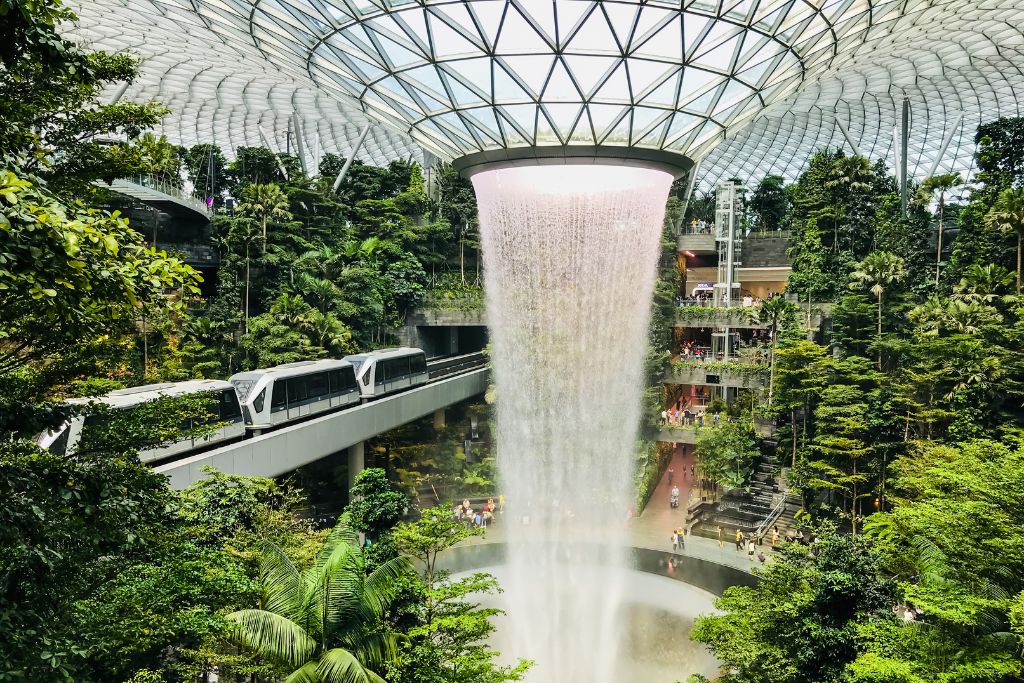
Biophilic design represents a transformative approach in architecture and urban planning, aimed at integrating natural elements and nature-based solutions into the built environment. This approach not only promotes sustainability but also enhances the quality of life for inhabitants.
The philosophy underlying biophilic design is grounded in the understanding that humans possess an inherent connection to nature, which can be cultivated through the incorporation of elements such as natural light, vegetation, and outdoor spaces.
By emphasizing health benefits and overall well-being, biophilic design plays a crucial role in developing livable cities that foster community resilience and encourage environmental stewardship, improving urban ecosystems and community involvement.
Why is Biophilic Design Important?
Biophilic design is a vital component of contemporary urban planning, as it significantly contributes to health benefits, enhances quality of life, promotes sustainability, and reduces the ecological footprint within communities.
By incorporating natural elements and green spaces into urban environments, cities can improve air quality and mitigate the effects of urban heat islands, while fostering a stronger connection between residents and their surroundings.
This design approach not only enhances visual aesthetics but also supports economic growth, community engagement, and social equity, thereby positioning it as an essential element of sustainable city initiatives.
What are the Benefits of Biophilic Design?
The advantages of biophilic design are numerous and encompass health benefits, enhanced well-being, increased community engagement, and reduced urban heat island effect, all while promoting sustainability within urban settings.
By integrating natural elements such as green roofs, living walls, urban greening strategies, and habitat restoration, biophilic design fosters biodiversity and delivers essential ecosystem services that contribute to improved air quality and reduced noise pollution. These design innovations can also yield economic advantages, including increased real estate values, decreased healthcare expenditures, and enhanced property values due to improved environmental impact.
The incorporation of natural features into urban spaces cultivates tranquil environments that can significantly enhance mental health, alleviating stress, promoting social interaction among residents, and fostering a strong human-nature connection.
By encouraging community participation in the design and maintenance of these green spaces, urban areas not only foster a greater sense of ownership but also facilitate connections among diverse populations, enhancing social cohesion and cultural identity.
This collaborative approach enhances the quality of life in cities and contributes to the development of vibrant ecosystems, ultimately leading to a more resilient urban environment where both people and nature can thrive in harmony, supporting urban sustainability and city resilience.
How Can Cities Promote Biophilic Design in Private Developments?
Cities can effectively promote biophilic design within private developments through a series of strategic initiatives, which include the implementation of regulatory frameworks, the provision of design incentives, and the fostering of public-private partnerships.
By establishing comprehensive zoning laws and building regulations that encourage the integration of natural elements and green spaces into architectural designs, municipalities can cultivate an environment that supports sustainable urban planning.
This collaborative approach not only enhances community resilience and environmental awareness but also strengthens the economic advantages associated with biophilic developments.
1. Offer Incentives and Tax Breaks
Offering design incentives, green certifications, and tax breaks serves as an effective strategy for municipalities to promote the adoption of biophilic design in private developments. By providing financial benefits to developers who incorporate natural elements, sustainable materials, energy efficiency, and innovative design strategies, cities can stimulate economic growth while simultaneously enhancing community well-being.
These incentives not only foster ecological restoration and urban greening but also contribute to long-term environmental sustainability and climate resilience.
Furthermore, cities can enhance these initiatives by implementing regulatory adjustments and planning policies, such as streamlining the permitting processes for projects that include green roofs or community gardens. For instance, New York City has successfully enacted a zoning resolution that incentivizes developers for creating green spaces, ultimately contributing to a more vibrant urban environment.
Additionally, various municipalities are exploring grant opportunities and funding opportunities for projects that focus on renewable energy installations or energy-efficient construction, illustrating the beneficial intersection of economic incentives and sustainable practices.
By analyzing successful case studies, it becomes evident that when cities prioritize these incentives, they establish a foundation for a more resilient and environmentally conscious future.
2. Create Biophilic Design Guidelines
The establishment of comprehensive biophilic design guidelines is essential for ensuring that private developments align with urban planning objectives centered on sustainability, community integration, and land use planning. These guidelines should delineate best practices for the incorporation of natural elements, such as vegetation, natural light, outdoor spaces, and local flora, into new construction projects.
By implementing clear design strategies and nature integration, municipalities can enhance community spaces and foster a sense of connection between individuals and the environment, thereby promoting social sustainability and ecosystem health.
These guidelines serve a critical role in environmental education and community design by informing developers and architects about the intrinsic value of nature within urban contexts. They also promote community engagement and stakeholder collaboration by inviting local stakeholders to contribute ideas that reflect their environmental aspirations.
This collaborative approach not only benefits individual projects but also facilitates a cultural shift towards valuing greenery and biodiversity in urban architecture.
Ultimately, the integration of natural elements in developments enhances the aesthetic appeal of public areas, supports green building initiatives, and contributes to improved mental well-being, air quality, and climate resilience, thereby creating healthier and more adaptable urban environments.
3. Partner with Developers and Architects
.jpg_01.jpeg)
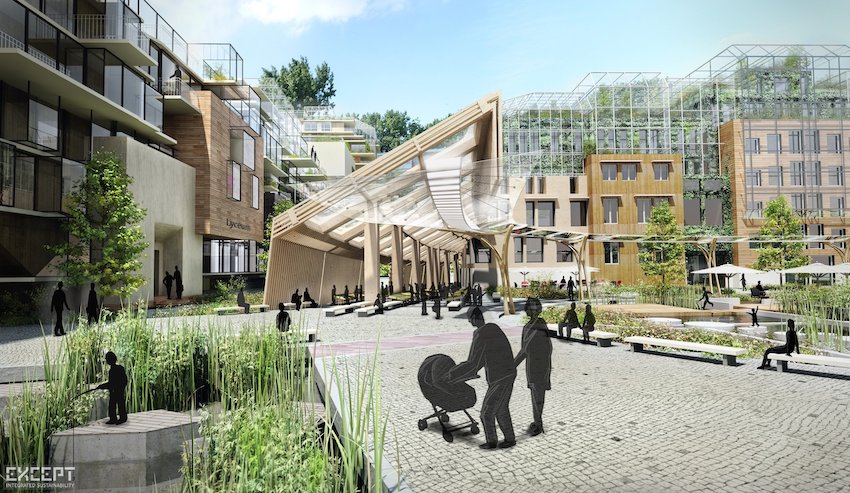
Establishing robust partnerships with developers and architects is essential for promoting biophilic design and ensuring its successful implementation in private developments. By engaging in close collaboration with these key stakeholders, city planners can exchange best practices, innovative design strategies, and insights into community needs, thereby fostering an environment conducive to sustainability, creativity, and creative placemaking. Such public-private partnerships can result in projects that enhance urban ecology while providing significant health benefits to residents.
These collaborations facilitate a seamless exchange of ideas, paving the way for solutions that address both aesthetic appeal and ecological functionality. By incorporating green spaces, natural materials, passive design, and sustainable practices into urban planning, developers and city planners can create environments that fulfill the immediate needs of the community while also contributing to long-term wellness and biodiversity.
This synergy among stakeholders amplifies the positive impacts of biophilic design, aiding in the creation of vibrant, livable urban spaces that promote a deeper connection between individuals and nature, ultimately enhancing the quality of life, livability, and social equity for all urban inhabitants.
What are Some Examples of Biophilic Design in Private Developments?
Numerous instances of biophilic design in private developments demonstrate the successful integration of natural elements, sustainable practices, and building regulations within urban environments.
Innovative architectural approaches, including the use of green roofs, living walls, and biodiversity corridors, alongside community spaces that emphasize outdoor accessibility, walkability, and pedestrian pathways, serve as prime examples of how biophilic design can enhance quality of life while promoting biodiversity and environmental stewardship.
These initiatives not only improve visual aesthetics but also reinforce the concept that nature can coexist harmoniously with urban living.
1. Incorporating Natural Elements in Building Design
Incorporating natural elements into building design is a fundamental aspect of biophilic design that significantly enhances both the aesthetics, cultural identity, and functionality of urban developments. By integrating features such as expansive windows to maximize natural light, indoor gardens, nature access, and materials that reflect local ecosystems, architects can create environments that foster a connection between individuals and nature while promoting health benefits, public health, and well-being for occupants.
These elements not only enhance the visual appeal of the urban landscape but also contribute to climate adaptation, urban forestry, and sustainability initiatives.
The integration of features such as green roofs, planted facades, and water elements like ponds or fountains can create a calming atmosphere that alleviates stress and improves mood. Furthermore, these additions encourage community engagement and interaction, resulting in environments where individuals can come together and connect with their surroundings. This, in turn, fosters a sense of belonging and enhances overall quality of life, contributing to social cohesion and public health.
Adopting sustainable building practices not only reduces energy consumption but also establishes healthier indoor environments, ultimately demonstrating that sustainable architecture has the potential to play a pivotal role in cultivating thriving communities and improving public health.
2. Creating Green Spaces and Rooftop Gardens
The establishment of green spaces and rooftop gardens represents a fundamental strategy in biophilic design that enhances urban environments and promotes community engagement. These green areas not only provide residents with access to nature but also serve as essential habitats for local wildlife, thus improving urban biodiversity and the health of urban ecosystems.
Rooftop gardens can significantly contribute to energy efficiency and stormwater management, reducing the environmental impact of private developments while fostering the well-being of residents. Additionally, these green infrastructure solutions play a crucial role in ecosystem services and climate resilience.
Incorporating such greenery is essential for creating livable cities where inhabitants can thrive both physically and mentally. These natural spaces offer numerous benefits, including air purification, heat reduction, and opportunities for social interaction, ultimately enhancing the overall well-being of the community. Green infrastructure initiatives also help with water management and habitat restoration, contributing to the city’s resilience and quality of life.
Urban greening initiatives can help mitigate the urban heat island effect and decrease energy consumption, enabling cities to progress toward sustainability and improve urban planning outcomes.
By prioritizing green spaces, urban planners not only create visually appealing areas but also invest in the long-term health of their communities and the environment, thus making urban living more harmonious and regenerative. This approach aligns with planning policies that emphasize sustainable architecture and nature integration.
3. Using Sustainable Materials
The utilization of sustainable materials in biophilic design is critical for minimizing environmental impact and promoting the health of local ecosystems. By selecting eco-friendly building materials and implementing practices such as recycling and upcycling, architects can develop structures that align with sustainability objectives while contributing to the overall wellness of communities and reducing the ecological footprint of construction practices.
This approach not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of developments but also prioritizes ecological restoration, biodiversity, and the integration of nature-based solutions.
Incorporating these materials fosters a sense of connection between occupants and their natural surroundings, which is fundamental to biophilic design. The use of renewable resources, such as bamboo, reclaimed wood, and recycled metal, significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with construction activities and supports sustainable architecture.
As urbanization continues to rise, adherence to principles of environmental stewardship through green building practices becomes essential to ensure that future generations can enjoy healthy ecosystems and resilient communities.
Therefore, architects and designers bear the responsibility of selecting materials that not only enhance urban landscapes but also foster resilient communities, uphold the planet’s ecological integrity, and support urban sustainability.
What are the Challenges of Implementing Biophilic Design in Private Developments?
The implementation of biophilic design in private developments presents several challenges that may impede its successful integration into urban planning and community design.
Significant obstacles include financial constraints, insufficient community awareness, and stringent regulatory frameworks that may not adequately support the inclusion of natural elements in architectural designs. Additionally, building regulations and planning policies could pose challenges for incorporating biophilic elements effectively.
Effectively addressing these challenges is essential for creating an environment conducive to the flourishing of biophilic principles and promoting sustainable urban development. Stakeholder collaboration and community involvement are key to overcoming these barriers.
1. Cost and Budget Constraints
.jpg_10.jpeg)
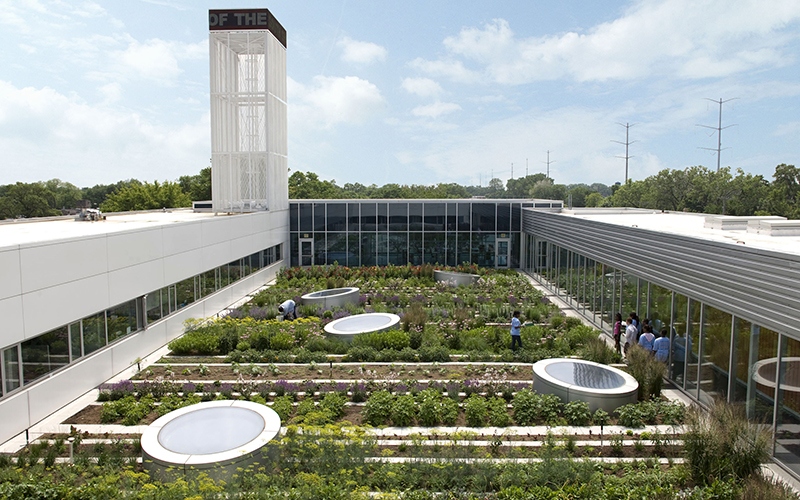
Cost and budget constraints represent a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of biophilic design in private developments, often discouraging developers from incorporating natural elements into their projects. This financial challenge can limit the scope of design innovations and hinder the realization of the long-term economic benefits associated with sustainable practices. Consequently, addressing cost concerns is essential to promote the growth of biophilic design within urban planning.
The integration of biophilic elements not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of urban spaces but also contributes to improved resident well-being and increased property values. This integration aligns with principles of social equity and community well-being.
Overcoming financial obstacles necessitates innovative urban planning strategies that prioritize these designs through potential incentives, grants, or subsidies. Collaborative efforts between government agencies and developers can facilitate the establishment of cost-effective solutions, such as phased implementation, which gradually incorporates natural elements into existing infrastructures. City officials and urban planners can provide essential support in this collaborative process.
Highlighting the quantifiable economic benefits stemming from reduced energy consumption and enhanced productivity can serve as a compelling argument, ultimately fostering societal acceptance and commitment to biophilic principles. Such benefits also contribute to the overall quality of life and urban sustainability.
2. Lack of Awareness and Education
A widespread lack of awareness and education concerning the principles and benefits of biophilic design can significantly hinder its adoption in private developments. Numerous stakeholders, including developers, city planners, and community members, may not fully grasp how biophilic design can enhance sustainability and improve quality of life. Promoting environmental education and fostering community engagement are essential measures to overcome this barrier. Strategies like urban agriculture policies and creative placemaking can also support awareness efforts.
To improve understanding and appreciation of biophilic principles, strategies such as workshops, community forums, and informational campaigns can be implemented. These initiatives should highlight the positive impacts of biophilic practices on mental health, productivity, and ecological balance. Engaging with environmental psychology experts can also contribute to these educational efforts.
Involving local organizations and experts in environmental psychology can also facilitate discussions that underscore the value of nature within urban contexts. Additionally, creating participatory projects that invite community input will give the power to stakeholders to advocate for the inclusion of biophilic elements in development plans, ensuring that the local environment is preserved and enhanced through thoughtful design. This approach supports principles of community involvement and stakeholder engagement.
3. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change presents a significant challenge in the implementation of biophilic design, as stakeholders may exhibit reluctance to adapt to new architectural strategies that emphasize the integration of nature. This hesitation often arises from concerns regarding deviations from traditional practices or the preservation of cultural heritage, which can impede innovation in urban planning and community development. Addressing this resistance is essential for cultivating an environment that embraces sustainable practices and supports innovative design strategies.
To effectively navigate these concerns, it is imperative for urban developers to engage with community members, fostering open dialogue regarding the benefits of biophilic design while respecting local customs. By integrating traditional knowledge and values with contemporary biophilic principles, architects can create spaces that resonate with residents. This approach also involves considering environmental regulations and community design guidelines.
Incorporating educational initiatives and showcasing successful examples from other culturally rich communities may illustrate how such approaches can enhance the quality of life without compromising cultural identity. Moreover, establishing partnerships with heritage organizations can further facilitate the creation of inclusive designs that honor the past while promoting a more sustainable future. This synergy can help bridge cultural identity with innovative architectural practices.
What are the Potential Solutions to Overcome these Challenges?
To address the challenges associated with the implementation of biophilic design in private developments, it is essential to explore a variety of potential solutions that prioritize community engagement, public awareness, and innovative design strategies. These solutions should also consider regulatory frameworks and public policy.
By fostering partnerships among stakeholders and promoting educational initiatives, urban areas can cultivate a supportive environment for biophilic principles, ensuring that the advantages of integrating nature are widely recognized and valued. Such collaboration can lead to the development of quality urban spaces and enhance the human-nature connection.
These approaches can facilitate sustainable urban development that emphasizes health and enhances community well-being. They also support the principles of environmental stewardship and urban sustainability.
1. Offering Financial Support and Incentives
Providing financial support and incentives represents a viable strategy to promote the adoption of biophilic design in private developments, effectively addressing the cost constraints that frequently impede implementation. Economic incentives, such as grants and tax breaks, can play a crucial role in this process.
By offering grants, tax incentives, or low-interest loans, municipalities can encourage developers to incorporate sustainable practices and natural elements into their projects. This financial support not only fosters economic growth but also enhances community well-being and promotes environmental stewardship. Funding opportunities and green certifications can further incentivize sustainable development.
Moreover, the introduction of specific mechanisms such as green building certifications or sustainability scorecards can further incentivize investments in biophilic initiatives. These strategies can result in reduced operational costs for developers and contribute to increased property values over time. Such measures also support sustainable architecture and green building practices.
In addition, cultivating partnerships between the public and private sectors can strengthen these efforts, ensuring a collective commitment to sustainable urban planning and urban biodiversity. Ultimately, the influence of these financial mechanisms transcends individual developments, contributing to a healthier urban ecosystem, enhanced ecosystem services, and a more resilient community as a whole.
2. Educating and Raising Awareness
Educating and raising awareness about biophilic design is imperative for establishing a supportive environment that embraces sustainable practices in urban development. By organizing workshops, seminars, and community events, municipalities can effectively inform stakeholders about the advantages of incorporating natural elements and nature-based solutions into architectural designs and the long-term benefits for health, public health, and quality of life.
This educational outreach has the potential to give the power to both residents and developers, fostering increased community engagement, community involvement, and participation in sustainability initiatives.
Comprehensive educational programs serve as a vital link between knowledge and action, encouraging individuals to recognize the connection between their built environment and overall well-being. Through hands-on experiences and collaborative projects, communities can gain valuable insights into how biophilic principles and passive design can enhance their surroundings.
Promoting a culture of environmental education cultivates a sense of stewardship among residents, motivating them to actively advocate for designs that prioritize nature. As awareness expands, so does the potential for innovative solutions that harmonize architecture with ecological systems, ultimately enriching urban life and promoting environmental stewardship.
3. Collaborating with Stakeholders
.jpg_11.jpeg)
Collaborating with stakeholders is essential for addressing the challenges associated with implementing biophilic design in private developments. This collaboration fosters a unified approach that aligns the interests of various parties involved in urban planning, green building, and community design.
By establishing public-private partnerships, cities can effectively leverage the expertise of developers, architects, and community members to devise innovative design solutions that prioritize sustainability, stakeholder collaboration, and enhance the quality of life.
Such partnerships not only incorporate diverse perspectives but also facilitate resource sharing, resulting in more comprehensive strategies that can be customized to meet local needs and foster social equity.
A notable example is the collaboration between the City of Chicago and local design firms, which led to the transformation of underutilized spaces into green roofs and urban gardens, thereby promoting biodiversity, urban greening, and community engagement.
This collaborative effort is critical for maximizing the potential of biophilic design, as it ensures that all stakeholders’ voices are considered and fosters a sense of ownership among them. Ultimately, this approach contributes to more sustainable urban development initiatives and improved urban ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is biophilic design and why is it important in urban planning?
Biophilic design is an approach to architecture and urban planning that incorporates elements of nature into the built environment. It is important because it has been shown to have numerous benefits for human health, environmental psychology, and well-being, as well as for the environment.
How can cities incentivize private developments to incorporate biophilic design and sustainable architecture?
One way cities can incentivize biophilic design in private developments is by offering tax breaks or other financial incentives to developers who incorporate natural elements into their projects. Cities can also create zoning regulations, building regulations, and planning policies that require a certain percentage of green space or natural elements in new developments.
Are there any successful examples of cities incentivizing biophilic design in private developments and public spaces?
Yes, there are several cities that have successfully incentivized biophilic design, such as Portland, Oregon, which offers a density bonus for developments that incorporate green roofs or living walls, and Singapore, which has a policy that requires all new buildings to have at least 50% of their rooftop covered in vegetation.
What are some potential challenges or barriers to implementing biophilic design incentives in private developments and urban sustainability projects?
One potential challenge is resistance from developers who may see biophilic design as an added cost or complication to their projects. Additionally, cities may face pushback from residents who may not understand the benefits of biophilic design or who may prefer more traditional architectural styles. Effective communication and community involvement are key to overcoming these barriers.
How can cities ensure that biophilic design incentives are equitable and accessible to all developers and enhance social cohesion?
Cities can promote equity by offering incentives to a wide range of developers, not just large corporations. They can also provide resources and support for smaller developers to incorporate biophilic elements into their projects. Additionally, cities can prioritize incentives for developments in underserved or low-income areas, enhancing social equity.
What are the potential long-term benefits of incentivizing biophilic design in private developments and public health initiatives?
Some potential long-term benefits include improved air and water quality, reduced urban heat island effect, and increased biodiversity in cities. Biophilic design can also have a positive impact on mental health and community well-being, leading to more sustainable and livable cities for all residents, while reducing the ecological footprint.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário