Impact of Biophilic Design on Childhood Development
In an era increasingly centered on health and well-being, the concepts of **Active Design** and **Biophilia** have emerged as significant methodologies for enhancing our environments. **Active Design** promotes physical activity through intentional architecture and urban planning, while **Biophilia** highlights the inherent connection humans have with nature.
This discussion will examine the principles and advantages of these approaches, their integration into buildings and communities, and their overall impact on **human health**. It will elucidate how these concepts can transform our **cities** and enhance our **quality of life**.
What Is Active Design?
Active Design represents an innovative approach in urban planning and architecture that prioritizes the integration of physical activity into everyday environments.
By employing design strategies that emphasize walkability, open spaces, and community engagement, Active Design seeks to enhance occupant well-being and promote healthier lifestyles.
This methodology incorporates features such as natural light, green spaces, and ergonomic design to create environments conducive to physical activity and social interaction.
The concept aligns with principles of environmental psychology and fosters a connection to nature, positioning itself as a crucial component in the development of sustainable cities and livable communities.
What Are the Principles of Active Design?
The principles of Active Design concentrate on the development of environments that facilitate physical activity through strategic spatial design and community-oriented features. These principles emphasize accessibility, connectivity to natural surroundings, and the incorporation of amenities that promote exercise and wellness, ultimately contributing to a healthier population.
By prioritizing natural ventilation, these environments can enhance indoor air quality, which is crucial for the overall health of the community. Furthermore, the integration of daylighting in design not only reduces energy consumption but also has significant positive impacts on mood and productivity.
Creating environments conducive to physical activity involves designing spaces that encourage walking, cycling, and social interaction, thereby strengthening community bonds. Such designs acknowledge the restorative benefits of nature and provide opportunities for restorative practices, ultimately resulting in improved physical and mental well-being for all users.
How Does Active Design Promote Physical Activity?
Active Design is essential in promoting physical activity by transforming public spaces and architectural designs into interactive environments that encourage movement.
By integrating features such as walkable pathways, recreational areas, and engaging outdoor spaces, Active Design creates opportunities for exercise, enhances social cohesion, and contributes significantly to the overall health and well-being of the community.
What Are the Benefits of Active Design?
The benefits of Active Design are multifaceted, significantly enhancing individual health, mental well-being, and community engagement. By fostering environments that prioritize physical activity, Active Design not only improves health outcomes for individuals but also cultivates stronger social bonds and promotes environmental sustainability through thoughtful urban planning.
This approach encourages regular movement among residents, effectively increasing physical activity levels, which can lead to reduced obesity rates and improved cardiovascular health.
Plus physical benefits, the emphasis on psychological well-being through design elements such as green spaces and communal areas creates restorative environments that significantly contribute to stress reduction and a sense of tranquility.
These inviting surroundings facilitate social interaction, enabling individuals to build relationships that are essential for emotional support. Furthermore, exposure to nature, often integrated into Active Design, has been shown to enhance mood and foster a sense of community, making it a vital component of contemporary urban living.
How Can Active Design Be Incorporated into Buildings and Communities?
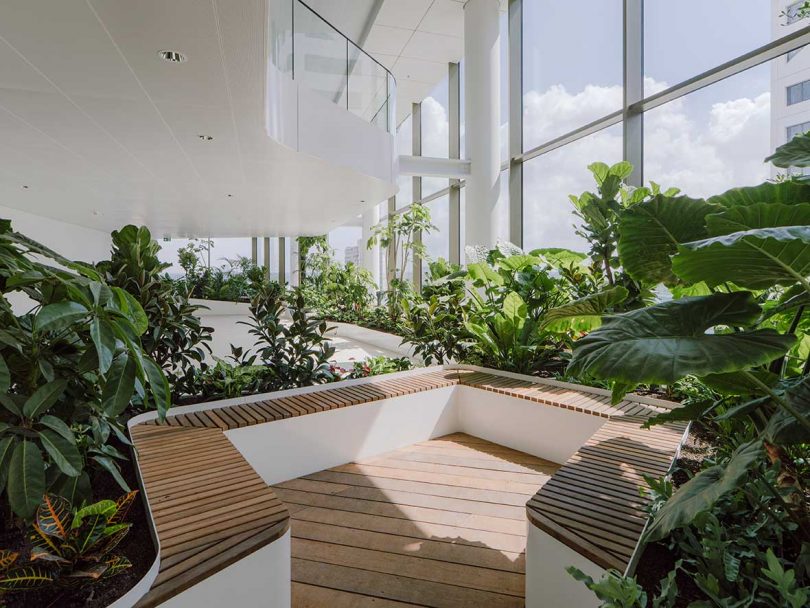
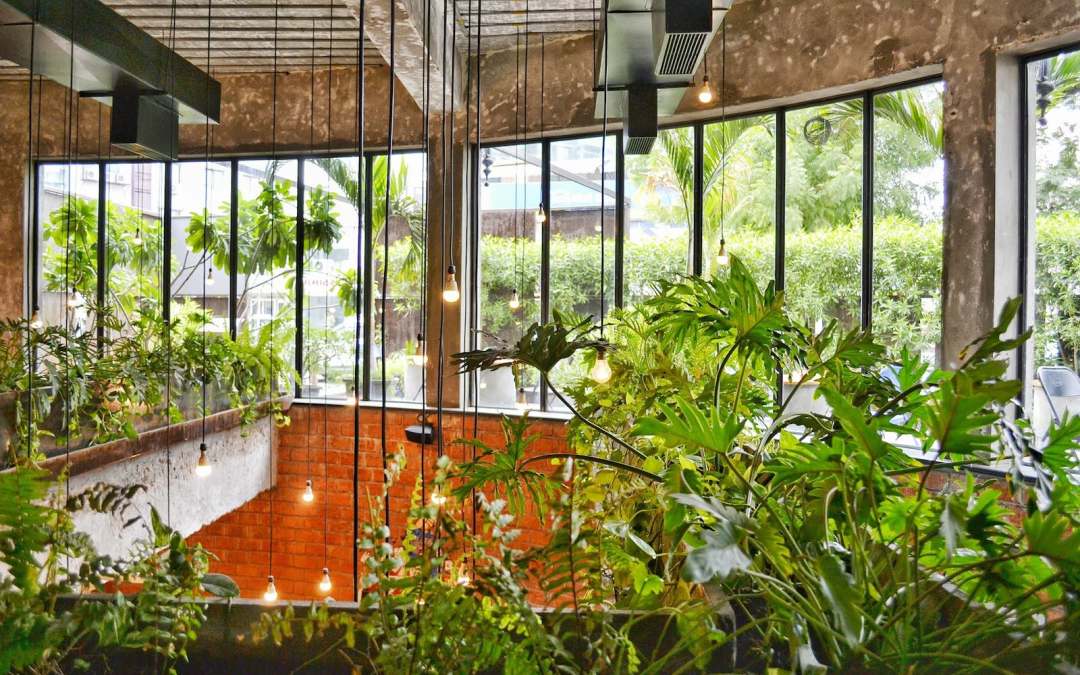
Incorporating Active Design into buildings and communities necessitates a comprehensive approach that takes into account the needs of users and the surrounding environment. This approach encompasses the implementation of design strategies that enhance walkability, provide green spaces, and promote community engagement, while also ensuring the integration of natural materials and biophilic elements.
To effectively execute these strategies, architects and urban planners should establish safe pedestrian pathways that connect residential areas with parks and communal spaces. Additionally, prioritizing the placement of windows and skylights can optimize the influx of natural light, thereby improving overall mood and productivity.
The inclusion of green roofs and vertical gardens not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of structures but also contributes to improved air quality, fostering healthier living environments. Furthermore, designing buildings with direct access to parks or natural areas strengthens the connection between individuals and nature, promoting well-being and encouraging outdoor activities.
Collectively, these actionable interventions play a vital role in establishing a vibrant and sustainable community framework.
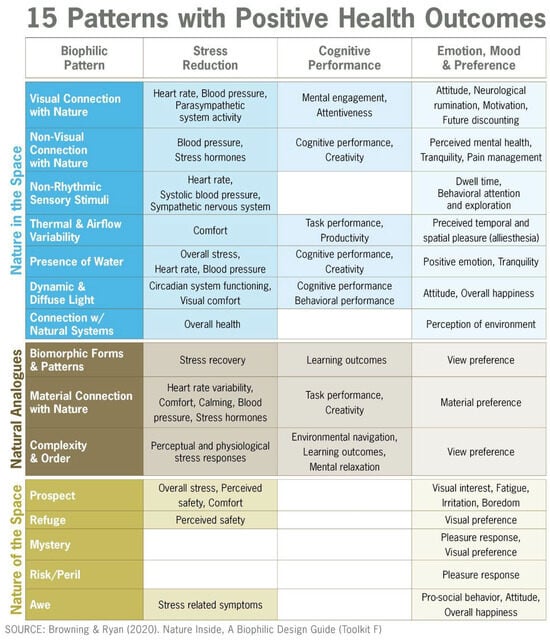
What Is Biophilia?
Biophilia refers to the innate human propensity to connect with nature and other living organisms, which plays a fundamental role in influencing our health and well-being.
This concept highlights the significance of integrating natural elements within design, illustrating how exposure to natural environments can improve mental health, alleviate stress, and foster a sense of community and belonging.
How Does Biophilia Affect Human Health and Well-being?
The impact of biophilia on human health and well-being is significant, as regular interaction with natural environments has been demonstrated to reduce stress levels, enhance mood, and improve overall health. By fostering a connection with nature, biophilia can lead to considerable advancements in mental health and psychological well-being.
Numerous empirical studies substantiate this connection, illustrating that the integration of nature in urban settings fosters restorative landscapes that yield tangible health benefits. For example, research shows that individuals who spend time in green spaces exhibit lower cortisol levels and improved emotional resilience.
Environments designed with health-oriented principles can also encourage physical activity, further establishing a link between natural settings and enhanced cardiovascular health.
This body of evidence underscores the importance of incorporating biophilic elements into design, creating spaces that support both mental and physical health, ultimately transforming living conditions into sanctuaries of health and wellness.
How Can Active Design and Biophilia Work Together?
Active Design and biophilia can effectively collaborate to establish environments that promote physical activity while simultaneously fostering a profound connection to nature.
By incorporating biophilic elements within the framework of Active Design principles, urban planners and architects can enhance the well-being of occupants, encourage an active lifestyle, and create restorative environments that yield benefits for both individuals and communities.
What Are Some Examples of Active Design and Biophilia in Practice?
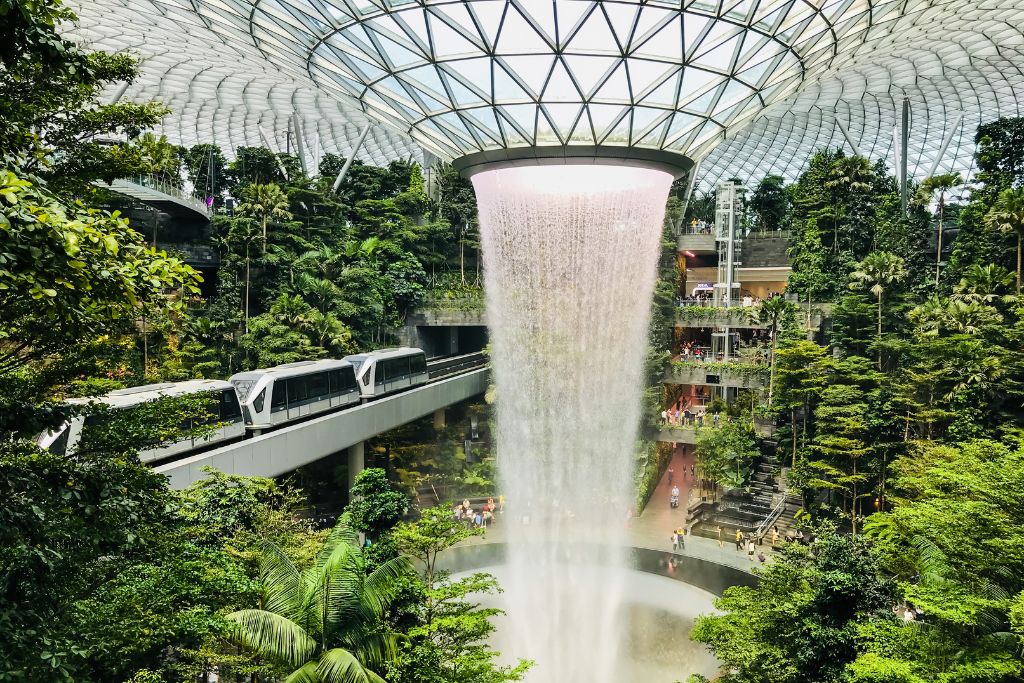
Examples of Active Design and biophilia can be observed in various urban and architectural projects that prioritize health, wellness, and exposure to nature. These initiatives serve as exemplary models for integrating green infrastructure, outdoor spaces, and immersive environments that promote physical activity and foster community engagement.
A noteworthy case study is the High Line in New York City, where innovative landscape architecture has transformed an abandoned rail line into a vibrant green space. This elevated park not only facilitates social interactions but also incorporates native plant species, thereby supporting local biodiversity.
Similarly, the Eden Project in Cornwall, UK, exemplifies adaptive design through its biodomes, which connect visitors to diverse ecosystems and promote a deeper understanding of environmental sustainability.
These examples illustrate how the thoughtful integration of landscape architecture and green spaces can contribute to healthier communities, emphasizing the importance of biophilia in contemporary design.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing Active Design and Biophilia?
The implementation of Active Design and biophilia presents a variety of challenges that urban planners, architects, and communities must effectively address.
These challenges encompass the need to balance developmental requirements with environmental sustainability, manage budget constraints, and foster community engagement throughout the design process.
How Can Active Design and Biophilia Be Used in Urban Planning?
Active design and biophilia can be effectively integrated into urban planning frameworks to cultivate healthier and more vibrant communities.
By emphasizing health-oriented design and fostering community engagement, urban planners have the opportunity to create environments that promote physical activity and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
What Are Some Successful Examples of Active Design and Biophilia in Urban Planning?
Several exemplary instances of Active Design and biophilia in urban planning illustrate innovative strategies for fostering healthy communities. These projects highlight the benefits of integrating green infrastructure, community spaces, and biophilic elements, which contribute to improved well-being and increased physical activity among residents.
Urban planners worldwide have adopted these principles, fundamentally transforming the conception and experience of urban environments. For example, the integration of recreational spaces, such as parks and trails, promotes active lifestyles, while the inclusion of nature connection features, such as living walls and green rooftops, cultivates a sense of tranquility amidst the demands of urban life.
A thoughtfully designed neighborhood not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the area but also significantly enriches social interactions among community members, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration. The synergy between intentional design and natural elements enhances the physical landscape and supports the overall health of communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Active Design?
Active Design is a set of design strategies that promote physical activity and healthy behaviors in built environments.
What is Biophilia?
Biophilia is the innate human connection to nature and the belief that incorporating natural elements into built environments can improve health and well-being.
How can Active Design and Biophilia work together?
Active Design and Biophilia can work together by incorporating natural elements and promoting physical activity in built environments, leading to improved health and well-being.
What are some examples of Active Design and Biophilia in action?
Examples of Active Design and Biophilia include incorporating natural lighting, greenery, and walking paths into buildings, as well as incorporating stairs and bike racks to promote physical activity.
How does Active Design and Biophilia benefit individuals and communities?
Active Design and Biophilia can benefit individuals and communities by improving physical and mental health, reducing stress, and promoting social interaction and community pride.
Can Active Design and Biophilia be implemented in all types of built environments?
Yes, Active Design and Biophilia can be applied to various built environments, including offices, schools, hospitals, and public spaces.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário