Maximizing Urban Biodiversity: Strategies for Sustainable City Development
Urban biodiversity represents a critical yet frequently neglected aspect of our cities, encompassing the diverse flora and fauna that thrive within urban environments.
As urban areas continue to expand and evolve, it is imperative to recognize the significance of urban biodiversity.
This article examines the importance of urban biodiversity, the threats it faces as a result of urbanization and pollution, and the numerous benefits that effective biodiversity strategies can confer upon urban areas.
By enhancing human health and improving resilience against climate change, promoting biodiversity has the potential to transform our cities into healthier and more vibrant spaces for all residents.
What is Urban Biodiversity?
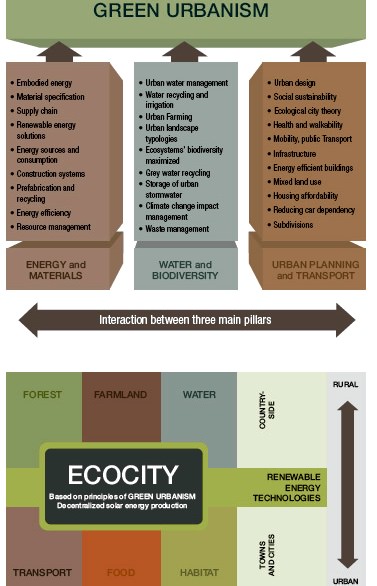
Urban biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, that inhabit urban environments. It encompasses the intricate interactions between native species and their urban habitats, highlighting the ways in which urban planning and development can impact ecological balance.
This diversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem health, providing valuable ecosystem services, and enhancing overall urban resilience. As cities continue to expand, understanding urban biodiversity is imperative for developing sustainable urban areas that prioritize ecological integrity in conjunction with human development.
Why is Urban Biodiversity Important?
Urban biodiversity is of paramount importance for several reasons, primarily due to its contribution to ecosystem services that benefit urban communities, including air and water purification, pollination, and climate regulation.
The presence of diverse flora and fauna enhances ecological resilience, allowing cities to adapt more effectively to the impacts of climate change. Promoting urban biodiversity supports environmental sustainability objectives by fostering green infrastructure and improving public health through increased access to nature and recreational opportunities in urban green spaces.
This rich ecological framework not only supports healthier environments but also plays a vital role in promoting social equity. Diverse wildlife habitats within urban areas can enhance community engagement and foster a sense of belonging as residents become involved in local conservation initiatives.
From an economic perspective, investing in urban biodiversity through strategic biodiversity management creates job opportunities in restoration and education, while simultaneously elevating property values as neighborhoods become greener and more appealing.
Ultimately, the integration of urban biodiversity significantly enhances the quality of life, ensuring that both present and future generations benefit from sustainable development practices.
What Threatens Urban Biodiversity?
Urban biodiversity is confronted with numerous challenges, predominantly as a result of rapid urbanization, which often results in habitat loss and fragmentation.
As urban areas expand, natural habitats are transformed into developed land, significantly affecting local flora and fauna. Moreover, urban pollution, arising from various human activities, undermines ecosystem health and reduces the quality of biodiversity.
The introduction of invasive species further exacerbates these issues by disrupting ecological balance, leading to the decline of native species and highlighting the urgent necessity for effective invasive species management within urban environments.
1. Urbanization
Urbanization serves as a primary driver of habitat loss, as natural landscapes are transformed into urban environments to accommodate growing populations and economic activities. This transition frequently results in habitat fragmentation, thereby reducing the available space for urban wildlife and adversely affecting biodiversity.
It is imperative that effective urban planning and land use strategies are employed to mitigate these impacts and promote sustainable development while preserving critical habitats.
The encroachment of urban areas not only diminishes the natural habitats of various species but also disrupts the delicate ecological balance that previously existed. As urban landscapes continue to expand, it is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of local ecosystems and wildlife.
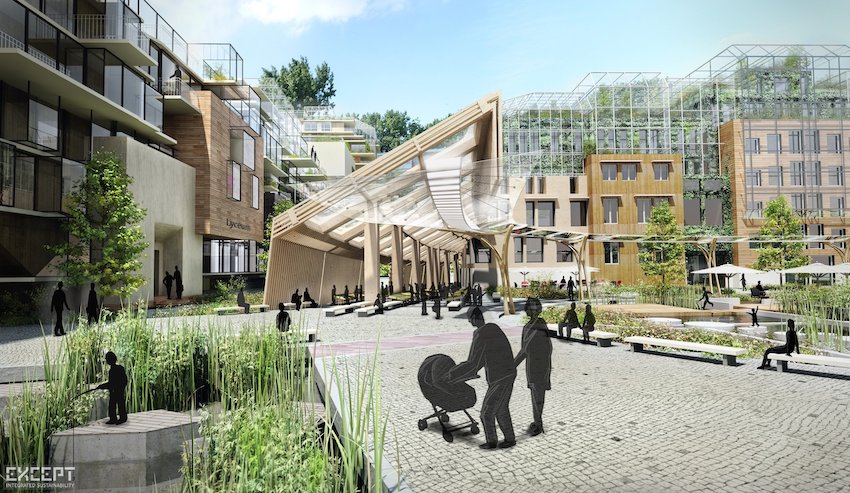
Implementing sustainable urban planning practices can help alleviate these detrimental effects. Strategies such as green zoning, which allocates areas for parks and green spaces, as well as promoting landscape connectivity to facilitate wildlife corridors, are key components of this approach.
These initiatives aim to foster a harmonious coexistence between urban development and the preservation of biodiversity, ensuring that future generations can appreciate the ecological richness afforded by vibrant natural habitats.
2. Pollution
Pollution, resulting from industrial activities, vehicular emissions, and improper waste disposal, presents a significant threat to urban biodiversity by degrading ecosystem health and adversely affecting local wildlife. Contaminants can permeate urban rivers and wetlands, disrupting water management systems and harming sensitive species.
Regular monitoring of biodiversity is essential to assess the impacts of pollution on urban ecosystems and to develop effective mitigation strategies aimed at preserving urban biodiversity.
This form of environmental degradation not only leads to the loss of species but also alters habitats, complicating the adaptability of local flora and fauna. Air pollution, particularly from automobile exhaust and industrial emissions, can result in respiratory issues in both humans and animals, further stressing urban wildlife.
Additionally, the accumulation of toxic substances in soil can disrupt plant growth and soil integrity, impeding the ability of local species to thrive.
Implementing stringent pollution control measures and conducting comprehensive biodiversity assessments are critical for fostering a healthier coexistence between urban development and the natural environment.
3. Habitat Loss
Habitat loss presents a significant challenge to urban biodiversity, as the transformation of natural environments into urban landscapes greatly diminishes habitat diversity and the availability of essential ecosystem services. This reduction not only restricts the variety of species able to thrive within urban areas but also adversely affects the ecological functions these systems provide, including carbon sequestration, flood mitigation, and enhancement of soil biodiversity.
The ramifications of such changes are substantial, as urban ecosystems depend on a diverse array of habitats to sustain their overall health. With a decline in habitat diversity, individual species face increased risks, and the complex ecological networks that facilitate interactions among them begin to disintegrate.
Community biodiversity initiatives focused on habitat restoration can effectively alleviate these impacts by promoting resilience and fostering ecological balance. By reintroducing native plant species and developing green corridors, urban planners and residents can improve connectivity between fragmented habitats, thereby cultivating a more vibrant and diverse urban ecosystem.
What are the Benefits of Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Implementing effective urban biodiversity strategies can provide significant benefits for both communities and the environment, such as the enhancement of urban green spaces, improved public health, and increased community engagement.
By prioritizing biodiversity in urban planning, cities can cultivate ecological resilience and support sustainable development initiatives that promote the well-being of local residents.
Additionally, the integration of nature-based solutions into urban design can enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban areas while simultaneously strengthening ecosystem services.
1. Improves Human Health and Well-being
Urban biodiversity plays a crucial role in improving human health and well-being by facilitating access to green spaces that encourage physical activity, mental relaxation, and social interaction. These urban green spaces are essential components of social equity, fostering community cohesion while enhancing environmental sustainability and public health outcomes.
Research has demonstrated that areas rich in biodiversity contribute to lower stress levels, improved air quality, and better overall health for urban residents.
Furthermore, studies indicate that regions characterized by diverse plant and animal species provide significant psychological benefits, as natural environments are associated with reduced incidences of anxiety and depression.
Case studies in cities such as Vancouver and Singapore illustrate that the integration of parks and gardens into urban landscapes not only enhances ecological awareness among residents but also promotes healthier lifestyles by providing greater opportunities for walking, recreation, and interaction with nature.
As communities become increasingly engaged with their green spaces, they develop a heightened sense of belonging and responsibility towards their urban ecosystems, ultimately leading to improved public health outcomes.
2. Increases Resilience to Climate Change
Enhancing urban biodiversity significantly increases the resilience of urban ecosystems to the impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events and rising temperatures. Diverse ecosystems possess greater ecological resilience, enabling them to adapt and recover more effectively from disturbances. By implementing adaptive management practices, cities can cultivate biodiversity that supports climate adaptation strategies and mitigates the urban heat island effect.
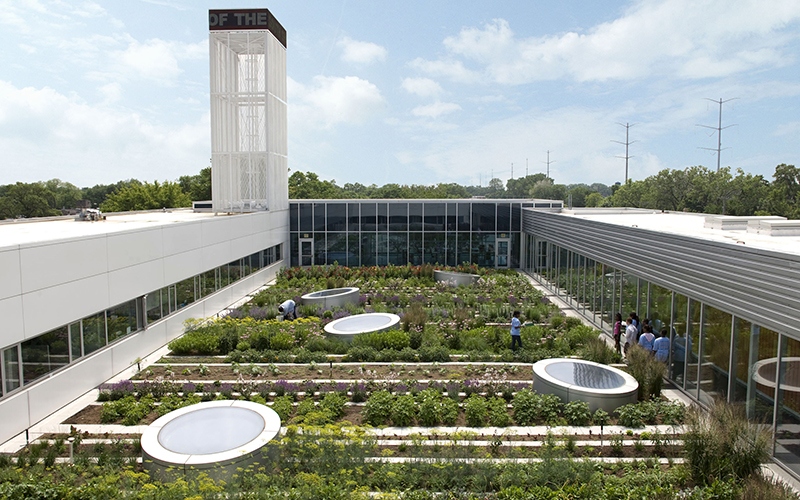
Incorporating elements such as urban forestry, green roofs, and habitat connectivity can transform the urban landscape into a dynamic network of ecological systems. These strategies not only provide support for local wildlife and plant species, but also contribute to enhanced air quality, improved stormwater management, and the overall well-being of the community.
For example, green roofs can serve as essential habitats for pollinators and other species while simultaneously reducing heat in densely populated areas. Additionally, establishing wildlife corridors and enhancing existing green spaces can facilitate movement and interaction among species, ultimately resulting in healthier and more resilient urban ecosystems.
3. Enhances Urban Aesthetics
Urban biodiversity significantly enhances the aesthetics of urban landscapes, creating a more visually appealing and inviting environment for both residents and visitors. By incorporating biophilic design principles, cities can effectively integrate nature into their architecture and urban spaces, thereby promoting ecological diversity and fostering positive interactions with the natural world.
This integration is essential, as it not only enhances the visual character of communities but also supports important concepts such as landscape connectivity, which is vital for fostering healthier ecosystems. For example, urban parks that are connected by green corridors can serve as critical habitats for a variety of species while also providing educational opportunities for the public to learn about their local environment.
Initiatives such as green roofs and vertical gardens exemplify biophilic design strategies that enhance biodiversity, mitigate urban heat, and improve air quality. By nurturing an appreciation for these natural elements, citizens can engage actively in environmental education, thereby cultivating a deeper commitment to the preservation and enhancement of urban nature.
What are the Key Elements of Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Key elements of effective urban biodiversity strategies encompass the development of green infrastructure, the promotion of biodiversity-friendly buildings, and the establishment of ecological corridors that connect urban habitats.
These strategies not only enhance urban ecosystems but also support species conservation and facilitate the movement of wildlife across urban landscapes.
By integrating these components, cities can formulate a cohesive approach to biodiversity management that fosters ecological resilience and enhances community engagement.
1. Green Spaces and Parks
Green spaces and urban parks are essential in promoting urban biodiversity by providing habitats for various species and offering recreational opportunities for residents. These areas contribute to habitat diversity and foster community engagement, encouraging residents to connect with nature and participate in biodiversity initiatives.
Well-designed green spaces can function as biodiversity hotspots, enhancing ecological networks within urban environments.
The importance of these spaces goes beyond aesthetics; effective design and management practices can transform urban gardens into vital wildlife corridors that facilitate the movement of species and enhance the ecological resilience of urban areas.
Community involvement through participatory planning practices give the power tos residents to shape their green environments, cultivating a sense of ownership and stewardship that further strengthens local biodiversity.
By incorporating native plants, creating varied topographies, and integrating water features, urban planners can ensure that these areas flourish not only as recreational spaces but also as critical ecosystems that support both wildlife and community well-being.
2. Sustainable Land Use Planning
Sustainable land use planning is fundamental for promoting urban biodiversity, as it emphasizes the preservation of natural habitats and the integration of ecological principles within development processes.
By implementing effective biodiversity management strategies, cities can enhance efforts for habitat restoration and mitigate the adverse effects of urbanization on local ecosystems. Sustainable land use planning ensures that urban development is in alignment with environmental sustainability objectives.
This comprehensive approach involves assessing biodiversity indices to evaluate the health of urban ecosystems and to safeguard areas of high habitat quality. Cities such as Singapore have achieved notable success through green infrastructure initiatives, which include the development of parks and green roofs that support a diverse range of wildlife.
Moreover, cities can adopt ecological governance frameworks that encourage stakeholder participation, thereby ensuring that both community needs and environmental priorities are adequately addressed.
These best practices underscore the critical relationship between urban development and ecological conservation, ultimately fostering resilient urban landscapes that sustain biodiversity for future generations.
3. Biodiversity-friendly Buildings and Infrastructure
Biodiversity-friendly buildings and infrastructure play a significant role in enhancing urban ecosystems by integrating design elements that support ecological diversity and promote species conservation. Features such as green roofs, living walls, and pollinator pathways enhance urban habitats and advance nature-based solutions within the urban landscape.
The incorporation of biodiversity into urban design not only enriches the built environment but also cultivates a sense of ecological awareness among residents.
These structures can serve as essential corridors for urban wildlife, improving habitat connectivity and mitigating the barriers that species often encounter in urban settings. For example, innovative projects like the Bosco Verticale in Milan demonstrate how vertical gardens can attract birds and insects while simultaneously reducing urban heat.
Such developments not only advocate for sustainable architectural practices but also improve the quality of life for inhabitants by providing access to nature, enhancing air quality, and creating opportunities for community engagement.
By prioritizing biodiversity in urban planning, cities can enhance their resilience to climate change and promote overall urban health.
4. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are crucial in promoting urban biodiversity, as they enable communities to actively engage with their local ecosystems and comprehend the significance of biodiversity conservation. Environmental education initiatives can enhance ecological literacy among residents, allowing them to recognize the value of urban green spaces and the role of native species in sustaining ecosystem health.
By participating in programs that focus on community biodiversity monitoring, individuals can contribute to the understanding of local species and their habitats, ultimately strengthening biodiversity resilience.
Initiatives such as workshops, guided nature walks, and citizen science mobile applications give the power to residents to document their observations, facilitating the tracking of ecological changes over time.
These experiences not only enhance personal knowledge but also instill a collective responsibility for reducing ecological footprints. The connections established through these programs foster a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life within urban environments, reinforcing the concept that even small actions can significantly contribute to broader conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Urban Biodiversity Strategies are plans and initiatives aimed at promoting and preserving natural habitats, wildlife, and plant species in urban areas.
2. Why are Urban Biodiversity Strategies important?
Urban Biodiversity Strategies are important because they help to maintain a balance between the development of urban areas and the conservation of natural ecosystems. They also provide numerous benefits, such as improving air and water quality, promoting natural pest control, and enhancing the overall quality of life in cities.
3. Who is responsible for implementing Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Urban Biodiversity Strategies are usually implemented by local governments, but they often require the collaboration and support of various stakeholders, including residents, businesses, and community organizations.
4. What are some common components of Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Some common components of Urban Biodiversity Strategies include creating green spaces, such as parks and gardens, implementing sustainable land management practices, protecting natural habitats, promoting native species, and educating the community about the importance of biodiversity.
5. How can individuals contribute to Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Individuals can contribute to Urban Biodiversity Strategies by participating in community initiatives, supporting local conservation efforts, practicing sustainable habits, such as reducing waste and using eco-friendly products, and advocating for biodiversity-friendly policies.
6. What are some successful examples of Urban Biodiversity Strategies?
Some successful examples of Urban Biodiversity Strategies include the MillionTreesNYC program in New York City, which aims to plant one million trees across the city, and the Biodiversity Action Plan in London, which focuses on restoring and preserving biodiversity in the city’s green spaces.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário