Adaptive Reuse of Buildings for Biophilic Designs.
The adaptive reuse of buildings revitalizes historic structures, transforming them into dynamic spaces that not only respect their historical significance but also embrace modern sustainability practices.
This approach conserves valuable resources and incorporates biophilic design principles, thereby creating environments that foster the well-being of both individuals and nature.
This article examines the importance of adaptive reuse, outlining its benefits and presenting real-world examples that illustrate how repurposed buildings can contribute to community well-being. Additionally, it addresses the key factors that contribute to successful adaptive reuse and the challenges that may arise throughout the process.
What is Adaptive Reuse of Buildings?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
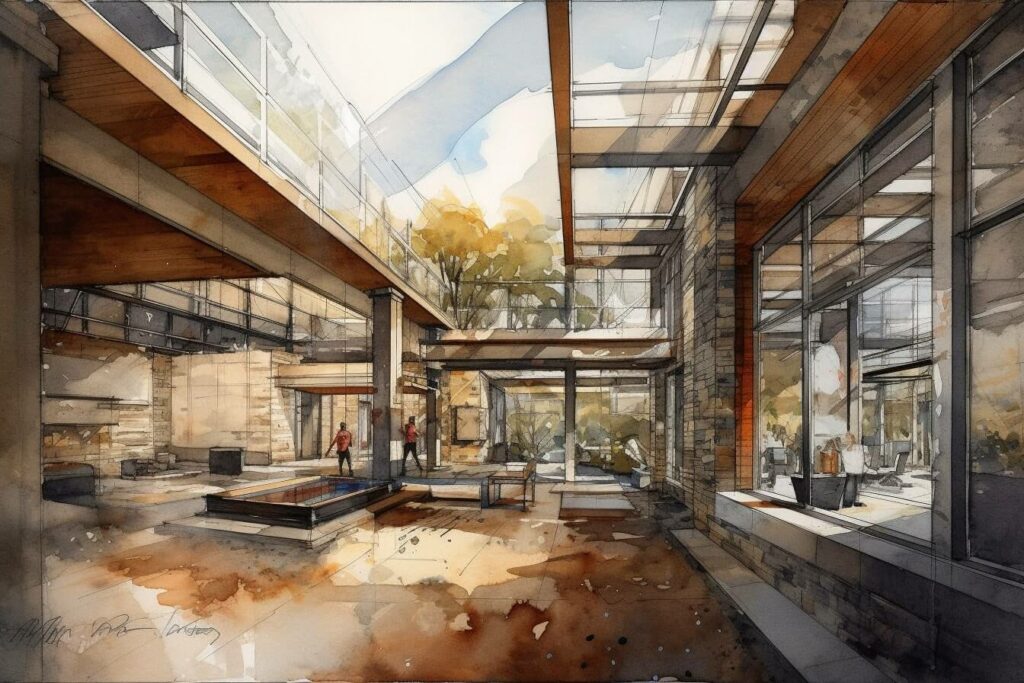
Adaptive reuse of buildings is the process of repurposing existing structures for new functions while preserving their historical and architectural integrity, a practice rooted in adaptive architecture and architectural preservation.
This practice of sustainable architecture not only safeguards cultural heritage and historic buildings through historic preservation but also encourages urban revitalization through innovative design and community engagement.
By reimagining existing spaces, adaptive reuse diminishes the necessity for new construction, thereby minimizing environmental impact, promoting a circular economy, and supporting urban ecology through ecological restoration.
Essential strategies in adaptive reuse encompass building retrofitting, which improves energy efficiency and building performance, and the application of design thinking that emphasizes user experience and the creation of community spaces.
Why is it Important?
The significance of adaptive reuse is underscored by its capacity to promote environmental design and sustainability. By repurposing existing structures, it effectively reduces waste and conserves resources. This approach not only revitalizes urban areas but also fosters community development by creating multi-functional spaces that enhance social sustainability and improve the well-being of residents.
Furthermore, adaptive reuse contributes to ecological balance by incorporating nature-inspired design elements, thus improving urban biodiversity and enhancing the aesthetic value of neighborhoods.
Engaging the community in the adaptive reuse process is essential, as it ensures that revitalized spaces align with local needs while cultivating a sense of ownership among residents. This engagement, in turn, strengthens social ties and encourages cultural expression within the community.
From an economic perspective, the refurbishment of older buildings presents a cost-effective alternative to new construction, resulting in job creation and increased local investment. By emphasizing ecological architecture, adaptive reuse ultimately supports public health by promoting active lifestyles through walkable environments and access to green spaces, which are critical components of vibrant and sustainable urban living.
What is Biophilic Design?
Biophilic design represents a progressive approach aimed at fostering a connection between individuals and nature through architecture and urban design, thereby enhancing health and well-being within built environments.
This design philosophy prioritizes the integration of natural elements, including indoor gardens, living walls, natural materials, and daylighting, into architectural spaces.
By emphasizing the sensory experiences of users, biophilic design not only improves indoor air quality but also minimizes the ecological footprint of buildings, thereby promoting a sustainable and thriving ecosystem.
How Does it Benefit People and the Environment?
The advantages of biophilic design are significant for both individuals and the environment, resulting in healthier indoor spaces that enhance psychological well-being. This is achieved through improved natural ventilation, access to open spaces, and optimized daylighting.
By fostering urban biodiversity and promoting resource efficiency, biophilic design plays a crucial role in creating a more resilient and sustainable built environment that meets the needs of the community. The integration of natural elements into architectural practices not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also encourages community engagement and fosters a sense of belonging.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that biophilic design not only improves mood but also contributes to reductions in stress and anxiety levels. For instance, a case study conducted in a corporate environment indicated that employees who worked in settings that incorporated natural elements experienced a 15% increase in overall well-being and productivity.
Furthermore, energy-efficient solutions integrated within these designs have been shown to reduce energy consumption by as much as 30%, yielding benefits for both the economy and the ecosystem. By establishing a connection between individuals and nature, biophilic designs promote a deeper appreciation of biodiversity and ultimately support conservation efforts that can have lasting impacts on local environments.
Examples of Adaptive Reuse for Biophilic Designs
Numerous exemplary cases of adaptive reuse effectively demonstrate the incorporation of biophilic design principles, nature integration, and sensory experience, showcasing innovative strategies in green building and community engagement.
These projects illustrate how adaptive reuse can revitalize historic structures, transforming them into vibrant community gardens, sustainable housing developments, or mixed-use spaces that enhance urban ecology and biodiversity.
Such initiatives not only preserve architectural heritage but also contribute to a healthier environment for both inhabitants and visitors.
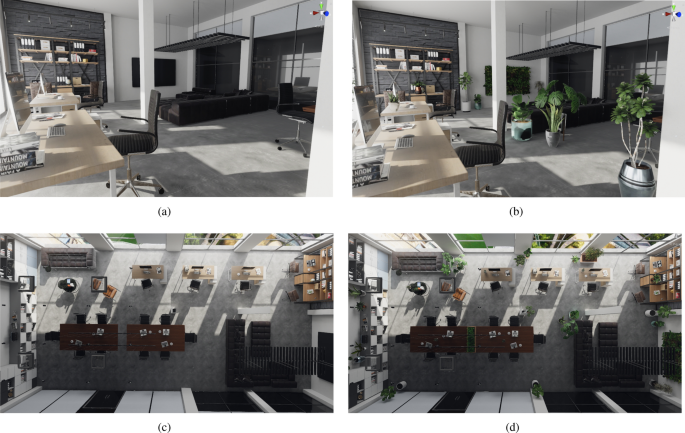
1. Converting Old Warehouses into Green Office Spaces
The conversion of old warehouses into green office spaces serves as an exemplary model of adaptive reuse, creating dynamic environments that emphasize energy efficiency, tenant engagement, and natural ventilation. This transformation typically involves the incorporation of sustainable materials, daylighting techniques, and biophilic design elements, resulting in workspaces that enhance productivity while promoting environmental responsibility.
In this innovative repurposing process, architects frequently prioritize open floor plans that feature large windows and skylights to optimize natural light, thereby reducing the dependence on artificial lighting. The integration of elements such as green roofs, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and water-saving fixtures further contributes to decreased utility costs and a diminished carbon footprint.
As these green office environments are developed, tenants experience benefits such as improved air quality, aesthetically inspiring surroundings, and a strengthened sense of community. This comprehensive approach not only enhances employee well-being but also attracts eco-conscious businesses, illustrating that sustainability is in harmony with the evolving needs of contemporary workplaces.
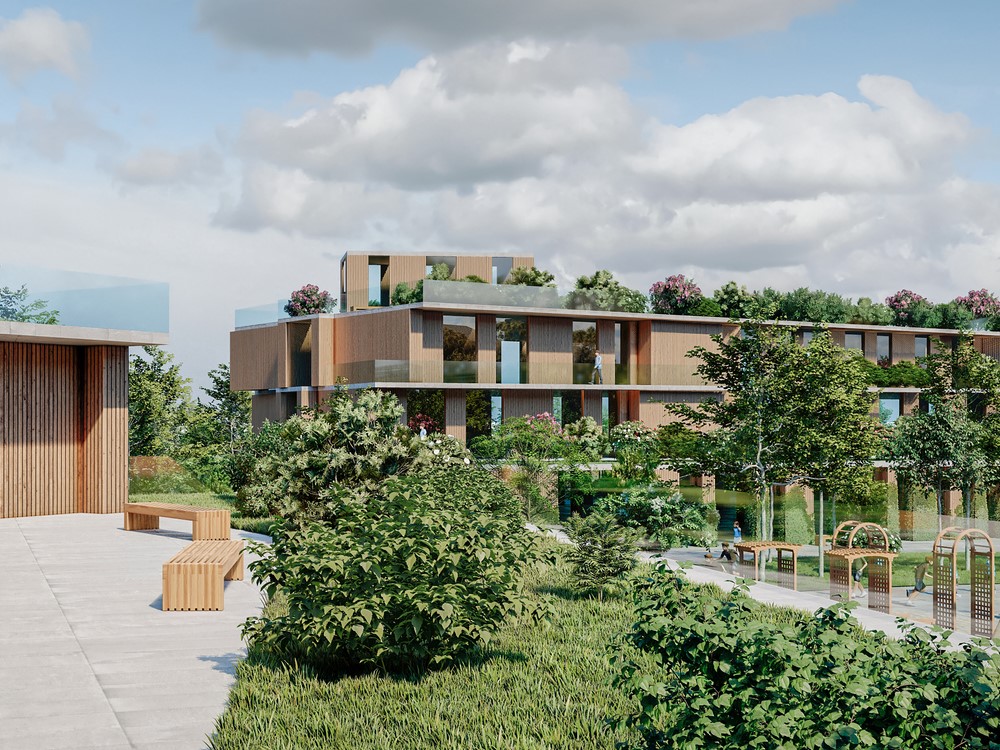
2. Transforming Abandoned Factories into Community Gardens
.jpg_01.jpeg)
Transforming abandoned factories into community gardens exemplifies effective adaptive reuse strategies that promote urban renewal, enhance connectivity with nature, and encourage community engagement. These gardens not only contribute to local biodiversity but also serve as public art installations that instill a sense of ownership and pride among residents.
By repurposing these neglected spaces, neighborhoods create vibrant venues for social interaction, education, and sustainability. Community gardens provide practical opportunities for local residents to learn about gardening practices while simultaneously enhancing the aesthetic appeal of urban landscapes.
Moreover, these initiatives foster collaboration among diverse groups, facilitating the development of relationships and strengthening community ties. The integration of greenery into previously industrial areas promotes ecological balance by providing habitats for pollinators and wildlife.
In summary, such transformations not only enhance the environment but also enable communities to take an active role in nurturing their surroundings, contributing to a healthier and greener future.
3. Renovating Old Schools into Sustainable Housing
Renovating old schools into sustainable housing represents a significant adaptive reuse initiative that honors cultural heritage while addressing the pressing demand for affordable living spaces.
Such renovations frequently incorporate multi-functional areas designed to promote health and well-being, integrating place-making strategies to create vibrant communities that reflect the history and character of the original structures.
The transformation process presents various challenges, including the need for structural integrity assessments and the delicate balance of preserving historical elements while integrating modern amenities.
Successful projects typically necessitate collaboration with local authorities to navigate zoning laws and building codes, ensuring that these repurposed sites comply with current safety and accessibility standards, achieving architectural adaptability.
The community derives substantial benefits from these initiatives, as they not only enhance housing availability but also cultivate a sense of belonging and pride among residents.
By implementing sustainable design practices, such as energy-efficient systems, green spaces, and climate-responsive design, these projects contribute not only to environmental objectives but also to the overall improvement of quality of life within the neighborhood.
Factors to Consider for Successful Adaptive Reuse
Successful adaptive reuse projects necessitate meticulous consideration of several critical factors, including the structural integrity of the building, its historical context, location, and the surrounding environment, in addition to cost and budget constraints.
The implementation of site-specific design principles and sustainable architecture is essential to ensure that the new use aligns with the community’s needs and enhances resilience to future challenges.
By thoroughly understanding these factors, stakeholders can optimize the potential of existing structures while promoting sustainable practices, environmental design, and fostering community engagement.
1. Building’s Structural Integrity and Retrofit
Evaluating a building’s structural integrity is a critical consideration in adaptive reuse and building retrofit, as it directly influences compliance with building codes and the overall feasibility of the project.
Conducting energy audits and assessments of resource efficiency ensures that the renovation is both sustainable and cost-effective, facilitating appropriate design adaptations that honor the original architecture while adhering to modern standards. Incorporating biophilic design elements and passive design strategies can further enhance building performance and user experience.
A comprehensive assessment typically includes a combination of visual inspections, material testing, and load calculations, which together yield insights into any existing weaknesses and necessary reinforcements. This process also involves site analysis to determine the best ways to integrate natural materials and improve spatial dynamics.
By adhering to established building codes, project teams can mitigate risks, thereby ensuring safety and reliability for future occupants.
The integration of energy audits not only identifies areas for improvement regarding energy consumption but also aligns the project with environmental objectives, enhancing overall resource efficiency and promoting energy efficiency.
This holistic approach to renovation fosters sustainable practices that respect historical significance while accommodating contemporary energy demands and promoting resilience planning.
2. Location and Surrounding Environment and Urban Ecology
The location and surrounding environment are critical factors in the success of adaptive reuse projects, significantly influencing community development and urban landscapes. Selecting sites with accessible infrastructure while considering the environmental impact is essential to ensure that the development contributes positively to the neighborhood, resulting in mixed-use spaces that address various community needs and promote urban ecology.
Such projects not only revitalize underutilized spaces but also foster social interaction and stimulate economic activity. When evaluating potential sites, it is imperative to conduct comprehensive assessments of existing conditions, including zoning regulations, historical significance, and environmental evaluations. Incorporating nature-based solutions and green infrastructure can further enhance urban greening efforts.
Engaging with the community can reveal valuable insights into local needs and preferences, thereby fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the transformed area. Strategies that incorporate green spaces, sustainable practices, and urban greening are essential for minimizing ecological footprints, ensuring that adaptive reuse serves as a model for responsible urban enhancement while promoting both environmental stewardship and vibrant community life.
3. Cost and Budget and Resource Efficiency
Careful planning of costs and budgets is essential in adaptive reuse, as financial constraints can significantly impact project viability and scope. Achieving a balance between resource efficiency and economic sustainability ensures that the renovation meets financial objectives while effectively engaging tenants and fostering a sense of community and ownership in the new space. Implementing adaptive strategies can further enhance both financial and environmental outcomes.
Innovative budgeting strategies are instrumental in fulfilling these goals. For example, repurposing existing materials and reclaimed materials can substantially reduce costs while minimizing waste.
By collaborating with local suppliers and establishing partnerships, projects can leverage local resources, which not only lowers transportation costs but also strengthens economic ties within the community. Implementing energy-efficient solutions reduces long-term operational expenses and resonates with environmentally conscious tenants, thus fostering a dedicated and engaged resident base. Additionally, incorporating biophilic elements such as indoor plants and vertical gardens can enhance the aesthetic experience for tenants.
These practices have a positive effect on occupancy rates, ultimately enhancing both financial performance and community relationships, rendering the adaptive reuse project a comprehensive success, and contributing to the overall wellness architecture.
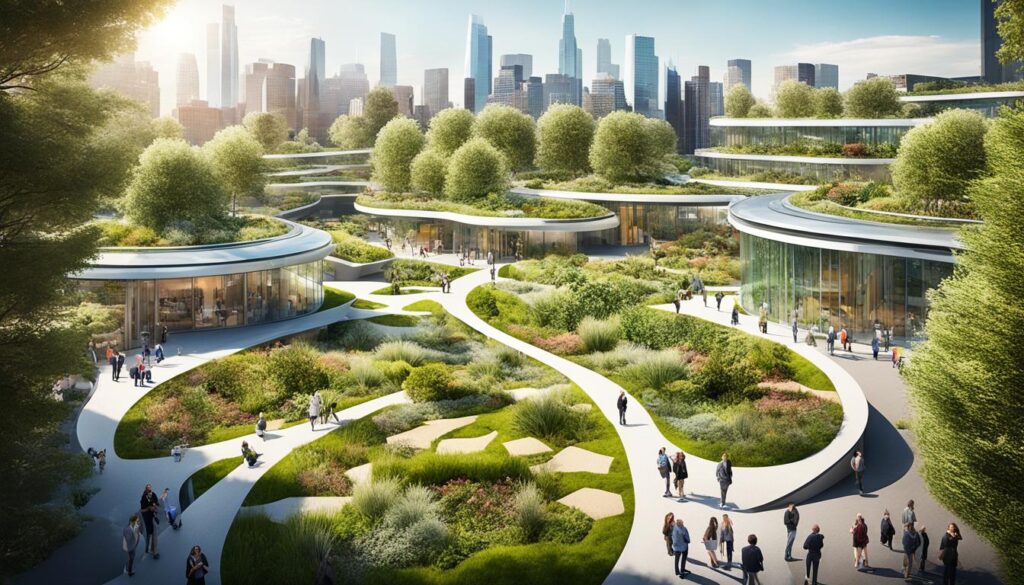
Challenges and Solutions for Adaptive Reuse and Adaptive Architecture
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Adaptive reuse projects frequently encounter a range of challenges, including navigating zoning regulations, ensuring compliance with historic preservation guidelines, adhering to architectural preservation standards, and addressing potential community resistance.
These obstacles can impede the successful transformation of buildings; however, the implementation of effective solutions and the establishment of open communication with stakeholders can facilitate the overcoming of these barriers. Creative reuse and integrated design approaches can help navigate these challenges effectively.
This approach ensures that the project aligns with both regulatory requirements and community expectations.
1. Zoning and Building Codes and Historic Districts
Zoning and building codes are essential considerations in adaptive reuse, as they dictate the permissible uses and modifications of existing structures. A thorough understanding of these regulations facilitates effective adaptive management and the application of design principles that promote resource efficiency while ensuring compliance with legal standards and historical context.
Navigating the complexities of these codes can present challenges for developers and designers aiming to repurpose older buildings. Therefore, it is crucial for stakeholders to engage in comprehensive research and maintain open communication channels with local authorities to ensure that projects align with municipal objectives. Understanding zoning laws and construction techniques applicable to historic districts is vital for successful project outcomes.
Adopting a proactive approach may involve seeking variances or exploring overlay districts, which can provide alternative guidelines that are better suited to the unique characteristics of the site. This process may include performance metrics to evaluate the impact of variances on building performance.
Ultimately, successfully harmonizing these projects with community standards not only enhances the built environment but also fosters a sense of place and continuity within the community.
2. Historic Preservation and Cultural Heritage
Ensuring historic preservation presents a significant challenge in the realm of adaptive reuse, as it necessitates a careful balance between retaining architectural heritage and meeting modern functionality and safety standards. Engaging the community in preservation initiatives fosters local pride and promotes resilience, thereby enabling projects to honor cultural heritage and landscapes while adapting to contemporary needs.
This multifaceted endeavor not only safeguards buildings with historical significance but also revitalizes neighborhoods by merging old-world charm with contemporary uses. Effective strategies typically involve collaboration among architects, historians, and local residents, ensuring that diverse perspectives are considered and the unique narratives associated with these structures are preserved. This collaboration can enhance the overall spatial experience and place-making efforts.
By actively incorporating community feedback, developers can create adaptive reuse projects that honor the past while satisfying the requirements of current users. Ultimately, successful preservation can act as a catalyst for economic growth, enhance local identity, and contribute to a sustainable future, seamlessly intertwining history with innovation and architectural identity.
3. Community Resistance and Social Equity
Community resistance can present significant challenges to adaptive reuse projects, often arising from concerns regarding gentrification, displacement, and the potential loss of cultural identity. Actively engaging the public and involving stakeholders in the planning process is crucial to alleviating these concerns, thereby promoting social sustainability, social equity, and fostering tenant engagement through transparent communication and a shared vision.
A comprehensive understanding of the root causes of this resistance is essential; it frequently stems from a lack of trust between developers and residents, as well as from historical grievances that communities have faced. To address these issues, it is vital to foster an inclusive dialogue in which community members feel heard and valued. This can be achieved through public engagement strategies such as workshops, surveys, and open forums.
Techniques such as workshops, surveys, and open forums can be utilized to gather input and cultivate a sense of ownership over the project. These methods can also help address concerns related to cultural heritage and historical preservation.
Furthermore, emphasizing design adaptability—allowing for flexibility in the utilization of spaces—can effectively address local needs, ensuring that developments not only respect but also enhance the unique identity of the community. Incorporating contextual design and adaptive landscapes will contribute to the overall success of the project.
The Benefits of Combining Adaptive Reuse and Biophilic Design in Urban Revitalization
The combination of adaptive reuse and biophilic design fosters a powerful synergy that enhances health and well-being while revitalizing urban environments. This integration promotes community spaces enriched with natural elements and supports urban biodiversity, resulting in vibrant ecosystems that benefit both people and the environment. Incorporating nature integration and human-centered design can further enhance the sensory experience and overall wellness of occupants.
By facilitating connections between individuals and their surroundings, this approach encourages healthier lifestyles and strengthens social ties. Features such as green roofs, living walls, and nature-infused interiors not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also improve air quality and reduce stress, thereby promoting mental well-being and human-nature connection. Incorporating open spaces and adaptive strategies can further support a regenerative design approach.
Such initiatives have the potential to stimulate community engagement, uniting individuals for events and activities that celebrate local culture and heritage. As urban areas increasingly prioritize ecological sustainability, the merging of adaptive reuse with biophilic principles paves the way for innovative solutions that address urban challenges while nurturing the environment and enhancing the quality of life for all residents. These projects can also contribute to ecological restoration and climate-responsive design, promoting both environmental and social sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the concept of Adaptive Reuse of Buildings for Biophilic Designs and Sustainable Practices?
.jpg_11.jpeg)
The concept of Adaptive Reuse of Buildings for Biophilic Designs involves repurposing existing structures and incorporating elements of nature into the design to create a more sustainable and eco-friendly building. This approach promotes the use of sustainable materials and green building practices.
Why is Adaptive Reuse important for Biophilic Designs and Urban Planning?
Adaptive Reuse is important for Biophilic Designs because it allows for the preservation of existing structures, contributing to historic preservation and cultural heritage, while also promoting a connection to nature through the use of sustainable materials, ecological restoration, and the incorporation of natural elements in the design. This approach supports sustainable architecture and environmental stewardship.
What are some examples of Biophilic Designs in Adaptive Reuse projects?
Examples of Biophilic Designs in Adaptive Reuse projects include the conversion of old warehouses into green-roofed office spaces, the transformation of abandoned factories into urban gardens with vertical gardens and urban greening initiatives, and the renovation of historic buildings with natural lighting, daylighting, and natural ventilation systems. These projects exemplify sustainable practices, ecological footprint reduction, and urban revitalization.
How does Adaptive Reuse of Buildings for Biophilic Designs benefit the environment?
Adaptive Reuse of Buildings for Biophilic Designs benefits the environment by reducing the need for new construction and materials, which in turn decreases carbon emissions and promotes a more sustainable use of resources. This approach supports energy efficiency, building performance, and the circular economy by utilizing reclaimed materials and enhancing the ecological footprint of urban areas.
What are the challenges of implementing Adaptive Reuse for Biophilic Designs?
One of the main challenges of implementing Adaptive Reuse for Biophilic Designs is the need for careful planning and coordination between designers, architects, and engineers to ensure the building meets both functional and sustainable requirements. This process involves design innovation, site analysis, and adaptive strategies to enhance architectural adaptability and integrate biophilic elements effectively.
How can Biophilic Designs in Adaptive Reuse projects improve the well-being of occupants?
Biophilic Designs in Adaptive Reuse projects promote a connection to nature, which has been shown to reduce stress, improve mental health, and increase productivity and overall well-being of occupants. These designs often incorporate indoor plants, nature-based solutions, and sensory experience enhancements, contributing to wellness architecture, health and well-being, and the development of restorative environments.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário