Discovering More About Biophilic Urban Facades
In an era characterized by rapid urbanization, biophilic urban facades have emerged as a crucial solution that integrates nature with architecture.
These innovative designs not only enhance the visual aesthetics of buildings but also confer significant environmental and health benefits.
Incorporating elements such as greenery, natural light, and water features, biophilic designs promote a deeper connection between individuals and their urban environments.
This article examines the importance of biophilic facades, their components, and the transformative impact they can have on urban living.
Why Are Biophilic Urban Facades Important?
Biophilic urban facades are essential in enhancing the relationship between architecture and nature, thereby fostering a robust human-nature connection that is critical for sustainable urban living.
These designs incorporate elements such as living walls, green roofs, and vertical gardens, which transform urban landscapes into restorative environments that not only improve air quality but also promote biodiversity and principles of ecological design.
By integrating natural features and sustainable materials, biophilic facades play a significant role in climate resilience, providing solutions to urban challenges such as the heat island effect while enhancing community vitality and aesthetic appeal.
Furthermore, these facades support social interaction and community engagement, ultimately contributing to the creation of livable cities where residents can thrive in harmony with nature.
How Do Biophilic Urban Facades Benefit the Environment?
Biophilic urban facades provide substantial environmental benefits by advancing urban greening initiatives, which enhance biodiversity and deliver essential ecosystem services for urban habitats. These facades incorporate a range of nature-based solutions, including living walls and green roofs, which actively contribute to improving air quality, reducing noise pollution, and offering habitats for urban wildlife.
The principles of biophilic design promote energy efficiency through passive design strategies, optimizing natural ventilation and daylighting while minimizing the environmental impact of urban developments. Through careful architectural innovation and landscape integration, these facades not only mitigate the effects of climate change but also foster a healthier urban ecosystem.
By incorporating a diverse array of plant species, these designs cultivate rich biodiversity that supports pollinators and other vital wildlife, thereby creating vibrant ecosystems within the urban landscape. The vegetation serves as a natural air filter, capturing particulate matter and absorbing carbon dioxide, which enhances overall air quality.
Furthermore, biophilic facades enhance a city’s resilience to extreme weather events by effectively managing stormwater runoff and reducing urban heat islands, ultimately contributing to the development of more sustainable and livable cities.
In summary, these environmentally conscious designs not only enhance the aesthetic value of urban spaces but also represent a crucial step toward achieving a holistic urban ecology.
How Do Biophilic Urban Facades Benefit Human Health?
Biophilic urban facades provide significant health benefits by creating environments that enhance human well-being through engagement with nature and sensory experiences. These designs establish restorative spaces that promote psychological wellness and alleviate stress, utilizing the principles of environmental psychology to strengthen the human-nature relationship.
The integration of natural elements, such as living walls and green rooftops, enriches urban landscapes and encourages residents to connect with nature on a daily basis. This connection not only transforms urban areas into vibrant ecosystems but also plays a critical role in mitigating feelings of isolation by fostering inviting spaces for social interaction and conversation.
As neighborhoods adopt this therapeutic design approach, the outcome is a more resilient community characterized by strong social bonds and shared experiences. Increased interaction with their environments facilitates higher levels of physical activity and enhanced mental clarity for individuals, thereby underscoring the essential role of nature therapy in urban planning and design.
What Are the Elements of Biophilic Urban Facades?
The elements of biophilic urban facades consist of a range of design strategies aimed at fostering a connection to nature within the built environment. These strategies incorporate essential components such as greenery, natural light, and sustainable materials.
The inclusion of living walls and vertical gardens not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of these facades but also provides critical ecological functions, including the promotion of urban biodiversity and the improvement of air quality.
The use of natural materials is vital in creating a facade that is both tactile and visually attractive, while the integration of water features can assist in microclimate regulation and enhance sensory experiences.
By prioritizing these elements, architectural design can cultivate an environment that aligns with ecological aesthetics and supports health and wellness.
1. Greenery
Greenery constitutes a fundamental element of biophilic urban facades, incorporating features such as living walls and vertical gardens that enhance urban biodiversity and provide essential ecosystem services.
These green installations not only augment the visual appeal of urban landscapes but also play a crucial role in regulating temperature, improving air quality, and supporting wildlife habitats within urban environments.
By integrating a variety of plant species, urban designers can establish microclimates that promote ecological balance while offering sensory experiences that connect residents to nature. The incorporation of greenery within facade systems is vital for fostering sustainable urbanism and enhancing community vitality.
Such initiatives are instrumental in addressing urban heat island effects, thereby creating cooler environments that enable residents to enjoy outdoor spaces with greater comfort.
The presence of plants assists in filtering pollutants and absorbing carbon dioxide, significantly enhancing the overall air quality in densely populated areas.
Along with these ecological benefits, greenery contributes to the aesthetic value of neighborhoods, thereby promoting mental well-being and fostering community pride.
As cities continue to evolve, the integration of additional plant life into architectural designs has the potential to transform urban areas into verdant havens that support both human and environmental health.
2. Natural Light
Natural light serves as a pivotal component of biophilic urban facades, significantly impacting both the aesthetic quality and health benefits of the built environment.
By optimizing daylighting through innovative architectural design, these facades enhance interior environments, diminish the dependence on artificial lighting, and promote energy efficiency.
The incorporation of large windows, skylights, and reflective surfaces facilitates the penetration of natural light into spaces, thereby creating restorative environments that foster well-being and productivity.
Research has established a strong correlation between exposure to natural light and various health benefits, including enhanced mood and cognitive function, underscoring its importance in sustainable architectural practices.
Adopting this approach not only elevates the visual appeal of urban structures but also contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and minimizing the carbon footprint associated with artificial lighting.
The integration of biophilic design principles fosters a harmonious relationship between natural ecosystems and urban living, allowing residents to establish a deeper connection with nature.
Moreover, strategically positioned light wells and green walls can improve air quality and biodiversity, thereby creating healthier urban environments.
In this manner, the effective utilization of natural light serves a dual purpose: enriching the lives of individuals while promoting a greener and more sustainable cityscape.
3. Natural Materials
Natural materials are essential components of biophilic urban facades, promoting sustainable architecture that aligns with ecological design principles. By incorporating materials such as wood, stone, and reclaimed resources, architects can significantly mitigate the environmental impact of their designs while simultaneously enhancing aesthetic appeal and fostering a connection to nature.
The tactile qualities and organic forms of natural materials create a warm, inviting atmosphere that encourages social interaction and community engagement. Additionally, these materials typically possess lower embodied energy and promote sustainability, which aligns with the objectives of green architecture and urban resilience.
Moreover, the integration of natural materials within urban environments plays a crucial role in enhancing biodiversity. By incorporating living walls and green roofs, architects not only enrich the visual landscape but also provide habitats for local wildlife, thereby supporting urban ecology.
These design choices contribute actively to improvements in air quality and temperature regulation, which are essential in mitigating urban heat island effects. As more cities adopt these principles, they cultivate a cultural shift towards sustainability, encouraging communities to appreciate the value of natural connections within built environments.
This holistic approach ultimately results in healthier, more vibrant urban spaces that promote well-being for both residents and the planet.
4. Water Features
Water features are a critical component of biophilic urban facades, significantly enhancing both the aesthetic and ecological value of urban environments. The integration of elements such as fountains, ponds, and rain gardens contributes to microclimate regulation and improves overall environmental quality.
The soothing sounds and visual movements of water features create a tranquil atmosphere, promoting relaxation and alleviating stress among urban residents. Additionally, these features function as natural filters, enhancing water quality and providing habitats for various species, thereby enriching urban biodiversity.
Moreover, water features encourage community engagement by facilitating social interactions and recreational activities, which in turn makes public spaces more vibrant and appealing. The incorporation of diverse water elements into urban landscapes not only transforms their visual appeal but also fosters a deeper connection between citizens and their environment, establishing a foundation for healthier and more sustainable urban living.
What Are the Types of Biophilic Urban Facades?
Biophilic urban facades can be classified into several distinct categories, each providing unique advantages for urban environments while fostering a connection to nature.
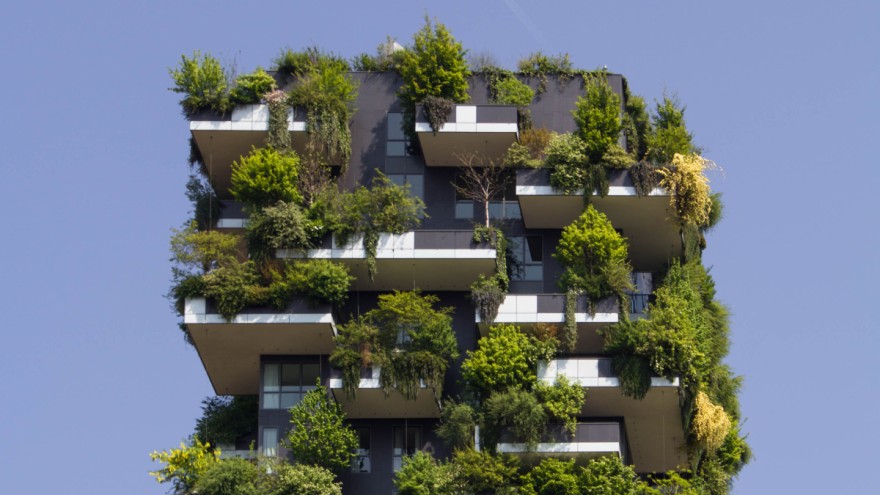
Among these categories, vertical gardens and living walls are particularly noteworthy for their capacity to transform buildings into green habitats that support urban biodiversity while enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Green roofs also play a vital role in managing stormwater and improving thermal insulation, thereby mitigating the urban heat island effect.
Furthermore, green balconies afford residents direct access to nature, underscoring the significance of outdoor spaces in urban planning and community well-being.
Collectively, these facade types exemplify the principles of sustainable urbanism and environmental stewardship.
1. Vertical Gardens
Vertical gardens represent a transformative solution in the realm of biophilic urban facades, effectively integrating greenery into the vertical surfaces of buildings to enhance urban greening initiatives and promote biodiversity. These components of living architecture not only beautify urban landscapes but also contribute to improved air quality, reduced noise pollution, and the provision of habitats for various species.
By incorporating a diverse array of plant species, vertical gardens establish a dynamic visual connection to nature, fostering a sense of place attachment among urban residents. They employ innovative irrigation and support systems that enhance ecological design, aligning with principles of sustainable urbanism.
In an era where urbanization increasingly encroaches upon natural habitats, the significance of vertical gardens transcends mere aesthetic appeal; they serve as vital components in promoting environmental resilience. Vertical gardens contribute to urban biodiversity by attracting pollinators and other wildlife, thereby creating mini-ecosystems capable of thriving even within densely populated areas.
Furthermore, these green walls can mitigate the urban heat island effect, resulting in cooler microclimates within city environments.
The careful selection of plant species not only enhances the visual interest of a facade but also optimizes climate regulation by capturing rainwater and filtering pollutants. This multifunctional approach solidifies the role of vertical gardens as essential elements in modern architectural design, harmonizing urban living with the intrinsic beauty of nature.
2. Living Walls
Living walls represent an innovative aspect of biophilic urban facades, integrating vegetation to establish verdant surfaces that enhance the ecological aesthetics of urban environments. These installations not only improve the visual appeal of buildings but also contribute to urban habitats by delivering essential ecosystem services, such as air purification and temperature regulation.
By integrating living walls into the architectural landscape, urban planners and designers foster a welcoming atmosphere that promotes interaction among community members. These vibrant green spaces serve as natural sound barriers, effectively absorbing noise and mitigating the urban heat island effect, thus enhancing overall microclimates.
The selection of diverse plant species can attract local pollinators, supporting ecological balance while encouraging a deeper appreciation for nature within the community.
The presence of living walls significantly enhances residents’ well-being by providing tranquil environments that connect individuals with the natural world, ultimately nurturing a sense of belonging and collective responsibility towards environmental preservation.
3. Green Roofs
Green roofs represent a critical component of biophilic urban facades, offering a multifunctional solution that enhances urban resilience and promotes ecological design. By covering rooftops with vegetation, green roofs effectively manage stormwater, thereby reducing runoff and improving water quality while also mitigating the urban heat island effect.
Furthermore, they contribute to energy efficiency by providing insulation, which aids in regulating building temperatures and decreasing reliance on HVAC systems. The integration of diverse plant species on green roofs supports urban biodiversity and creates restorative environments that enhance the overall quality of life for city residents.
These innovative systems can significantly alleviate the burden on urban drainage systems during periods of heavy rainfall, a factor that is increasingly important in the context of climate change. The vegetation absorbs and filters rainwater, allowing it to gradually infiltrate the soil or evaporate, rather than overwhelming sewer systems.
By reducing energy consumption through improved thermal performance, green roofs play a vital role in lowering greenhouse gas emissions, which is essential for addressing global warming. Their ability to attract various pollinators and other wildlife not only reintroduces nature into densely populated urban environments but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the natural world among urban inhabitants, ultimately contributing to healthier and more vibrant communities.
4. Green Balconies
Green balconies serve as an accessible manifestation of biophilic urban facades, enabling residents to engage directly with nature and enjoy outdoor spaces within urban environments. These balconies can be designed with a variety of plants and vegetation, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of buildings while simultaneously promoting biodiversity and improving air quality.
By integrating greenery into both private and communal balconies, urban planners can cultivate community engagement and reinforce the vital human-nature relationship essential for creating livable cities. Furthermore, green balconies contribute to mental well-being by providing restorative spaces that allow individuals to connect with their environment.
The incorporation of these green spaces not only enhances the visual landscape of urban areas but also fosters social interactions among residents, thereby creating a sense of belonging and community. As individuals congregate in these verdant areas, informal exchanges and collaborative gardening efforts become commonplace, thereby strengthening neighborhood ties.
Such initiatives can also serve as educational platforms, offering valuable insights into sustainable practices and biodiversity. Ultimately, the integration of green balconies into the urban fabric promotes a holistic approach to city living, where nature and community coexist harmoniously, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life for all residents involved.
What Are the Benefits of Biophilic Urban Facades for Cities?
Biophilic urban facades provide numerous benefits for cities, effectively addressing critical challenges such as the urban heat island effect, air quality enhancement, biodiversity improvement, and overall aesthetic value.
By incorporating nature-based solutions into urban settings, these facades play a significant role in reducing temperatures and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, they enhance air quality through natural filtration processes and support urban biodiversity by creating habitats for various species.
Along with their environmental advantages, biophilic facades improve the visual landscape of urban areas, fostering a sense of community and place while promoting social interaction and engagement among residents.
1. Improves Air Quality
One of the most significant advantages of biophilic urban facades is their capacity to enhance air quality through the integration of plants and natural ventilation systems. These facades leverage ecosystem services provided by greenery, which filter pollutants and particulate matter, leading to cleaner air for urban residents.
The incorporation of vegetation also contributes to urban biodiversity by creating habitats for various species, thereby enhancing the ecological balance of the area. Improved air quality not only benefits the environment but also has direct health implications for the community, reducing respiratory issues and promoting overall wellness.
Moreover, these innovative structures can play a crucial role in moderating temperature fluctuations and mitigating the urban heat island effect, which is a pressing concern in densely populated regions. By incorporating a diverse array of plants, urban landscapes become more resilient, facilitating better water management and decreasing stormwater runoff.
The abundant greenery not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also fosters a deeper connection between individuals and their environment. As residents benefit from cleaner air, mental health improvements can be observed through reduced stress levels, highlighting the essential role of nature in enhancing urban living conditions.
2. Reduces Urban Heat Island Effect
Biophilic urban facades are instrumental in mitigating the urban heat island effect, a phenomenon characterized by significantly higher temperatures in urban areas compared to their rural counterparts. By integrating greenery and sustainable design features, these facades can effectively lower surface and air temperatures through natural cooling mechanisms, thereby enhancing climate resilience.
The strategic incorporation of green infrastructure aligns with passive design principles that optimize energy efficiency and reduce dependence on mechanical cooling systems. As urban areas confront escalating temperatures and the challenges posed by climate change, biophilic design emerges as a viable solution for creating more comfortable and sustainable urban environments.
Furthermore, these designs promote increased biodiversity and enhance air quality, both of which are critical to sustainable urban ecosystems. By selecting plant species that are well-suited to local climates, urban areas can ensure that their biophilic facades efficiently manage heat while minimizing the need for maintenance and irrigation.
Additionally, such features contribute to stormwater management by reducing runoff and mitigating flooding risks, thereby supporting broader sustainability objectives. The adoption of biophilic design not only addresses immediate climatic challenges but also fosters long-term ecological benefits for urban communities.
3. Increases Biodiversity
Biophilic urban facades play a significant role in enhancing biodiversity within urban environments by providing essential habitats and resources for a diverse array of species. The integration of living walls, green roofs, and other nature-based solutions fosters the creation of urban habitats that support local wildlife while adhering to ecological design principles.
This enhancement of biodiversity not only contributes to environmental equilibrium but also promotes community engagement with nature, thereby raising awareness about ecological issues and the importance of conserving natural resources. By prioritizing the incorporation of nature in urban design, cities can establish rich ecosystems that benefit both residents and the environment.
Such innovative designs serve as an essential link between urban living and nature, transforming concrete landscapes into vibrant green spaces. These features attract a variety of flora and fauna, enhancing ecological networks and creating sanctuaries for pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects.
Furthermore, these biophilic elements often function as educational platforms, enabling community members to gain insights into local ecosystems and sustainable practices. The presence of green features encourages social interactions, cultivating a sense of connection among residents and their surroundings.
Ultimately, biophilic urban facades are crucial not only in mitigating urban heat but also in fostering a deeper respect and understanding of nature within the urban population.
4. Enhances Aesthetics
The aesthetic appeal of biophilic urban facades represents one of their most significant benefits, as they create visually engaging environments that enhance the overall quality of urban life. By employing design strategies that incorporate greenery, natural materials, and innovative architectural elements, these facades establish a strong visual connection to nature, transforming urban landscapes into vibrant and inviting spaces.
This enhancement of aesthetics not only contributes to community well-being but also promotes social interaction and place attachment among residents. Ultimately, biophilic urban facades exemplify the potential for architecture to harmoniously work together with the natural environment.
Such designs can evoke positive emotions and foster a sense of belonging, further encouraging individuals to connect with their surroundings and with one another. The integration of natural elements mitigates the harshness often associated with urban environments while invoking a serene atmosphere, inviting people to gather, converse, and engage in shared experiences.
Whether through lush vertical gardens or accentuated green roofs, these facades elevate the overall ambiance, nurturing a sense of community and togetherness. Through these visually captivating designs, urban areas can evolve beyond mere living spaces; they can transform into thriving ecosystems that foster emotional connections and enhance the well-being of all residents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are biophilic urban facades?
Biophilic urban facades refer to the design and incorporation of nature into buildings and structures in urban areas. This can include living green walls, vertical gardens, and other forms of vegetation on the exterior of buildings.
Why are biophilic urban facades important?
Biophilic urban facades provide numerous benefits, such as improving air quality, reducing urban heat island effect, and increasing biodiversity in cities. They also have a positive impact on mental health, as studies have shown that access to nature can decrease stress and improve overall well-being.
How are biophilic urban facades constructed?
Biophilic urban facades can be constructed using a variety of methods, such as pre-grown panels, modular systems, or individual plants attached to a support structure. The specific method used will depend on the building’s design, location, and budget.
What types of vegetation can be used for biophilic urban facades?
A wide range of plants can be used for biophilic urban facades, including vines, shrubs, and small trees. Some popular choices include ivy, ferns, and succulents. The type of plant selected will depend on factors such as climate, sun exposure, and maintenance requirements.
Are there any maintenance requirements for biophilic urban facades?
Yes, like any other living elements, biophilic urban facades require regular maintenance to thrive. This can include watering, pruning, and monitoring for pests and diseases. The level of maintenance will depend on the type of vegetation used and the specific location of the facade.
What are the cost implications of incorporating biophilic urban facades?
The cost of incorporating biophilic urban facades will vary depending on factors such as the size of the project, the type of vegetation used, and the maintenance requirements. While there may be initial costs associated with installation, the long-term benefits and cost savings from improved energy efficiency and increased property value can outweigh these costs.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário