How Regulations are Boosting Green Roofs in Cities
As urban areas continue to expand and develop, the necessity of sustainable practices becomes increasingly apparent.
Green roofs provide numerous advantages, including environmental enhancement, economic stimulation, and the promotion of stronger social connections within communities.
This document examines the significance of green roofs, the regulations that facilitate their implementation in urban settings, and highlights cities that are at the forefront of promoting these eco-friendly solutions.
It is essential to recognize how green roofs not only improve the aesthetics of our landscapes but also contribute to a healthier planet and community.
Why Are Green Roofs Important?
Green roofs have become an essential element in urban planning and sustainable architecture, offering a range of benefits that include support for environmental policy initiatives, enhancement of biodiversity, and effective stormwater management strategies.
As urban areas confront the challenges posed by the urban heat island effect and the need for climate resilience, green roofs not only help mitigate these issues but also contribute to energy efficiency and public health improvement.
The integration of such green infrastructure into urban design holds the potential to reshape cityscapes while providing ecological advantages that are critical for a sustainable future.
Moreover, the implementation of effective landscaping practices in green roofs can significantly enhance the aesthetic appeal and overall real estate value of urban properties.
1. Environmental Benefits
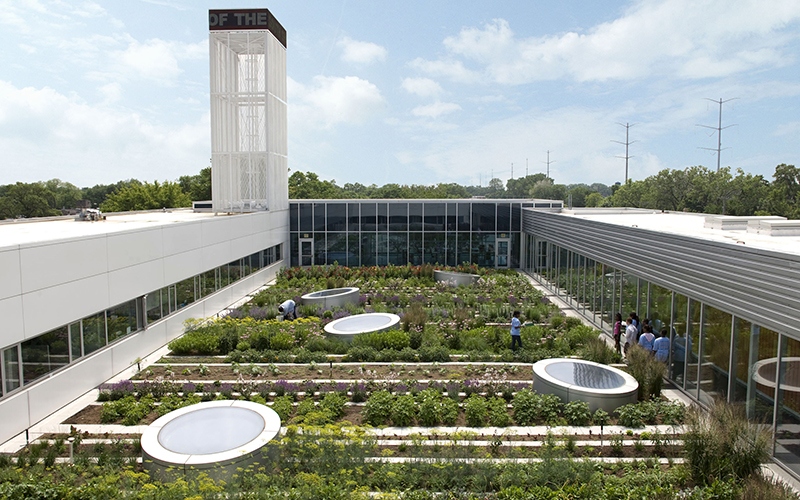
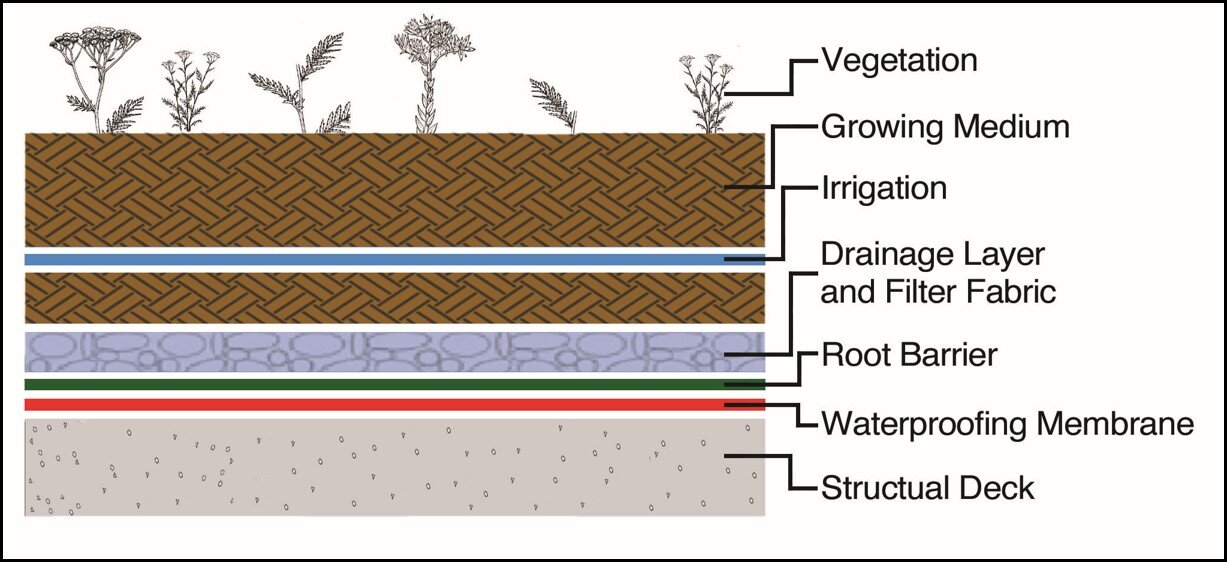
The environmental benefits of green roofs are significant, primarily contributing to enhanced biodiversity, effective stormwater management, and improved energy efficiency within urban environments. These roofs provide essential habitats for various species, especially when designed with native plants that support local ecosystems.
By incorporating a diverse array of vegetation types, including flowering perennials, sedums, and grasses, these green spaces become vital refuges for pollinators and other wildlife. It is essential to ensure adequate soil depth and appropriate substrate composition to sustain plant health and optimize water retention. Regular maintenance, including periodic irrigation and weeding, is necessary to foster a thriving ecosystem.
Green roofs not only help mitigate urban heat islands but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of cities, thereby promoting sustainable urban development. Through comprehensive environmental assessments, the integration of these green spaces can significantly strengthen urban sustainability initiatives and further support surrounding biodiversity.
2. Economic Benefits
Green roofs significantly enhance the ecological landscape of urban areas while providing substantial economic benefits, including increased real estate value and property tax incentives for building owners.
By implementing green building practices, properties featuring green roofs can attain LEED certification, which frequently leads to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills over time. The widespread adoption of green roofs stimulates local economies by creating green jobs and offering funding opportunities for sustainable urban development projects.
These environmentally friendly installations play a crucial role in stormwater management, which can lead to a reduction in city infrastructure costs by decreasing the need for extensive drainage systems. Cities such as Toronto and Chicago have demonstrated impressive returns on investment from their green roof initiatives, reporting enhanced property values and diminished urban heat island effects.
Furthermore, government programs often provide financial incentives, including tax credits, grants, and low-interest loans, to encourage businesses and homeowners to invest in these sustainable solutions.
Consequently, green roofs not only advance environmental sustainability but also present a compelling argument for economic sustainability that benefits communities as a whole.
3. Social Benefits
The social benefits of implementing green roofs in urban environments are significant, encompassing enhancements in public health, increased community engagement, and improved social equity.
Green roofs can function as spaces for urban agriculture or community gardens, yielding fresh produce while fostering interactions among residents. The aesthetic value of green roofs contributes to the beautification of urban areas and plays a crucial role in climate adaptation strategies, promoting well-being and alleviating stress among urban inhabitants.
These innovative installations not only revitalize underutilized spaces into vibrant community hubs but also give the power to residents by actively involving them in decision-making processes concerning their environment.
Projects such as the Brooklyn Grange in New York exemplify how rooftop farms can create employment opportunities, educate individuals on sustainable practices, and enhance access to nutritious food in underserved neighborhoods.
Such initiatives unite communities, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration, which are essential for cultivating a resilient social fabric. With increased green coverage, neighborhoods experience a reduction in urban heat island effects, leading to improved air quality and promoting overall health.
Thus, these urban agricultural initiatives are vital for advancing social equity within urban settings.
How Are Green Roofs Regulated In Cities?
The regulation of green roofs in urban environments is governed by a combination of local government regulations, building codes, and zoning laws aimed at ensuring effective implementation and compliance.
These urban regulations establish installation guidelines and design standards that promote the development of green roofs, frequently accompanied by government incentives for property owners and developers.
By fostering regulatory compliance, municipalities can encourage the adoption of green roofs as an essential component of sustainable urban development.
1. Local Government Regulations
Local government regulations play a substantial role in the adoption of green roofs, with specific ordinances and policy frameworks designed to address urban ecology and environmental assessments. These regulations typically establish requirements for green roof design, maintenance, and performance, ensuring alignment with sustainability goals and broader city planning objectives.
Through the implementation of zoning laws and incentives, local authorities not only promote green infrastructure but also encourage community engagement in environmental stewardship. For example, cities such as Toronto and San Francisco have instituted mandatory green roof requirements for new developments, effectively transforming their skylines while enhancing biodiversity and mitigating urban heat.
These regulations contribute to the management of stormwater runoff, the improvement of air quality, and the promotion of energy efficiency. Consequently, urban planners and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the importance of integrating green roofs into their comprehensive strategies for climate resilience, which is vital for developing sustainable cities capable of adapting to future challenges.
2. Building Codes And Standards
Building codes and standards play a critical role in the effective integration of green roofs into urban architecture by establishing essential construction regulations and installation guidelines. These codes ensure regulatory compliance while promoting best practices in design, maintenance, and safety, thereby maximizing the benefits associated with green roofs.
Codes set forth by the International Green Construction Code (IgCC) and local municipal ordinances specifically outline requirements for structural integrity, stormwater management protocols, and criteria for plant selection. These regulations collectively influence the design and installation of these living roofs.
For instance, urban planners and architects can enhance both compliance and sustainability by integrating rainwater harvesting systems that adhere to these standards, which effectively reduces runoff and improves irrigation efficiency.
Furthermore, many cities are implementing incentivization strategies, such as tax credits and expedited permits for projects that comply with rigorous green roofing standards. These initiatives not only cultivate a culture of compliance but also encourage innovation in sustainable design practices.
3. Incentive Programs
Incentive programs play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of green roofs by providing financial support through government incentives and funding opportunities that encourage property owners to invest in green technology. These initiatives may include property tax benefits, grants, and rebates designed to alleviate the financial burden associated with green roof installations.
In numerous urban areas, local governments have established specific rebate programs aimed at subsidizing the costs of green roof systems, thereby offering financial relief that directly benefits property owners. For example, states such as New York and California have implemented initiatives that not only facilitate immediate savings through rebates but also enhance long-term property values and reduce stormwater management expenses.
Successful programs in cities like Philadelphia have illustrated that incentivizing green roofs can yield significant environmental advantages, including improved air quality and decreased urban heat, while also contributing to sustainability objectives. Such economic and regulatory frameworks are essential in promoting the widespread adoption of environmentally friendly practices, ultimately enhancing urban resilience.
What Cities Have Implemented Regulations For Green Roofs?
Numerous cities worldwide have effectively implemented regulations concerning green roofs as an integral component of their comprehensive city planning and environmental policy initiatives, aimed at promoting sustainable urban development.
These municipalities have acknowledged the significance of regulatory compliance in advancing the ecological benefits of green roofs and enhancing climate resilience within urban settings. Through the adoption of innovative policies, they are establishing benchmarks for sustainable cities and serving as a source of inspiration for other urban areas to emulate.
1. Chicago, Illinois
Chicago has established itself as a leader in the implementation of green roofs, supported by urban planning policies that advocate for the installation of these sustainable structures in both residential and commercial buildings. The city has introduced government incentives that promote biodiversity and enhance the ecological advantages of green roofs, reflecting a strong commitment to innovative environmental policy.
Significantly, initiatives such as the Chicago Climate Action Plan and the Green Roof Grant Program have been instrumental in facilitating this green transformation. By offering financial assistance and technical support, these programs have give the power toed numerous property owners to convert their rooftops into vibrant green spaces.
Notable projects, including the City Hall green roof and the Center for Green Technology, serve as exemplary models of successful implementation, effectively reducing urban heat and improving stormwater management.
The establishment of these green spaces not only enriches local ecosystems by fostering the growth of diverse flora and fauna but also contributes positively to the overall health and well-being of Chicago’s residents.
2. Portland, Oregon
Portland is at the forefront of sustainability initiatives, having implemented comprehensive green infrastructure policies that promote the installation of green roofs as a vital component of urban ecology. The city’s zoning laws facilitate community engagement in the green roof movement, resulting in widespread adoption and innovative designs that enhance the urban landscape.
These efforts are not merely bureaucratic; they reflect a profound commitment to improving community well-being and environmental health. Local organizations collaborate closely with residents to educate them about the benefits of green roofs, including improved air quality, effective stormwater management, and increased biodiversity.
Specific projects, such as the Tilikum Crossing, feature lush green roofs that serve as public gathering spaces, exemplifying how green infrastructure can seamlessly integrate functionality with aesthetics. Initiatives of this nature demonstrate that Portland not only prioritizes sustainable urban practices but also actively fosters community involvement, ensuring that the voices of its citizens play a pivotal role in shaping a greener future.
3. Toronto, Canada
Toronto has made substantial progress in promoting green roofs through the efforts of its Green Building Council and thorough environmental assessments. The city has established comprehensive climate action plans that support regulations for green roofs, thereby enhancing its capacity for climate resilience while fostering urban biodiversity.
These initiatives encompass financial incentives for developers, streamlined approval processes, and educational programs aimed at raising awareness regarding the advantages of green roofing. By involving stakeholders in the planning phases, the city has ensured that these projects are aligned not only with sustainability objectives but also with the needs of the community.
The positive impacts of these regulations are evident, as urban areas experience improved air quality, reduced heat island effects, and expanded recreational spaces for residents. These endeavors significantly contribute to advancing environmental stewardship and sustainable urban living, positioning Toronto as a leader in climate action.
4. Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen is widely recognized for its innovative approach to urban resilience, particularly through the incorporation of green roofs into its climate adaptation strategies to address urban flooding and enhance biodiversity. The city has established comprehensive community outreach programs aimed at educating citizens on the benefits of green roofs, while simultaneously encouraging their participation in sustainable urban development.
These initiatives not only support environmental sustainability but also cultivate a sense of ownership among residents, effectively making them stakeholders in the ecological future of their community. For instance, the successful implementation of the green roof on the Sankt Peder’s Stræde building exemplifies how such projects can mitigate rainwater runoff while also providing recreational space for residents.
Furthermore, the city has organized workshops and public discussions that actively engage citizens in the design process, ensuring that these green spaces align with the needs and aspirations of the community. Consequently, Copenhagen continues to serve as a leading model for integrating nature into urban living, inspiring other cities confronted with similar challenges.
5. Melbourne, Australia
Melbourne has implemented progressive environmental policies that underscore the significance of green roofs in enhancing urban ecology and promoting sustainable development. Through effective regulatory compliance and the integration of green technology, the city has set a benchmark for others seeking to adopt successful green roof initiatives.
The city’s comprehensive environmental policy framework not only encourages the construction of green roofs but also provides incentives for businesses and homeowners to invest in sustainable practices. The realization of projects such as Council House 2, which features an impressive green roof that aids in stormwater management and improves air quality, exemplifies how innovation can contribute to sustainability.
Numerous local initiatives, including grants and workshops, have cultivated a culture of environmental stewardship among residents, fostering a collaborative approach to enhancing the urban landscape.
By establishing a supportive environment for these initiatives, Melbourne illustrates how cities can effectively integrate nature into the built environment, yielding both ecological and social benefits.
What Are The Benefits Of Green Roof Regulations?
The implementation of regulations for green roofs provides numerous benefits that strengthen the sustainability of urban environments, thereby contributing to the advancement of sustainable cities and enhancing urban resilience.
These regulations not only facilitate climate adaptation but also support policy frameworks that prioritize ecological advantages, ensuring that cities are equipped to thrive amidst environmental challenges.
1. Encourages Sustainability
Green roof regulations are essential in promoting sustainability initiatives within urban landscapes by integrating green technology and fostering community engagement in environmental practices. Through the implementation of these regulations, cities have the potential to significantly reduce their ecological footprint and enhance their overall environmental impact.
These initiatives cultivate a culture of sustainability, ensuring that urban development aligns with ecological responsibility. For example, cities such as Chicago have introduced comprehensive policies that incentivize the installation of green roofs, resulting in reduced stormwater runoff and improved air quality.
Community organizations frequently collaborate with local governments to educate residents about the advantages of these green spaces, which in turn increases public participation. Such partnerships not only enhance urban biodiversity but also strengthen community pride, as citizens actively engage in the development of vibrant, green environments that promote healthier lifestyles and foster social connections.
2. Reduces Urban Heat Island Effect
One of the primary advantages of green roof regulations lies in their effectiveness in mitigating the urban heat island effect, which plays a significant role in enhancing climate resilience and energy efficiency within urban areas. By increasing vegetation cover and promoting ecological benefits, green roofs contribute to the reduction of heat retention in cities.
Research demonstrates that green roofs can decrease surface temperatures by as much as 30% compared to traditional rooftops, primarily through the mechanisms of evapotranspiration and shading. Evapotranspiration involves the release of moisture by plants, which subsequently cools the surrounding air, while the plants provide a natural barrier against solar radiation.
Furthermore, studies indicate that urban areas with extensive green roofing can experience a reduction in energy consumption in nearby buildings by up to 25%, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. This enhancement of energy efficiency not only improves the sustainability of urban environments but also bolsters their overall climate resilience as they adapt to rising temperatures and changing weather patterns.
3. Improves Air Quality
Green roof regulations play a pivotal role in enhancing air quality by facilitating pollution control measures and amplifying the ecological benefits associated with urban greening. These roofs effectively filter pollutants, sequester carbon, and promote biodiversity, ultimately leading to improved public health outcomes for residents.
Research demonstrates that urban areas equipped with green roofs can reduce airborne particulate matter by as much as 60%, thereby producing a significant positive impact on the local environment. For example, cities such as Stuttgart, which have implemented extensive green roof initiatives, have reported a notable decrease in respiratory issues associated with pollution.
Studies indicate that each square meter of green roof has the capacity to absorb approximately 2.4 kg of carbon dioxide annually, representing a substantial contribution to the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions. This collective effort not only alleviates air pollution but also encourages healthier lifestyles among urban residents, thereby fostering a stronger community connection to nature.
4. Increases Biodiversity
By implementing green roof regulations, municipalities can substantially enhance biodiversity through the creation of habitats and the incorporation of native plant species within urban environments. These green spaces serve as vital habitats for diverse flora and fauna, fostering community engagement and cultivating a greater appreciation for local ecosystems.
Green roofs not only alleviate urban heat but also support a variety of vegetation types, including drought-resistant succulents and native wildflowers, which in turn attract essential pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The integration of diverse plant species can lead to the formation of microhabitats, thereby enhancing ecological functions such as pest control and nutrient cycling.
Community initiatives that include workshops and educational programs give the power to residents to recognize the significance of these green spaces. Such programs promote local stewardship and encourage practices aimed at conserving biodiversity, enabling individuals to connect with nature and understand their role in maintaining ecological balance.
5. Reduces Energy Consumption
Green roof regulations play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption by improving thermal insulation and promoting climate adaptation strategies within urban buildings. These roofs contribute to the regulation of indoor temperatures, resulting in a decreased dependence on renewable energy sources for heating and cooling.
The implementation of green roofs has consistently demonstrated a significant reduction in energy demand, with numerous studies underscoring their effectiveness in maintaining comfortable indoor conditions.
For example, research conducted in New York City revealed that buildings outfitted with green roofs could experience a reduction in cooling energy use by as much as 50% during peak summer months. Additionally, a case study in Toronto indicated that green roofs could diminish heating requirements during winter, leading to considerable cost savings for both residents and businesses.
This innovative approach not only enhances building efficiency but also supports broader urban sustainability objectives by mitigating the urban heat island effect.
6. Enhances Aesthetics
Green roof regulations significantly enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban environments, contributing to urban beautification and the establishment of green infrastructure that transforms cityscapes. These roofs can also accommodate community gardens, providing engaging spaces for residents and fostering a connection to nature.
By integrating vibrant greenery, green roofs soften the harsh lines of concrete buildings and create visually appealing landscapes that elevate the surrounding atmosphere. Careful design considerations, such as the selection of native plants and the incorporation of varied textures and heights, can result in stunning landscapes that evolve with the changing seasons.
Successful initiatives like New York City’s Brooklyn Botanic Garden and Chicago’s City Hall roof garden exemplify how these projects promote community interaction while enhancing air quality and biodiversity. Ultimately, such efforts lead to healthier, more attractive urban areas that residents can take pride in.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are green roofs and why are they important for cities?
Green roofs are rooftops that are covered with vegetation and soil, providing a natural layer on top of buildings. They are important for cities because they help reduce urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and promote biodiversity.
What are regulations promoting green roofs in cities?
Regulations promoting green roofs in cities are laws or policies that require or incentivize the installation of green roofs on new or existing buildings. These regulations may include tax incentives, building codes, or zoning ordinances.
What are the benefits of having regulations promoting green roofs in cities?
The benefits of having regulations promoting green roofs in cities include reducing energy consumption, improving stormwater management, increasing property value, and creating green spaces for residents to enjoy.
Which cities have implemented regulations promoting green roofs?
Many cities around the world have implemented regulations promoting green roofs, including Toronto, Chicago, and Copenhagen. These cities have seen significant environmental and economic benefits from their green roof policies.
What are some common requirements in regulations promoting green roofs?
Common requirements in regulations promoting green roofs may include minimum square footage of green roof per building, specific types of vegetation to be used, and maintenance guidelines. These requirements may vary depending on the city and its specific goals.
What can individuals do to support regulations promoting green roofs in cities?
Individuals can support regulations promoting green roofs in cities by advocating for their implementation, participating in community initiatives to install green roofs, and considering installing a green roof on their own property. They can also support businesses and organizations that prioritize sustainability and green initiatives.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário