The Role of Urban Planning in Sustaining Biodiversity.
Urban planning plays a critical role in balancing the needs of expanding populations while preserving biodiversity that sustains our ecosystems and promotes sustainable development.
As cities continue to grow, it is essential to understand the relationship between urbanization and biodiversity, as well as the environmental impact of such growth.
This article examines the significance of biodiversity, the impact of urbanization on natural environments, and how strategic urban planning and urban design can foster conservation efforts and ecological balance.
By analyzing both the challenges and achievements in incorporating biodiversity into urban design, this discussion will reveal practical methods through which individuals can contribute to this important cause.
We invite you to explore how urban development can be harmonized with natural ecosystems, promoting ecological networks and climate resilience.
What is Urban Planning?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
Urban planning is a complex discipline that encompasses the design and regulation of land use, as well as the development of urban environments, with the objective of creating functional and sustainable cities through integrated planning.
This field includes various components, such as zoning regulations, urban design principles, transportation planning, and community engagement, all of which are intended to optimize public health, environmental sustainability, and overall quality of life.
Effective urban planning integrates green spaces, sustainable transportation systems, and adaptive reuse strategies to minimize ecological footprints, enhance urban biodiversity, and promote social equity and resilience in the context of urbanization.
Why is Biodiversity Important?
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining the health and functionality of ecosystems, as it provides critical ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation, all of which are vital for urban resilience and climate adaptation.
It plays a pivotal role in habitat conservation and ensures ecological diversity, which is necessary for resilience against environmental changes. The loss of biodiversity can result in significant environmental consequences, including diminished food security, weakened natural resources, and impaired ecosystem health, thereby highlighting the imperative for effective conservation strategies and heightened environmental awareness.
The interconnectedness of various species fosters a balanced ecosystem, where each organism fulfills a specific role, contributing to overall ecological integrity.
Wildlife protection measures are crucial for preserving these species and their habitats, especially in regions threatened by urbanization and climate change. The implementation of sustainable practices and ecological design can substantially mitigate negative impacts on biodiversity.
By promoting conservation strategies that facilitate the coexistence of human activities and wildlife, communities can play a vital role in safeguarding our planet’s rich natural heritage through stakeholder involvement.
Furthermore, efforts should also focus on educating and involving local populations in wildlife protection initiatives, ensuring that future generations recognize and uphold the importance of biodiversity conservation.
How Does Urbanization Affect Biodiversity?
Urbanization has a substantial impact on biodiversity by fundamentally altering natural habitats and creating fragmented ecosystems, leading to habitat fragmentation, which can disrupt species populations and diminish ecological diversity.
As urban areas expand, the conversion of natural landscapes into urban environments frequently results in habitat loss and degradation, adversely affecting wildlife corridors and local flora and fauna.
It is essential to understand the relationship between urban ecosystems and biodiversity in order to develop effective strategies that promote environmental sustainability and facilitate habitat restoration within urban settings.
What are the Negative Impacts of Urbanization on Biodiversity?
The negative impacts of urbanization on biodiversity are significant, primarily evident through habitat loss, pollution, and the disruption of species preservation efforts. As urban areas expand, natural habitats are frequently destroyed or modified, resulting in habitat fragmentation that isolates urban wildlife populations and reduces their genetic diversity.
Pollution stemming from urban runoff and industrial activities further exacerbates these challenges, presenting considerable threats to local ecosystems and the health of urban wildlife.
The phenomenon of the urban heat island effect, where cities experience notably higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas, can have adverse effects on both flora and fauna. Elevated temperatures can disrupt species’ breeding cycles, migration patterns, and food availability, thereby altering the delicate balance of ecosystems.
For instance, amphibians and reptiles, which rely on specific temperature ranges for their survival, are particularly susceptible to these environmental changes.
Moreover, air quality and water pollution contribute to the decline of sensitive species, including certain fish populations that are severely impacted by toxic runoff. Collectively, these factors paint a concerning picture of how urbanization diminishes biodiversity and disrupts the intricate web of life that sustains our environments.
What are the Positive Impacts of Urbanization on Biodiversity?
Despite the challenges associated with urbanization, it can yield positive effects on biodiversity when approached through sustainable practices and innovative urban design. Initiatives such as the establishment of green infrastructure, community gardens, and wildlife corridors can significantly enhance urban biodiversity by providing essential habitats and resources for local flora and fauna and promoting habitat enhancement.
Increased community engagement in conservation efforts can foster ecological awareness and encourage practices that support biodiversity within urban landscapes, contributing to habitat preservation.
Cities such as Singapore have illustrated how vertical gardens and rooftop plantings can transform urban environments into vibrant ecosystems. Likewise, the High Line in New York City has successfully repurposed an old railway into a lush public park, creating a habitat for various bird species while enhancing the city’s green space.
These projects exemplify how urban ecosystems can flourish through creative spatial planning and active citizen participation. As residents become more engaged in urban gardening and nature conservation, they not only contribute to biodiversity but also cultivate a sense of stewardship, reinforcing the vital connection between people and their environment and promoting ecological restoration.
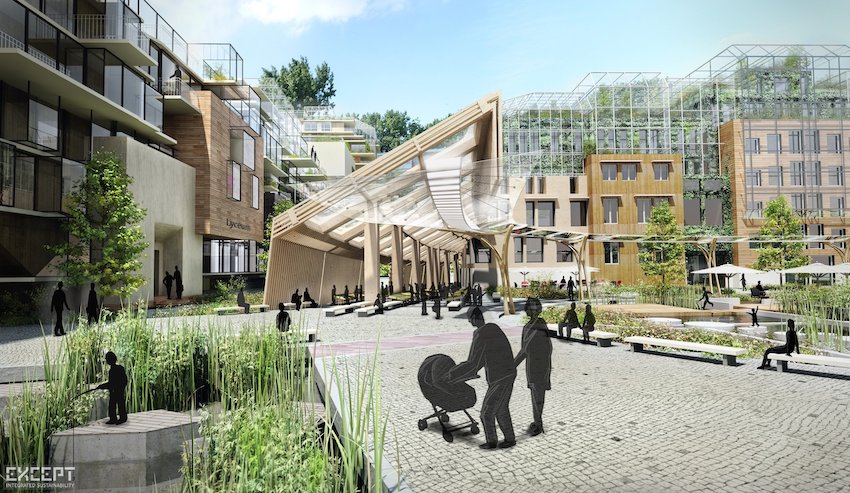
What is the Role of Urban Planning in Sustaining Biodiversity?
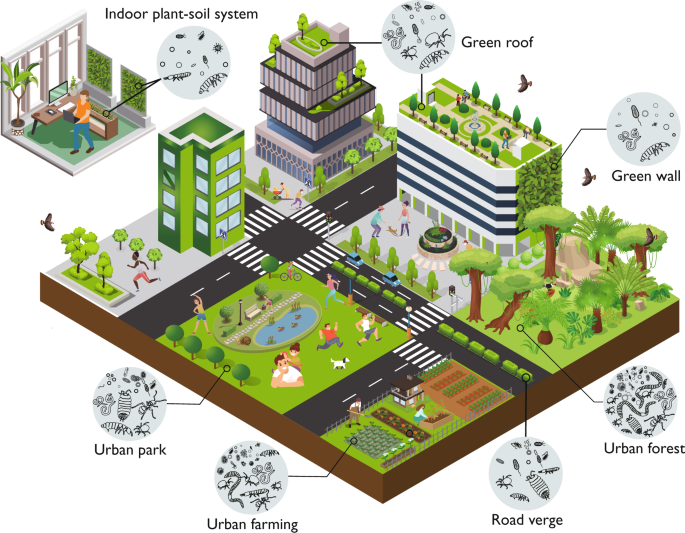
Urban planning is essential for sustaining biodiversity by incorporating habitat conservation strategies and promoting the establishment of green spaces and urban greenways within urban areas.
Effective urban planning involves the implementation of strategic land use and zoning regulations that prioritize ecological integrity and facilitate interconnectivity among urban habitats, enhancing landscape connectivity.
By integrating principles of sustainable development, urban planners can design environments that not only support urban biodiversity but also enhance the quality of life for residents through ecological design.
How Can Urban Planning Help Preserve Biodiversity?
.jpg_01.jpeg)
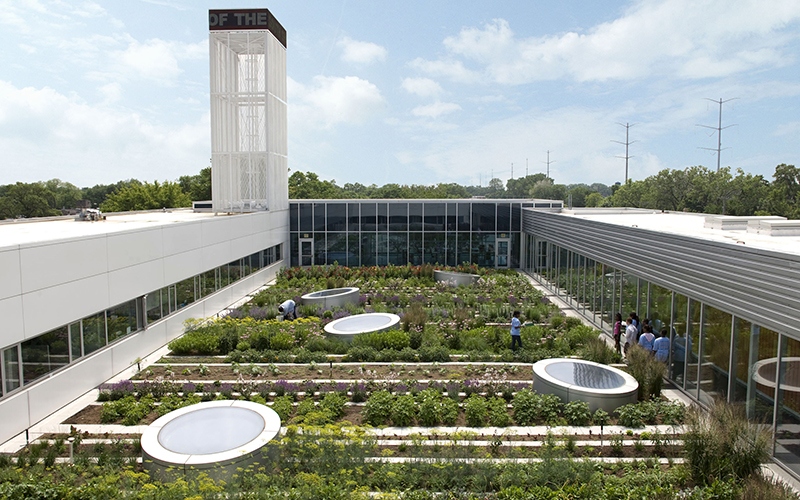
Urban planning plays a crucial role in preserving biodiversity through the strategic design and integration of green spaces, wildlife corridors, and conservation strategies aimed at enhancing habitat quality within urban environments.
By prioritizing the protection of biodiversity hotspots and implementing environmentally sustainable planning policies, urban planners can create interconnected landscapes that support a diverse range of species and promote ecological balance and urban sustainability. This approach is vital for mitigating the adverse effects of urbanization and ensuring sustainable development.
Incorporating practices such as the establishment of green roofs and vertical gardens not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of urban areas but also provides essential habitats for pollinators and birds, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
The implementation of permeable surfaces, such as bioswales and rain gardens, facilitates improved stormwater management while enhancing soil health and supporting native plant species. Furthermore, integrating public transportation with pedestrian pathways can strengthen habitat linkages, enabling wildlife movement and maintaining genetic diversity.
These thoughtful strategies emphasize the significance of urban ecosystems in fostering resilience against environmental changes and underscore the necessity for progressive planning policies that advocate for biodiversity preservation and urban renewal.
What are Some Examples of Successful Urban Planning Strategies for Biodiversity Conservation?
Successful urban planning strategies for biodiversity conservation encompass the implementation of green infrastructure, urban agriculture, and the establishment of public parks that serve as essential habitats for urban wildlife, demonstrating successful habitat connectivity.
Cities such as Singapore and Melbourne have adopted innovative approaches to seamlessly integrate nature into urban design, thereby promoting biodiversity while enhancing community engagement and overall quality of life. These strategies highlight the potential for urban environments to coexist with and support diverse ecosystems through participatory planning.
For example, Singapore’s Gardens by the Bay project features vertical gardens and bio-domes that attract a variety of species, while Melbourne’s strategic urban forest initiatives aim to increase canopy cover, providing both shade and habitats.
These initiatives not only mitigate urban heat effects but also encourage community involvement, fostering a closer relationship between residents and their natural surroundings.
By prioritizing green spaces and ecological corridors, urban planners are developing a framework for sustainable cities that honor natural ecosystems and actively engage the public in the preservation of their local environments, fostering environmental justice and placemaking.
What are the Challenges of Incorporating Biodiversity in Urban Planning and Urban Policy?
Incorporating biodiversity into urban planning presents a number of challenges, including insufficient awareness and understanding among decision-makers, limited funding and resources for implementation, and potential conflicts with economic development objectives. Additionally, challenges related to urbanization, zoning regulations, and transportation planning further complicate the integration of green infrastructure and sustainable development into city planning.
These challenges can impede the integration of effective biodiversity strategies into urban policies, often leading to missed opportunities for sustainable practices and ecological preservation. Addressing these issues is essential for fostering resilient urban ecosystems and promoting urban sustainability.
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
A significant challenge in integrating biodiversity into urban planning is the insufficient awareness and understanding among stakeholders regarding the importance of ecological diversity, ecosystem services, and climate resilience. Many decision-makers tend to prioritize immediate economic development over long-term environmental sustainability, which results in inadequate support for policies and practices that promote biodiversity and landscape architecture. Therefore, enhancing ecological awareness through education and outreach is essential to overcoming this obstacle.
This awareness is vital not only for policymakers but also for the general public, as it encourages community engagement in biodiversity conservation efforts. By promoting environmental education initiatives that highlight the benefits of diverse ecosystems—such as improved air quality, enhanced recreational spaces, and increased resilience to climate change—urban communities can become advocates for more sustainable practices.
Workshops, community programs, and interactive campaigns can enable residents to actively participate in local biodiversity projects, including tree planting and habitat restoration. With informed citizens and engaged stakeholders, urban environments can evolve to support a rich tapestry of life, ultimately resulting in healthier communities and thriving ecosystems.
Lack of Funding and Resources
Issues related to habitat fragmentation and urban design further exacerbate the challenges in securing funding for biodiversity initiatives.
The lack of funding and resources for biodiversity initiatives presents a significant challenge to effective urban planning and conservation strategies. Numerous urban projects aimed at enhancing biodiversity, green infrastructure, and habitat preservation frequently encounter financial constraints, which limit their capacity to achieve desired ecological outcomes.
Securing sufficient funding and fostering partnerships with stakeholders are essential steps in integrating biodiversity priorities within urban planning frameworks.
To address these financial challenges, urban planners must seek innovative funding solutions that extend beyond traditional government grants. Collaboration with community stakeholders, including local organizations and grassroots movements, can amplify underrepresented voices, ensuring that environmental justice remains a priority in decision-making processes.
By promoting public-private partnerships and actively engaging citizens in funding initiatives, planners can develop sustainable models that not only bolster biodiversity but also tackle the social equity issues that are prevalent in urban environments.
Furthermore, efforts to educate and raise awareness about the significance of biodiversity can mobilize community resources and enthusiasm, ultimately contributing to the creation of more resilient urban ecosystems.
Conflict with Economic Development
Conflicts between economic development and biodiversity conservation often arise during urban planning processes, as development projects typically prioritize land use for commercial or residential purposes over ecological considerations. This tension can result in habitat degradation and a loss of biodiversity, making it essential for urban planners to achieve a balance between growth and conservation.
The implementation of sustainable practices can help to mitigate these conflicts while promoting both economic and ecological health.
Urban planners are increasingly tasked with creating frameworks that stimulate economic growth while simultaneously protecting vital ecosystems and wildlife habitats. This necessitates a reevaluation of traditional urban policies, advocating for integrated solutions that include mixed-use developments, green spaces, and biodiversity-friendly initiatives.
For instance, the incorporation of green infrastructure, such as parks, green roofs, and wildlife corridors, can enhance urban resilience while providing habitats for various species.
Ultimately, adopting a more holistic approach to urban development can foster a mutually beneficial relationship between economic progress and the preservation of natural resources, thereby paving the way for a sustainable future characterized by sustainable practices and social equity.
What Can Individuals Do to Support Biodiversity in Urban Areas and Promote Environmental Justice?
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Individuals significantly contribute to supporting biodiversity in urban areas through various actions, including the planting of native species, supporting local conservation initiatives, and participating in community gardens.
By engaging in these activities, residents can enhance urban biodiversity, reduce their ecological footprint, and contribute positively to the health of local ecosystems.
Moreover, advocating for urban planning policies that prioritize biodiversity and sustainable architecture can magnify individual efforts and promote a more sustainable urban environment.
Plant Native Species in Your Garden
Planting native species in one’s garden serves as an effective strategy to support urban biodiversity and enhance habitat quality for local wildlife. Native plants are inherently adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, thereby providing essential resources for pollinators and other species within urban ecosystems. By cultivating a diverse array of native flora, individuals can establish thriving habitats that contribute to ecological balance and resilience.
Furthermore, these plants typically require less maintenance and water, which significantly reduces the reliance on chemical fertilizers and pesticides. For example, incorporating species such as Black-eyed Susans and Coneflowers can attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, while shrubs such as Serviceberry not only provide sustenance for birds but also offer aesthetic seasonal beauty.
By prioritizing native plants, gardeners can promote ecosystem services such as soil stabilization and air purification, thus enhancing the sustainability of urban landscapes and improving public health.
These initiatives also play a vital role in educating the community about the importance of preserving local flora, ultimately fostering a stronger connection between residents and their environment and encouraging community engagement.
Support Local Conservation Efforts
Supporting local conservation efforts is crucial for enhancing biodiversity in urban areas, as these initiatives primarily focus on protecting and restoring critical habitats. By volunteering time or resources to local organizations, individuals can contribute to projects that promote ecological awareness, environmental impact mitigation, and environmental sustainability.
Engaging with community-driven conservation strategies, such as ecological restoration and urban renewal projects, can significantly amplify the impact of individual actions and foster a stronger connection to nature.
One effective method to support such initiatives is by participating in local clean-up events, where volunteers assist in removing litter from parks or waterways, thereby safeguarding ecosystems from pollution.
Additionally, attending workshops and educational programs organized by these grassroots movements can enhance understanding of ecological issues and inspire proactive measures against climate change. Supporting native plant gardens and wildlife corridors not only beautifies neighborhoods but also provides essential habitats for species in need.
By championing local conservation campaigns, individuals reinforce the message that environmental stewardship begins at home, thereby encouraging collective community action.
Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle for Urban Sustainability
Practicing the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle can significantly enhance urban biodiversity by minimizing waste and mitigating overall environmental impact. By decreasing the demand for new resources, individuals contribute to alleviating the pressure on natural habitats and promote sustainable practices, including urban agriculture and sustainable transportation, that benefit local ecosystems.
This conscientious approach to consumption fosters a culture of environmental stewardship and urban ecology, encouraging others to adopt similar habits.
This proactive strategy not only reduces pollution but also promotes the responsible management of natural resources, which is essential for the preservation of urban wildlife. For example, when communities participate in recycling programs, less plastic and waste enter local ecosystems, thereby safeguarding the flora and fauna that reside in these areas.
Simple actions, such as opting for sustainable products or engaging in local clean-up initiatives, can create significant ripple effects, motivating fellow urban residents to prioritize their environmental responsibilities.
Ultimately, fostering a collective awareness about waste reduction can lead to healthier urban environments where biodiversity flourishes, underscoring that each individual’s effort is vital to achieving a sustainable future.
Advocate for Biodiversity-friendly Urban Planning Policies
Advocating for biodiversity-friendly urban planning policies is essential for the creation of sustainable environments that promote ecological balance, landscape connectivity, and resilience. Such advocacy not only enhances the quality of life for current residents but also ensures that future generations inherit vibrant ecosystems and urban habitats.
To effectively advocate for change, individuals should begin by educating themselves on local biodiversity issues, urban ecosystems, and consider forming or joining grassroots movements that focus on urban policy reform and sustainable development.
Participating in city council meetings, collaborating with local environmental organizations, including those focused on land use and habitat preservation, and initiating community-driven campaigns are practical steps that enable citizens to express their concerns and suggestions.
By fostering dialogue between community members and policymakers, it becomes possible to underscore the importance of integrating biodiversity into urban development and urban design. This collaborative approach ultimately contributes to the establishment of more sustainable and inclusive cities that promote ecological balance and urban sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of urban planning in sustaining biodiversity and ecological networks?
.jpg_11.jpeg)
Urban planning plays a crucial role in preserving and protecting biodiversity in cities by identifying and designating green spaces, such as public parks and community gardens, regulating development, and promoting sustainable practices that include climate resilience and conservation strategies.
How does urban planning impact biodiversity and urban habitats?
Urban planning decisions, such as the location and design of buildings and infrastructure, can greatly impact the natural habitats, native species, and species diversity within a city. Proper planning can help mitigate negative effects such as habitat fragmentation and promote biodiversity and urban resilience.
What are some specific strategies used in urban planning to sustain biodiversity and ecological restoration?
Some common strategies include creating green spaces, wildlife corridors, and urban greenways, utilizing green infrastructure, implementing zoning regulations to protect natural areas, and incorporating biodiversity considerations into development projects. This also involves integrating stormwater management and soil health practices to maintain ecological balance.
Why is it important to consider biodiversity and urban ecology in urban planning?
Biodiversity provides numerous benefits to cities, such as improved air quality, climate regulation, and mental well-being. It is also vital for supporting the ecosystem services that sustain human life, including urban agriculture and urban wildlife habitats. By including biodiversity in urban planning, we can create more resilient and livable cities that can better adapt to climate change.
How can community involvement and participatory planning contribute to sustaining biodiversity through urban planning?
Community involvement is essential for successful urban planning and can help identify and prioritize areas for conservation and sustainable development. Engaging local residents can also increase support and awareness for biodiversity initiatives, promote environmental justice, and ensure social equity in urban design decisions.
Can urban planning and development coexist with biodiversity conservation and habitat connectivity?
Absolutely. With careful planning and implementation of sustainable practices, urban areas can continue to develop and thrive while supporting biodiversity. Collaboration between urban planners, developers, and conservationists is key in finding a balance between development and conservation.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.












Publicar comentário