Community Involvement in Biophilic Urban Planning.
In an era characterized by urbanization that often marginalizes natural elements, biophilic urban planning represents a progressive approach that seeks to reconnect individuals with their environment.
This article examines the critical importance of community involvement in the development of these green spaces, emphasizing the role of public participation and stakeholder engagement in fostering ecological health and community resilience.
By incorporating local perspectives and nature integration, the advantages of biophilic design can be maximized, ranging from enhanced mental health to increased economic opportunities and improved environmental stewardship.
Through compelling case studies, land use planning, and practical steps for community participation, this discussion highlights how neighborhoods can transform urban landscapes into thriving ecosystems that promote well-being, sustainability, and urban biodiversity.
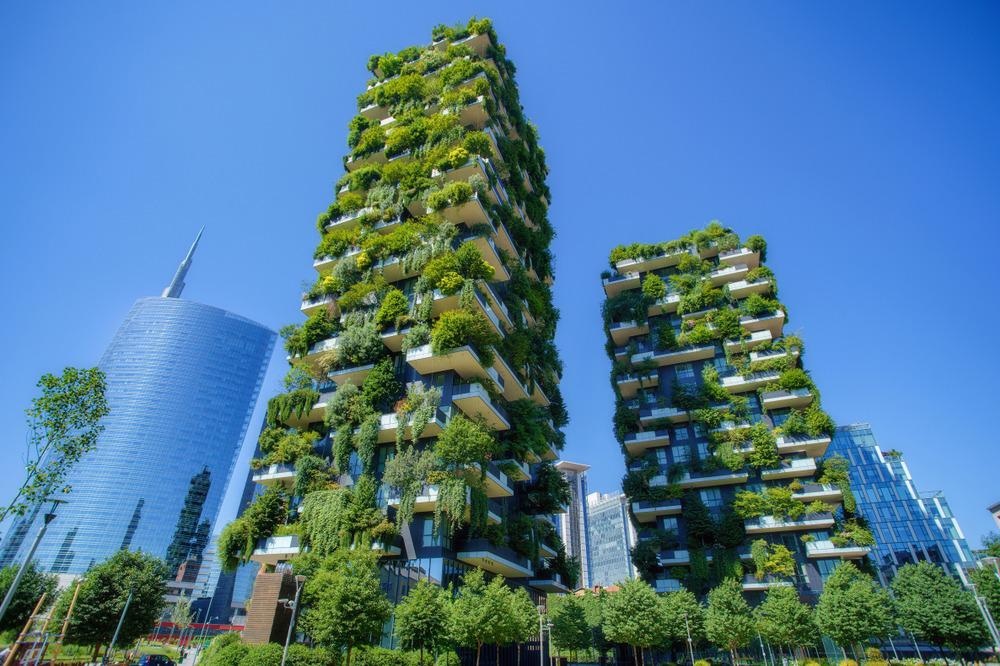
What is Biophilic Urban Planning?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
Biophilic urban planning is a design methodology aimed at integrating natural elements into urban settings, highlighting the fundamental relationship between humans and the natural environment through biophilic principles and nature connectivity.
This approach prioritizes the creation of spaces that enhance urban aesthetics while simultaneously fostering community involvement, ecological awareness, and environmental psychology through principles of sustainable development.
By incorporating green spaces, community gardens, and nature-based solutions, biophilic design seeks to improve the quality of life in urban areas, promote social engagement among residents, and enhance community well-being, all while addressing pressing challenges such as climate resilience, urban biodiversity, and the urban heat island effect.
Why is Community Involvement Important in Biophilic Urban Planning?
Community involvement is essential in biophilic urban planning, as it ensures that the needs and aspirations of local residents are adequately reflected in the design and implementation of urban spaces, thereby fostering social equity and community partnerships.
Engaging community members cultivates a sense of ownership and responsibility, resulting in more effective participation of stakeholders in the decision-making process, and promoting collaborative design and citizen activism. Furthermore, when citizens actively participate in the planning of public spaces, they bring valuable insights, cultural heritage, and collective memory to the table, thereby enhancing social networks, fostering environmental education, and contributing to heritage conservation.
This collaborative approach ultimately fortifies community resilience, promotes sustainable practices and restoration ecology, and supports the development of adaptive reuse strategies.
How Does Community Involvement Benefit Biophilic Urban Planning?
Community involvement in biophilic urban planning offers a multitude of benefits that enhance both the environment and the quality of life for local residents, thereby promoting community health and supporting urban ecology. When communities actively engage in the planning and design of urban spaces, they cultivate social cohesion and a sense of place by creating environments that reflect their unique cultural values and provide recreational opportunities, fostering place attachment.
This engagement fosters improved environmental stewardship and urban lifestyle, as citizens become invested in habitat restoration and the protection of urban ecosystems, ultimately contributing to the resilience, sustainability, and ecological footprint reduction of their neighborhoods.
This collaborative governance model encourages stakeholders to prioritize health benefits and public health initiatives, resulting in enhanced mental and physical well-being, and the promotion of healthy communities. For example, community gardens not only supply fresh produce but also function as social hubs, reinforcing connections among residents, and promoting active transportation and walkability. The revitalization of public parks can mitigate the urban heat island effect, resulting in lower healthcare costs and increased outdoor activity, thereby directly enhancing the quality of life and promoting urban regeneration.
Furthermore, the social capital generated through shared projects can lead to greater civic engagement, empowering individuals to advocate for their needs and collaborate on sustainable solutions, including integrated planning and participatory governance. Such initiatives underscore the significant impact that community involvement and participatory planning have on transforming urban landscapes into healthier, more vibrant spaces through urban regeneration and nature immersion.
What are the Challenges of Implementing Community Involvement in Biophilic Urban Planning?
Implementing community involvement in biophilic urban planning presents several challenges that urban planners and local governance must navigate to ensure equitable public participation and promote inclusive design.
Resource allocation is often a critical factor influencing the success of engagement initiatives; when funding is limited, outreach efforts may be impeded, thereby restricting access for marginalized groups who stand to benefit the most from environmental justice and urban art initiatives.
Additionally, communication barriers—arising from language differences, cultural nuances, or a general lack of information—can obstruct meaningful dialogue between stakeholders and community members, hindering the development of cultural landscapes and urban social networks.
Engaging marginalized communities also requires an understanding of their unique perspectives and histories, necessitating a sensitive approach to these discussions and a commitment to environmental justice and social equity.
Ultimately, the complexities inherent in these interactions highlight the necessity for effective urban policy that prioritizes inclusivity and collective memory, ensuring that all voices are heard and taken into account during the planning process.
Examples of Successful Community Involvement in Biophilic Urban Planning
Successful instances of community involvement in biophilic urban planning exemplify the beneficial effects of collaborative efforts in the creation of vibrant and accessible public spaces and urban forests.
These projects demonstrate that the integration of local culture and environmental stewardship can yield innovative solutions that promote social engagement, cultural identity, and enhance urban biodiversity.
By actively involving citizens in the design process, these initiatives not only improve neighborhood connectivity and walkability but also cultivate a sense of place identity and place-based education.
This approach ensures that developments are tailored to the unique needs of the community while effectively addressing challenges related to climate resilience, urban ecosystems, and ecological corridors.
Case Study 1: [City Name]
The city implemented outdoor learning programs to enhance ecological restoration and promote environmental education among residents, facilitating a deeper understanding of urban sustainability.
In [City Name], a significant case study exemplifies the impact of community participation in biophilic urban planning, emphasizing the integration of green infrastructure, public spaces, and urban wildlife habitats. This initiative actively engaged local residents through community workshops and public meetings, providing them with a platform to express their needs and preferences during the planning process, and encouraging community-led initiatives.
Consequently, the city successfully implemented features such as community gardens, green roofs, biodiversity hotspots, and ecological corridors, thereby enhancing urban ecosystems and fostering social engagement among residents.
The collaboration between local governance and community members facilitated innovative strategies, including the establishment of a dedicated advisory board composed of diverse stakeholders, to support collaborative design and civic engagement. This board played a crucial role in facilitating ongoing discussions regarding sustainable practices, urban design, and urban sustainability, ensuring that the voices of marginalized groups were adequately represented.
By incorporating feedback into the biophilic design elements, the city not only transformed public spaces but also strengthened social ties within neighborhoods and promoted community building. This initiative has set a precedent for future urban planning endeavors, harmonizing ecological benefits with the prioritization of community well-being, health and well-being, and ultimately contributing to a more resilient urban environment.
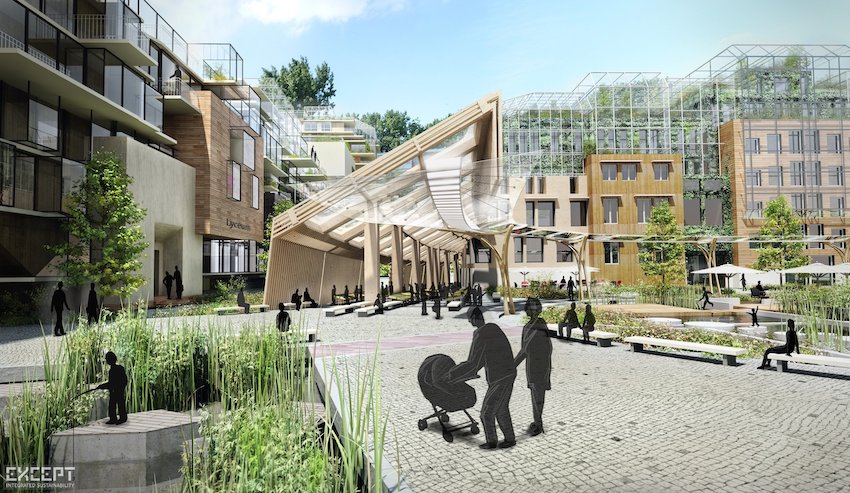
Case Study 2: [City Name]
![Case Study 2: [City Name]](https://files.autoblogging.ai/images/community-involvement-in-biophilic-urban-planning(bip9).jpg_01.jpeg)
A noteworthy case study can be observed in [City Name], where community engagement played a crucial role in enhancing urban biodiversity and urban agriculture through participatory planning processes. By actively involving residents in the design and implementation of green spaces, the city effectively integrated natural elements into the urban environment while simultaneously addressing ecological concerns, urban ecology, and promoting environmental education.
This successful collaboration resulted in the development of greenways, habitat restoration initiatives, and urban social fabric, yielding significant benefits for both local ecosystems and community well-being.
This initiative not only fostered a sense of ownership among local residents but also cultivated a deeper understanding of the importance of biodiversity, inclusive design, and sustainable practices. Through workshops, community workshops, and open forums, community members contributed their insights and aspirations, enabling the development of tailored solutions that reflected the unique characteristics of the community.
Consequently, enhanced green corridors and urban wildlife habitats emerged, supporting a variety of species and improving air quality. These participatory efforts raised awareness about environmental challenges, empowering the community to take active roles in preserving their natural surroundings, thereby reinforcing the notion that urban areas can coexist harmoniously with nature and support ecosystem services.
Case Study 3: [City Name]
In [City Name], a successful community project demonstrated how the integration of local culture into biophilic urban planning can yield significant health benefits, urban health, and enhance the sense of community.
Through collaborative planning efforts and design charrettes, residents were able to design recreational spaces that not only reflect their cultural heritage but also promote active transportation and nature therapy. This initiative not only improved community health outcomes and public health but also fostered social cohesion, environmental stewardship, and landscape architecture among participants.
By involving local residents in the decision-making process, the project encouraged sustainable practices, adaptive reuse, and participatory governance tailored to the specific needs and values of the community. Workshops and events highlighted traditional ecological knowledge and place-based education, inspiring initiatives that supported biodiversity, urban lifestyle, and enhanced urban green spaces.
As a result, there was a noticeable improvement in mental well-being, sensory experiences, and physical activity levels among community members, reinforcing their connection to the local culture and environment.
This project serves as a model for future endeavors aimed at strengthening community resources, urban regeneration, and resilience while addressing health disparities and promoting inclusivity in urban development.
How Can Communities Get Involved in Biophilic Urban Planning?
Communities can significantly contribute to biophilic urban planning through multiple avenues that promote public participation and collaboration.
By attending public meetings, residents have the opportunity to express their ideas and engage with local governance, ensuring that their perspectives are integrated into the planning process.
Participation in community organizations and advocacy groups enables individuals to connect with others who share similar objectives, while volunteering for biophilic projects and initiatives provides valuable hands-on experience and facilitates a direct impact on their local ecosystems and environment.
Furthermore, involvement in social media campaigns and online surveys can enhance community engagement and support citizen science efforts.
1. Participate in Public Meetings and Workshops
Participating in public meetings and workshops is an essential means for community members to engage in the biophilic urban planning process and influence local governance. These gatherings serve as a platform for residents to articulate their concerns, share ideas, and provide feedback on proposed projects, thereby ensuring that their voices are integral in shaping public spaces.
Active stakeholder engagement cultivates a sense of ownership among participants, motivating them to contribute to the sustainable development and urban regeneration of their neighborhoods.
These forums typically address a broad range of topics, including urban planning and:
- Environmental sustainability
- Transportation planning
- Park developments
- Housing initiatives
By attending, individuals not only acquire critical insights into the participatory planning process but also establish relationships with local officials and other community members. This collaboration is vital, as it aids in the formulation of policies that reflect the community’s needs and aspirations.
Ultimately, such collective efforts enhance civic responsibility and give the power to residents to take an active role in decision-making, underscoring the significance of community involvement in fostering thriving urban environments.
2. Join Community Organizations and Advocacy Groups
Joining community organizations and advocacy groups serves as an effective means for individuals to mobilize their efforts in biophilic urban planning and ecological health advocacy. This engagement allows them to connect with like-minded individuals and expand their urban social networks.
These groups typically focus on specific issues, such as environmental justice, urban biodiversity, or community health and well-being, providing a structured environment for collaborative action. By participating in these organizations, individuals can contribute to ongoing initiatives aimed at enhancing local ecosystems and promoting sustainable practices.
Becoming a member of such organizations presents invaluable networking opportunities that can foster fruitful partnerships and facilitate the sharing of resources. Participants often gain access to essential tools and information that are instrumental in informing their advocacy efforts, thereby simplifying the process of influencing urban policy on issues that significantly impact their communities.
The significance of collaboration cannot be overstated, as it cultivates a sense of place and belonging and encourages diverse voices to unite in advocating for meaningful change. This collective endeavor is crucial for creating resilient urban environments that prioritize ecological well-being and social equity, ensuring that all community members have the opportunity to thrive.
3. Volunteer for Biophilic Projects and Initiatives
Volunteering for biophilic projects and initiatives provides community members with valuable hands-on experience while making significant contributions to their local ecosystems and environment. These projects often encompass habitat restoration, community gardening, and the development of green spaces, offering individuals the opportunity to connect with nature and enhance their neighborhoods through urban agriculture and ecological restoration.
Participation in these activities promotes a sense of purpose, strengthens community ties, and encourages environmental stewardship and ecological restoration.
By engaging in these initiatives, individuals can observe the positive effects of their efforts firsthand, whether through planting trees that offer shade and oxygen or creating green roofs that support local wildlife.
This involvement not only enhances personal well-being but also fosters a spirit of collaboration that promotes collective responsibility for urban ecosystems and biodiversity hotspots. Such immersive experiences render nature more accessible, ignite a passion for urban sustainability, and invite additional community members to participate in nurturing a healthier and greener future for all.
Through these shared endeavors, volunteers cultivate enduring relationships while gaining insights into ecological balance and the significance of diverse habitats.
4. Engage in Social Media Campaigns and Online Surveys
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Engaging in social media campaigns and online surveys represents an effective mechanism for community members to articulate their opinions and influence biophilic urban planning and participatory governance initiatives. These digital platforms provide residents with the opportunity to convey their thoughts, feedback, and suggestions to local governance, ensuring their perspectives are integrated into the planning process.
By participating in online discussions, individuals can raise awareness of significant issues, thereby fostering a culture of citizen engagement and public participation.
These communication channels act as a vital link between local authorities and the community, facilitating connections and collaborative efforts among residents. The integration of interactive tools such as polls and forums promotes greater participation, thereby enriching the dialogue surrounding urban development.
Social media not only amplifies individual voices but also enables the organization of citizen activism campaigns that can rally citizens around shared objectives or concerns.
This comprehensive approach to gathering feedback ultimately enhances urban planning strategies, paving the way for more sustainable and livable environments that genuinely reflect the needs and aspirations of the community.
What are the Benefits of Biophilic Urban Planning for Communities?
The advantages of biophilic urban planning for communities encompass a comprehensive array of factors that significantly contribute to overall well-being and livability in urban settings through nature-based solutions and urban biodiversity.
By incorporating natural elements into urban design and landscape architecture, cities can improve environmental sustainability and promote healthier lifestyles among residents. This approach not only advances physical and mental health but also fosters social equity by ensuring equitable access to green spaces and recreational opportunities for all community members.
Ultimately, biophilic urban planning is instrumental in developing livable cities that prioritize community give the power toment and enhance the quality of life.
1. Improved Physical and Mental Health
Biophilic urban planning significantly enhances both physical and mental health by facilitating access to green spaces and opportunities for nature therapy and sensory experiences. Residing in proximity to natural environments encourages active transportation and outdoor activities, which have been shown to improve cardiovascular health and overall fitness levels.
Exposure to natural settings can reduce stress and elevate mood, contributing to improved mental health outcomes and enhanced quality of life for residents.
Recent studies indicate that urban areas that incorporate green spaces experience a 30% reduction in obesity rates, thus underscoring the direct impact of such environments on physical health.
A major report published in the Journal of Health Psychology revealed that individuals who partake in daily walks through parks experience a notable 40% reduction in anxiety levels compared to those situated in more urbanized, concrete environments.
These findings underscore the vital role of active transportation not only in promoting physical fitness but also in fostering a sense of community, ultimately leading to enhanced emotional well-being and a higher quality of life.
2. Increased Sense of Community and Social Cohesion
Biophilic urban planning enhances community engagement and social cohesion by establishing inclusive public spaces and outdoor learning environments that promote interaction and involvement among residents. When community members actively participate in the planning and design of their neighborhoods, they cultivate a stronger sense of place identity and feel a deeper connection to their environment, fostering a unique cultural identity.
This sense of belonging can lead to the development of robust social networks and support systems, ultimately contributing to a more resilient community and community well-being.
These design principles incorporate natural elements, such as greenery, water features, and open-air gathering areas, which not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban spaces but also act as catalysts for meaningful social interactions.
For instance, parks that feature native plant gardens can draw diverse groups of individuals who come together for community gardening initiatives or educational workshops, promoting ecosystem services and urban ecology.
Initiatives that prioritize these natural components, exemplified by the widely recognized ‘Park(ing) Day’ movement, effectively give the power to residents to reclaim public spaces, foster memorable interactions, and strengthen community identity.
This approach ultimately promotes deeper connections among diverse populations, reinforcing the importance of collaborative design and urban development.
3. Economic Benefits and Job Opportunities
The implementation of biophilic urban planning and biophilic design offers substantial economic benefits, including the creation of job opportunities within sectors such as green infrastructure, urban regeneration, and adaptive reuse. By investing in sustainable development practices, cities can attract businesses and stimulate local economies while simultaneously enhancing property values through the development of aesthetically pleasing public spaces and urban art.
The increasing demand for skilled labor in environmental design, landscape architecture, and sustainability initiatives can lead to long-term employment opportunities for members of the community, fostering community resilience and social equity.
Along with promoting job growth, these initiatives contribute to the overall revitalization of urban areas through placemaking and walkability improvements, rendering them more vibrant and desirable places to live and work. Local businesses typically experience increased foot traffic as neighborhoods become more appealing, resulting in higher sales and providing the potential for new ventures to emerge, supported by participatory governance and community engagement.
As property values appreciate due to improved amenities, green spaces, and urban biodiversity, homeowners benefit from increased equity, thereby fostering greater financial stability within the community. This also enhances the community’s sense of place and connectivity.
This interconnectedness underscores the essential role that biophilic urban planning and nature integration play, not only in improving environmental quality but also in driving economic resilience and social cohesion within local communities.
4. Environmental Sustainability and Resilience
Biophilic urban planning is a strategic approach that fosters environmental sustainability and resilience through the integration of natural elements within urban ecosystems, thereby helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change and reduce the urban heat island effect. By enhancing urban biodiversity through the development of green spaces, ecological corridors, and wildlife corridors, cities can more effectively adapt to environmental challenges while improving their overall ecological health. This methodology promotes a sustainable urban environment that benefits both residents and local wildlife, contributing to community well-being and place attachment.
The incorporation of native plants and trees is essential as it provides vital habitats for various species and contributes to improved air and water quality. Such practices enhance climate adaptation by reducing the occurrence of urban heat islands, facilitating rainwater absorption, and decreasing runoff, which can lead to flooding. Additionally, urban forests and community gardens serve as biodiversity hotspots and contribute to ecological restoration.
By prioritizing the preservation and enhancement of green infrastructure, urban planners can cultivate vibrant, resilient cities that are better prepared to address the uncertainties associated with climate events, while simultaneously supporting a thriving community of flora and fauna that enriches the lives of urban inhabitants. Through collaborative design and stakeholder engagement, these initiatives also promote social cohesion and collective memory.
Frequently Asked Questions
.jpg_11.jpeg)
What is meant by biophilic urban planning?
Biophilic urban planning is an approach to city planning that incorporates natural elements and principles to create a more sustainable and livable environment for both humans and wildlife, enhancing urban ecology and human-nature interaction.
Why is community involvement important in biophilic urban planning?
Community involvement is important in biophilic urban planning because it ensures that the needs and preferences of the local community are taken into consideration when designing and implementing green spaces, nature-based solutions, and outdoor learning environments in an urban setting. This participatory planning process enhances civic engagement and community partnerships.
How can community members get involved in biophilic urban planning?
Community members can get involved in biophilic urban planning by participating in public consultations, attending community meetings, and providing feedback and ideas on proposed projects. They can also join local environmental groups, engage in participatory governance, or volunteer for projects that promote biophilic design and urban policy in their city.
What are some benefits of community involvement in biophilic urban planning?
Community involvement in biophilic urban planning can lead to a stronger sense of ownership and pride in green spaces, improvements in mental and physical well-being for residents, and better decision-making that takes into account the needs of the local community. This fosters community-led initiatives and enhances social networks and urban social fabric.
How can biophilic urban planning benefit low-income communities?
Biophilic urban planning can benefit low-income communities by providing access to green spaces, community gardens, and nature-based solutions that improve air quality, reduce heat island effects, and reduce the risk of flooding. It can also create job opportunities in urban agriculture and ecological restoration, increase property values, and promote social equity, leading to economic benefits for residents.
What role do local governments play in promoting community involvement in biophilic urban planning?
Local governments play a crucial role in promoting community involvement in biophilic urban planning by providing opportunities for engagement, organizing community workshops and design charrettes, and actively seeking input from community members. They can also allocate resources and funding towards biophilic projects, inclusive design, and policies that benefit the community, enhancing public health initiatives and nature connectivity.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário