The Role of Virtual Reality in Planning Biophilic Spaces.
Biophilic design, an essential component of environmental psychology, is increasingly recognized as an effective method for creating spaces that foster a connection between individuals and nature, thereby enhancing well-being and promoting ecological sustainability.
This article investigates the convergence of biophilic design and virtual reality, demonstrating how immersive technologies are revolutionizing the design process through advanced architectural visualization and spatial planning.
The integration of virtual reality in biophilic spaces offers numerous advantages, including enhanced visualization tools, interactive educational experiences, and sensory stimulation that enriches the perception of space.
Furthermore, this discussion will encompass real-world examples and future possibilities, emphasizing the potential of virtual reality to transform our interactions with the natural world through design thinking and nature integration.
What is Biophilic Design?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
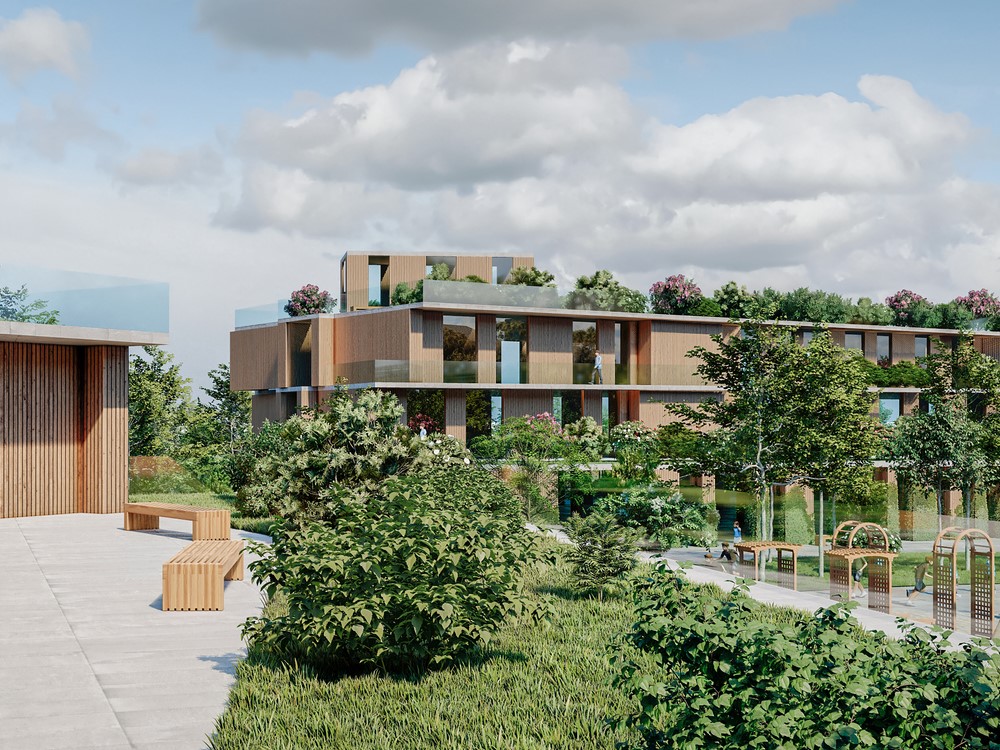
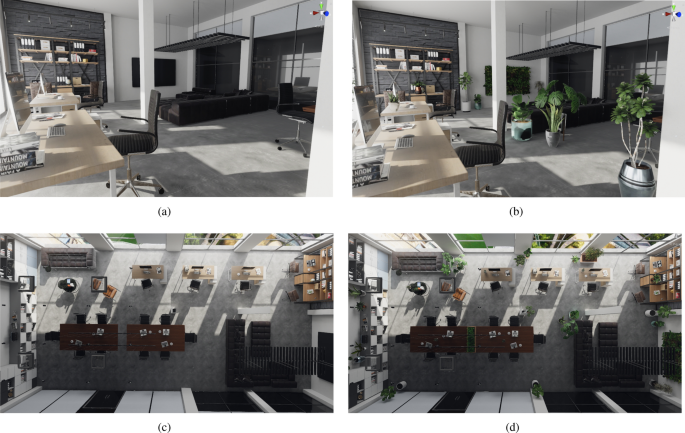
Biophilic Design represents an innovative approach that incorporates natural elements into architectural and urban environments to enhance psychological and emotional well-being. This design strategy emphasizes the crucial connection between individuals and nature, which has become increasingly important in contemporary urban settings where natural landscapes are often limited.
By integrating features such as natural light, greenery, and water elements, Biophilic Design aims to create immersive experiences that promote stress reduction, enhance user experience and emotional well-being, and improve overall quality of life through interaction with nature.
Additionally, it aligns with the principles of environmental sustainability and ecological footprint reduction, establishing itself as a vital component of modern landscape architecture and urban planning.
How Does Biophilic Design Benefit People and the Environment?
Biophilic Design offers numerous benefits for both individuals and the environment, establishing a harmonious relationship between human habitats and natural ecosystems through sustainable design and ecological sustainability. By promoting experiences with nature and enhancing spatial awareness, it facilitates cognitive benefits and interaction patterns, leading to improved focus and creativity.
The integration of green spaces, soundscapes, and biophilic elements can significantly reduce stress levels, stimulate sensory design, and enhance emotional well-being. From an environmental perspective, this design approach supports sustainability by fostering ecological restoration in urban areas, increasing biodiversity, improving air quality, and promoting habitat connectivity.
Research indicates that incorporating elements of nature into design processes can lead to an increase of up to 15% in productivity within workplace environments, highlighting its profound impact on user experience and user motivation. A study conducted by the University of Technology Sydney found that employees in biophilic settings reported a 37% reduction in stress and a 33% enhancement in overall satisfaction.
These benefits extend beyond mere aesthetics; they underscore the essential connection to nature that can promote healthier lifestyles, improved mental health, and foster community resilience. Embracing biophilic design not only enhances individual well-being and emotional response but also contributes to a sustainable future by enriching biodiversity, encouraging environmental stewardship, and reducing ecological footprint.
The Role of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design
Virtual Reality (VR) serves a transformative function in Biophilic Design by offering immersive experiences and design simulation that enable designers and users to engage with virtual environments prior to their physical construction.
Utilizing advanced 3D visualization techniques and three-dimensional modeling, VR allows designers to simulate biophilic elements within spaces, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these natural integrations can impact user experience, emotional response, and overall well-being.
Furthermore, it enhances the planning of community spaces by permitting stakeholders to offer real-time feedback on design concepts, thereby ensuring that the final product aligns with the intended emotional and cognitive benefits and addresses cultural significance.
How Does Virtual Reality Enhance the Design Process?
Virtual Reality (VR) significantly enhances the design process by equipping designers with innovative tools that improve interaction design and user experience design, ultimately resulting in more effective spatial planning and functional design. This technology allows designers to visualize concepts within a realistic context, facilitating rapid iteration based on user feedback, interaction patterns, and preferences, ensuring design effectiveness. Consequently, the integration of biophilic elements becomes more intuitive, ensuring that designs not only possess aesthetic appeal but also function effectively in terms of user engagement, sensory stimulation, and emotional response.
For instance, in a recent architectural project, designers utilized VR to simulate natural light patterns and soundscapes within a residential home, enabling clients to experience the space at various times of the day. This proactive engagement not only improved client satisfaction and user interaction but also led to design modifications that optimized energy efficiency and space utilization.
By employing interactive prototyping and simulation tools, both architects and product designers can explore a range of styles and layouts, fostering a genuine sense of ownership and place attachment among users. This user-centered design approach ensures that the final designs accurately reflect actual needs and preferences, paving the way for enhanced innovation and usability within the industry.
What are the Limitations of Using Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design?
While Virtual Reality (VR) offers numerous advantages in the realm of Biophilic Design, it also presents specific limitations that may impede its widespread adoption and effectiveness, particularly affecting participation in public spaces.
Factors such as the high costs associated with advanced VR technology, alongside accessibility issues for certain user groups, can restrict its implementation across various projects, affecting stakeholder engagement and community involvement. Additionally, the accuracy of virtual prototyping may be affected by technological constraints, which may not always capture the nuances of real-world environmental interactions, thereby limiting the depth of interaction with nature and nature immersion.
The rapid evolution of VR technology can result in significant obsolescence and adaptability challenges, leading organizations to view financial investments as precarious. Furthermore, the learning curve associated with utilizing VR tools poses another challenge, particularly for individuals who are not well-versed in digital technologies, affecting experiential learning and participatory design.
However, viable solutions do exist. Investing in user-friendly VR platforms and pursuing grants or subsidies aimed at enhancing accessibility, alongside fostering collaborative design with technology firms, can help mitigate these challenges. Furthermore, fostering partnerships with technology firms could facilitate resource sharing, promoting both innovation and inclusion in the integration of VR within Biophilic Design, and enhancing cultural significance of nature-based solutions.
Examples of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design
Numerous examples illustrate the significant integration of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design, demonstrating its ability to transform spaces into immersive experiences and virtual environments that cultivate a deeper connection with nature.
Through design simulation and architectural visualization, Virtual Reality enables designers and clients to explore potential projects prior to their realization, thereby enhancing user engagement, community involvement, and providing a platform for community feedback.
These applications exemplify how virtual environments can be customized to embody the ecological concepts inherent in Biophilic Design, ultimately rendering spaces more inviting, sustainable, and aligned with restoration ecology.
1. Virtual Reality Walkthroughs of Biophilic Spaces
.jpg_01.jpeg)
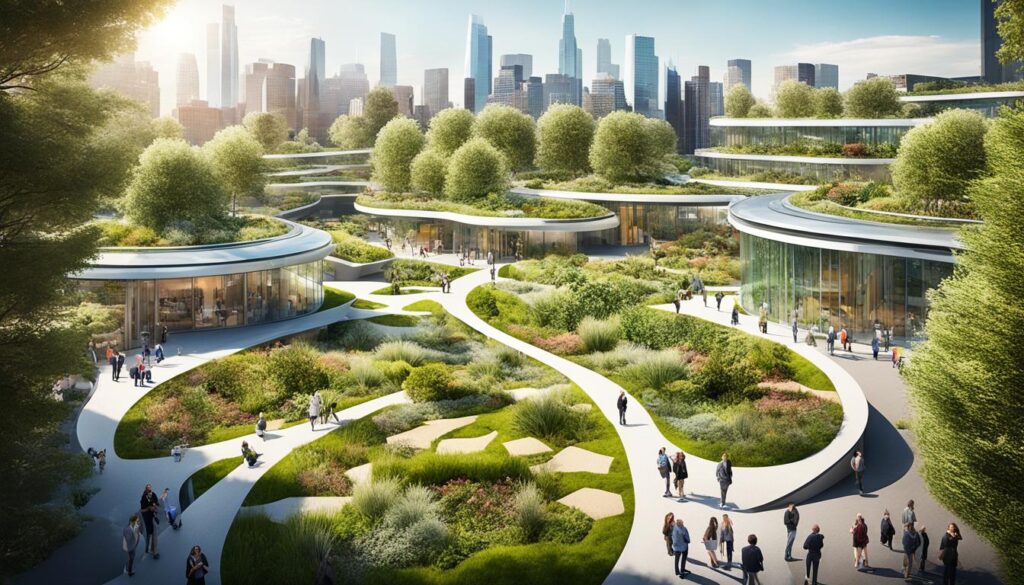
Virtual reality walkthroughs represent a transformative method for experiencing biophilic spaces prior to their construction, offering users an immersive preview of their future environments through interactive landscapes. This innovative approach significantly enhances the user experience by enabling individuals to navigate through virtual landscapes that incorporate natural elements, greenery, and nature therapy, thereby fostering a sense of place attachment and anticipation.
By simulating real-world interactions within these environments, designers are able to gather invaluable user feedback and refine their concepts to better align with user needs and design outcomes.
These digital explorations facilitate the visualization of cutting-edge design features, such as adaptive lighting that replicates the changing patterns of sunlight filtering through foliage, or water elements that produce soothing auditory effects, contributing to therapeutic landscapes.
For example, successful applications in urban architecture have enabled developers to engage stakeholders and foster community resilience by presenting communal gardens and open parks before the construction phase begins.
By prioritizing user engagement and interaction patterns, virtual walkthroughs ensure that the final designs resonate with the community, ultimately resulting in spaces that promote well-being, comfort, and sustainability. This aligns with the increasing trend towards nature-inspired environments.
2. Interactive Virtual Reality Experiences for Education and Training
Interactive Virtual Reality experiences represent significant educational tools and training tools, allowing individuals to engage with biophilic principles in a tangible manner, enhancing experiential design. These immersive programs offer participants experiences that foster environmental awareness, ecological sustainability, and sustainability while facilitating user feedback to refine educational content and design evaluation.
By establishing an engaging learning environment, these experiences enhance the understanding of ecological concepts, urban ecology, and underscore the importance of integrating nature into urban design.
The incorporation of VR technology in educational settings cultivates a sense of presence, enabling users to explore virtual environments that replicate natural settings and explore rural-urban interface. This approach not only deepens the comprehension of biophilic design, design principles, and habitat design but also encourages learners to contemplate their relationship with the environment, enhancing restorative environments.
Participants frequently report increased motivation and engagement, which contributes to improved knowledge retention and enhanced user experience. Furthermore, the inclusion of real-time feedback mechanisms allows educators to evaluate participants’ understanding of these principles and adapt the VR content as needed, ensuring that the learning experience remains relevant and impactful for diverse audiences through interactive landscapes and nature immersion.
3. Virtual Reality Simulations for Testing and Feedback: Enhancing User Engagement and Environmental Awareness
Virtual Reality simulations serve as an effective platform for testing design concepts and gathering user feedback, enabling designers to assess the psychological impact of biophilic elements on users within a controlled environment. By simulating various scenarios and interactions in user-centric spaces, designers can refine their strategies to enhance emotional well-being and user satisfaction. This iterative process is essential to ensure that the final design resonates with the intended audience while adhering to the principles of Biophilic Design and promoting environmental awareness.
These simulations facilitate immersive experiences that allow individuals to interact with proposed elements, such as natural light, greenery, and soundscapes, while their responses are monitored through various testing methods, including surveys and biometric feedback. This approach supports sensory stimulation and enhances the user interface design.
By carefully analyzing this data, designers can make informed decisions that align with principles rooted in environmental psychology, ultimately creating spaces that foster a stronger connection between users and their environments. The outcomes derived from this user-centric approach not only inform design choices but also lead to innovations that promote sustainable design practices, ensuring that the resulting spaces are both functional and enriching, with a focus on cognitive benefits and well-being.
How Can Virtual Reality Improve the Implementation of Biophilic Design?
Virtual Reality (VR) possesses the capacity to substantially enhance the application of Biophilic Design by improving architectural visualization techniques and offering a more accessible platform for stakeholders to engage with design concepts, promoting increased stakeholder engagement and interaction with nature.
By enabling realistic virtual representations of spaces, VR facilitates clearer communication of design intentions, which can lead to improved decision-making and collaboration among designers, clients, and the community, thus enhancing interaction design and emotional response.
Furthermore, the cost and time efficiencies associated with virtual prototyping can render the process of integrating biophilic elements more effective and streamlined, supporting sustainable design and ecological sustainability.
1. Improved Visualization and Communication: Bridging the Outdoor-Indoor Connection
One of the most significant advantages of employing Virtual Reality (VR) in Biophilic Design is the enhanced visualization and communication it provides for designers and stakeholders. By offering a three-dimensional immersive experience, VR enables users to engage with spaces as if they were physically present, thereby facilitating clearer communication of design concepts and intentions, and improving spatial awareness and the perception of space.
This improved visualization can lead to more well-considered choices processes and promote greater collaboration in the creation of user-centric environments that emphasize the integration of nature, fostering user motivation and place attachment.
In an era where design innovation relies heavily on stakeholder engagement, VR unveils creative ideas by allowing participants to navigate virtual environments that emulate real-life scenarios. This direct interaction transforms feedback mechanisms, making it easier for users to articulate their preferences and concerns, thereby ensuring that designs accurately reflect their needs and aspirations, and enhancing participatory design and community involvement.
By prioritizing user-centric designs, VR not only enhances collaboration but also fosters a deeper understanding of how natural elements can be seamlessly integrated into built environments. Ultimately, this approach results in spaces that resonate with both functionality and emotional well-being, supporting therapeutic landscapes and restorative environments.
2. Cost and Time Savings
The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) within the Biophilic Design process presents significant opportunities for cost and time savings, thereby streamlining the workflow from conception to implementation, while enhancing design processes and spatial dynamics.
Virtual prototyping enables designers to rapidly explore multiple design iterations, which reduces the necessity for physical models and minimizes project delays. This enhanced efficiency not only decreases expenses but also facilitates more agile responses to user feedback and design adjustments, ultimately resulting in improved overall outcomes, supporting innovative design and design effectiveness.
By employing immersive simulations, teams are able to visualize environmental impacts and spatial relationships in real-time, thereby fostering collaboration and creativity. For instance, architects can deliver virtual walkthroughs to clients, which supports more well-considered choices and promotes earlier involvement from stakeholders, enhancing collaborative design and digital twin applications.
These practices not only enhance communication but also mitigate the risks associated with misinterpretation of design concepts. Furthermore, this innovative approach accelerates the approval process, ensuring that project timelines remain intact while simultaneously reducing labor costs associated with revisions, supporting functional design and safety.
Ultimately, by adopting VR technology in the design landscape, firms can sustain a competitive edge and achieve sustainable project delivery, contributing to ecological sustainability and habitat connectivity.
3. Increased Accessibility and Inclusivity: Enhancing User Interface and Spatial Planning
.jpg_10.jpeg)
Virtual Reality significantly enhances accessibility and inclusivity in Biophilic Design by enabling diverse user groups to engage with design concepts in an interactive manner. By facilitating immersive experiences in virtual environments, individuals with varying abilities can actively participate in the design process, ensuring that spaces are appropriately tailored to meet diverse needs and enhancing spatial planning and sensory design.
This user-centric approach promotes increased community engagement and collaboration, ultimately resulting in designs that are more welcoming and representative of the community’s diversity, supporting community resilience and cultural significance.
Through the application of user-centered design principles, Virtual Reality empowers stakeholders to gather feedback from a wide range of users, including those with disabilities, the elderly, and culturally diverse groups. For example, a community center may employ VR simulations to allow prospective users to visualize and interact with the space prior to construction, fostering discussions that address everyone’s unique requirements, enhancing community involvement and design outcomes.
Such dynamic interactions not only enhance the design outcomes but also strengthen community relationships through collaboration, ensuring that the final solution reflects the contributions of all parties involved, supporting interaction patterns and place-making.
Future Possibilities of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design and Urban Planning
The future of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design presents significant opportunities for innovation, particularly in the incorporation of biophilic materials and technologies within the realm of urban planning and landscape architecture.
As VR technology continues to evolve, designers will increasingly have the capability to develop customized biophilic environments that cater to the specific needs and preferences of individual users. This trend represents a transition towards more sustainable design practices that prioritize user well-being and ecological sustainability while simultaneously addressing ecological challenges within urban contexts, enhancing habitat design and urban ecology.
1. Virtual Reality Integration with Biophilic Materials and Technology: Enhancing Sensory Stimulation and Nature-Based Solutions
The integration of Virtual Reality with biophilic materials and technology is set to transform the approach designers take in creating nature-centric spaces. By employing advanced simulation techniques, designers are able to assess the performance and aesthetic qualities of various materials within virtual environments, ensuring alignment with the principles of Biophilic Design. This innovative method not only enhances design innovation but also promotes sustainability by facilitating the selection of materials that have a positive impact on environmental ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and environmental impact assessments.
Consider a scenario in which architects utilize Virtual Reality to experiment with materials such as reclaimed wood, living walls, or algae-based composites, all while evaluating their ecological footprints in a simulated environment. This process supports design evaluation and landscape simulations.
Furthermore, technologies like augmented reality can enable real-time modifications to biophilic designs, providing immediate feedback on how different textures and colors interact with natural light, enhancing visual perception and aesthetics.
By incorporating these advanced tools, designers can cultivate a deeper connection to nature, ultimately resulting in the creation of spaces that are not only visually appealing but also contribute to the well-being of both users and the planet, supporting nature therapy and restorative environments.
These innovations represent a significant advancement toward sustainable design that prioritizes harmony with the natural world, enhancing ecological footprint considerations and habitat connectivity.
2. Virtual Reality for Biophilic Design in Urban Planning: Enhancing Public Spaces and Community Involvement
The application of Virtual Reality (VR) in urban planning offers significant opportunities for the integration of Biophilic Design principles within community spaces. By visualizing urban environments that are enriched with natural elements and ecological concepts, planners can develop more engaging and sustainable public spaces. This immersive approach not only enhances user experience and mental health but also promotes community involvement in the design process, ensuring that the needs and preferences of residents are thoroughly addressed through participatory design and interaction with nature.
For example, a recent project in a major metropolitan area employed VR technology to simulate a park designed with indigenous plant species and natural waterways. By enabling residents to navigate through the virtual environment, feedback sessions were conducted to gather insights into their preferences, allowing planners to tailor design features that align with the community’s ecological values, enhancing nature-based solutions and community spaces.
Successful implementations of VR have demonstrated how virtual reconstructions of spaces can incorporate features such as green roofs and urban forests, thereby enhancing biodiversity, promoting mental well-being, and providing therapeutic landscapes that integrate natural elements seamlessly.
With each innovative application, it becomes increasingly clear that this technology possesses the potential to bridge the gap between conceptual planning, spatial planning, and real-world ecological integration in urban settings, thereby enhancing urban ecology and sustainable design.
3. Virtual Reality for Personalized Biophilic Spaces and Nature-Based Solutions
The future of Virtual Reality in Biophilic Design encompasses the development of personalized biophilic environments that address individual preferences and promote emotional well-being. By utilizing user data and feedback, designers can employ VR technology to customize spaces that align with users’ desires for integration with nature, thereby enhancing their connection to the environment and supporting mental health through nature immersion.
This personalized approach not only enhances user satisfaction but also cultivates a deeper sense of place attachment, emotional engagement, and user motivation.
Incorporating advanced technologies, such as machine learning and biometric sensors, enables real-time adjustments based on users’ emotional states and physical interactions. For example, methodologies like user journey mapping can reveal how various biophilic elements—such as natural lighting, water features, plant life, and soundscapes—affect mood, cognitive benefits, and overall well-being.
By prioritizing user-centric design principles and human-centered design, these immersive environments can be specifically tailored to evoke targeted emotional responses, thus promoting tranquility and alleviating stress through nature therapy and restorative environments.
Ultimately, this integration of innovation and nature creates spaces that not only support emotional well-being and ecological sustainability but also encourage a meaningful connection to the natural world, enhancing spatial awareness and environmental psychology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of virtual reality in planning biophilic spaces and landscape architecture?
.jpg_11.jpeg)
Virtual reality allows designers and planners to experience and visualize biophilic design elements in a simulated environment, helping them make informed decisions and create more effective biophilic spaces through advanced architectural visualization and spatial dynamics.
How does virtual reality help in the planning process of biophilic spaces and interactive landscapes?
Virtual reality offers a more immersive and interactive experience compared to traditional 2D renderings, allowing planners to better understand the spatial relationships, spatial awareness, and potential impacts of biophilic elements on the overall design, fostering place-making and experiential design.
Can virtual reality be used to test and refine biophilic design concepts and design strategies?
Yes, virtual reality simulations can be used to test and refine biophilic design concepts and design strategies before they are implemented, saving time and resources in the planning process, and enhancing design effectiveness and design outcomes.
What are the benefits of using virtual reality in planning biophilic spaces and public spaces?
Virtual reality enables designers and planners to visualize and experience biophilic elements in a realistic and interactive way, leading to more effective and intentional biophilic design solutions that enhance user engagement and spatial utilization.
How can virtual reality enhance the user experience and perception of space in biophilic spaces?
By using virtual reality, designers can simulate the sensory and physiological responses of individuals in biophilic spaces, allowing them to create more impactful and engaging environments for users, which enhances sensory stimulation and user interaction with nature.
Is virtual reality widely used in the planning of biophilic spaces and interactive landscapes?
While still a relatively new technology in the field of design, virtual reality is increasingly being used in the planning process of biophilic spaces and interactive landscapes due to its ability to provide a more immersive and accurate representation of the final design, promoting innovative design and user-centered design.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário