New Frontiers: Biophilic Design in Extreme Urban Environments.
In an increasingly urbanized world, the integration of nature into our cities is more essential than ever. **Biophilic design** presents a novel approach to enhancing urban living by fostering a reconnection between individuals and the **natural environment**, emphasizing the importance of **nature integration** and **urban ecology** in **sustainable cities**.
This article delves into the fundamental principles of biophilic design, its significance within urban areas, and the numerous benefits it provides to **city dwellers**. We will address the challenges encountered when implementing these concepts in highly urbanized settings and showcase real-life examples of **successful integration**.
Furthermore, we will explore the future of biophilic design as an essential strategy for addressing **climate change**, **urban resilience**, and the ongoing **urbanization challenge**. This examination will reveal how **nature-infused spaces** can profoundly transform our cities and enhance our **quality of life**.
What is Biophilic Design?
.jpg_00.jpeg)
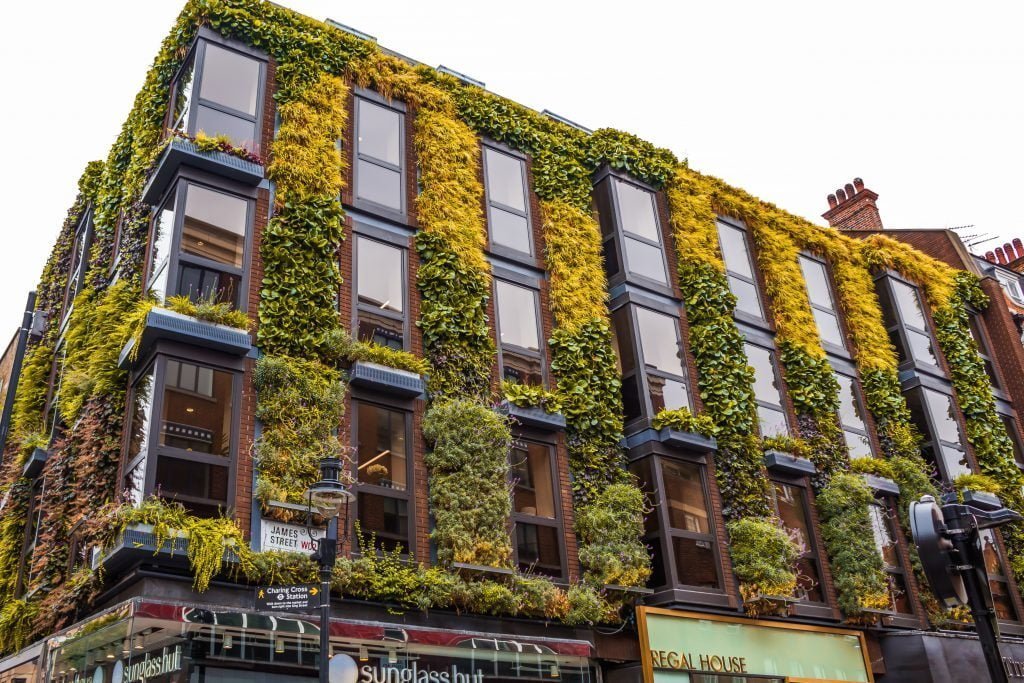
Biophilic design represents a progressive approach in architecture and urban planning, aimed at enhancing the connection between humans and nature by integrating natural elements within the built environment, especially in densely populated urban areas, through **living architecture** and **sustainable architecture** practices.
This design philosophy underscores the significance of incorporating natural materials, green spaces, **green infrastructure**, and biophilic features into everyday life, thereby promoting psychological well-being and **resilience** in urban contexts.
By emphasizing the connectivity to nature and sustainable architectural practices, biophilic design endeavors to create **restorative environments** that enhance the quality of life, promote **ecological awareness**, and foster environmental sustainability for communities residing in urban settings.
What are the Principles of Biophilic Design?
The principles of biophilic design are centered on enhancing the human experience by incorporating elements that foster a profound connection to nature, optimize sensory experiences, and promote environmental psychology within urban spaces, contributing to the **health and well-being** of urban residents.
These principles encompass the use of natural light, **green infrastructure**, and community engagement to develop outdoor areas that support **urban biodiversity** and overall well-being, enhancing the **aesthetic appeal** and **ecological integrity** of cities.
By integrating features such as living walls and roof gardens, urban designers can create vibrant habitats that not only improve air quality but also yield aesthetically pleasing landscapes that attract individuals. Nature-inspired design transcends mere aesthetics; it emphasizes the use of organic shapes, **local materials**, and natural materials to evoke a sense of calm and tranquility while promoting **environmental psychology**.
Communal gardens and park spaces can serve as focal points for community interactions, fostering social connections while also providing habitats for local wildlife. These elements work in concert to establish sustainable urban environments that prioritize both **ecological health**, **human-nature connection**, and human flourishing, promoting **social interaction** and community resilience.
Why is Biophilic Design Important in Urban Environments?
Biophilic design plays a crucial role in urban environments, particularly in areas characterized by extreme urban conditions. It promotes **urban biodiversity** and enhances community resilience against the impacts of climate change, supporting **urban wildlife** habitats.
By incorporating natural elements into urban planning—such as green spaces, **urban forestry**, and urban forests—biophilic design not only improves air quality but also fosters health benefits and **well-being metrics** among residents.
This approach mitigates the effects of **urban heat islands** and enhances the overall livability of cities, thereby making them more adaptable to changing climatic conditions through **climate adaptation** strategies.
What are the Benefits of Biophilic Design in Cities?
The benefits of biophilic design in urban environments are diverse and significant, contributing to the improvement of urban ecosystems, the enhancement of community well-being, and the elevation of the aesthetic value of public spaces.
By promoting connectivity with nature and integrating features such as green roofs, community gardens, **public parks**, and urban agriculture, biophilic design creates an environment that supports urban wildlife while enhancing the overall quality of life for residents through **mindfulness in design**.
This innovative approach not only promotes mental health by alleviating stress and anxiety but also fosters **urban social equity** by creating inclusive spaces that are accessible to all individuals, promoting **psychological benefits** and community cohesion.
Additionally, through the incorporation of natural elements, cities can achieve economic sustainability, as biophilic design tends to increase property values, attract tourism, and reduce the **ecological footprint** of urban areas.
These designs act as catalysts for community engagement, facilitating connections among residents and between individuals and their environment, thereby strengthening social ties.
The positive impacts of biophilic design extend well beyond mere aesthetics, fundamentally transforming urban spaces to support a harmonious coexistence between people and nature.
How Does Biophilic Design Improve Quality of Life in Urban Areas?
Biophilic design plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of life in urban environments by integrating elements such as urban greenery, nature therapy, and **restorative spaces** that promote both physical and mental well-being through **nature immersion**.
This design philosophy not only improves aesthetic appeal but also offers significant psychological advantages, fostering a sense of tranquility and a deeper connection to nature among urban residents.
By incorporating natural elements into the urban landscape, individuals can experience reduced stress levels and enhanced mental clarity. Access to parks and green spaces encourages outdoor activities, thereby promoting social interactions that strengthen community bonds. Nature therapy supports emotional healing, while restorative environments provide a refuge from the demands of daily life.
As cities increasingly acknowledge the value of such designs, they have the potential to evolve into vibrant ecosystems where residents can flourish, feeling rejuvenated and uplifted by their surroundings, experiencing the **cultural significance** of biophilic spaces.
Ultimately, the integration of urban greenery is fundamental to fostering a healthier lifestyle, underscoring the essential connection between nature and well-being.
What are the Challenges of Implementing Biophilic Design in Extreme Urban Environments?
.jpg_01.jpeg)
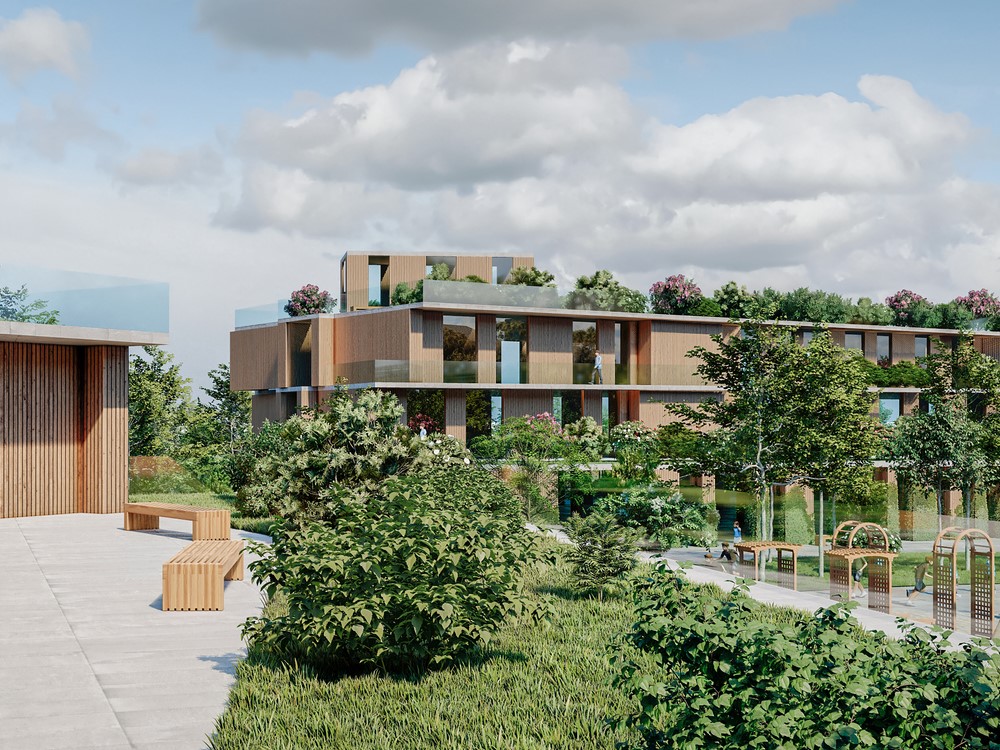
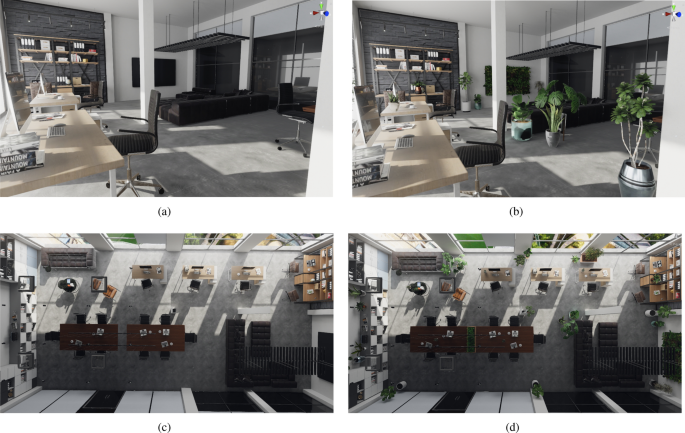
The implementation of biophilic design in extreme urban environments poses a variety of challenges that urban planners and architects must address. These challenges include space constraints, regulatory obstacles, and the necessity for **climate resilience** and adaptation through **nature-based solutions**.
Successfully navigating these issues necessitates innovative design approaches that harmonize the integration of natural elements with the requirements of densely populated areas, where the availability of green spaces and **sustainable architecture** is often constrained, requiring **ecological design**.
What are the Limitations of Biophilic Design in Highly Urbanized Areas?
The limitations of biophilic design in highly urbanized areas are frequently influenced by factors such as extensive urbanization, significant environmental impact, and insufficient community engagement in the planning process. These constraints can impede the successful integration of green spaces and natural elements within the urban fabric, thus affecting the overall efficacy of biophilic design initiatives and **health promotion** efforts.
In densely populated cities, the unyielding demand for space often leads to competing priorities, complicating efforts to allocate areas for ecological restoration, **green corridors**, or **green infrastructure**.
Additionally, the high costs associated with the implementation of sustainable features can present a considerable barrier, particularly in communities that are grappling with budget constraints or economic challenges.
Furthermore, the lack of involvement from local residents in the decision-making process may foster a sense of disconnection, ultimately diminishing the perceived value of biophilic elements. Without addressing these environmental, social, and economic limitations, the potential advantages of biophilic design may remain unfulfilled, leaving urban residents yearning for a connection to nature.
How Can Biophilic Design be Adapted to Extreme Urban Environments?
Adapting biophilic design to extreme urban environments necessitates the implementation of nature-based solutions tailored to the unique characteristics and challenges inherent in these settings. Through site-specific design strategies, urban planners can develop innovative green infrastructure, such as living walls and advanced water management systems, to enhance urban resilience and promote ecological sustainability.
For example, the integration of vertical gardens on high-rise buildings can effectively mitigate the urban heat island effect while providing essential habitats for local wildlife. The introduction of rain gardens, **water features**, and permeable pavements not only improves water management practices but also supports biodiversity by creating sanctuaries for native plants and wildlife amid concrete landscapes, contributing to **habitat restoration**.
These adaptive solutions serve to mitigate the impacts of climate change while concurrently creating visually appealing environments that engage community members, fostering a strengthened connection to nature, even in densely populated areas through **place-making**.
By prioritizing such transformations, cities can cultivate greener, more resilient ecosystems capable of thriving despite urban challenges.
What are Some Examples of Biophilic Design in Extreme Urban Environments?
Numerous instances of biophilic design in highly urbanized environments demonstrate the significant potential of architectural innovation to transform urban spaces into vibrant, nature-rich areas, through **nature-inspired innovation** and **mixed-use developments**.
These projects frequently emphasize urban regeneration and incorporate elements such as green roofs, living walls, and community gardens, which promote biodiversity and enhance the overall livability of cities.
How Have Cities Successfully Incorporated Biophilic Design?
Cities have successfully incorporated biophilic design by utilizing **adaptive reuse** of existing structures, integrating **vertical gardens** and **natural ventilation** to enhance **energy efficiency** and urban cooling, and fostering **community spaces** for **outdoor experiences** and **active transportation**.
Cities worldwide have effectively integrated biophilic design principles into their urban planning strategies, demonstrating the advantages of enhanced urban ecosystems and increased community engagement.
By incorporating green spaces, sustainable architecture, and connectivity with nature, these sustainable cities have significantly improved the overall quality of life for their residents and fostered more resilient urban environments, enhancing overall urban ecology.
Through various initiatives, including the establishment of community gardens, green roofs, and urban parks as vibrant community spaces, these urban centers have not only provided ecological benefits but have also cultivated a sense of belonging and pride among their residents.
For example, cities like Singapore and Amsterdam have prioritized nature-based solutions that promote biodiversity, subsequently enhancing mental well-being and encouraging social interaction through outdoor spaces and nature immersion.
These strategies have been shown to mitigate urban heat, improve air quality, and provide recreational spaces, thereby reintegrating natural elements into the urban landscape through nature integration and urban cooling.
Consequently, communities are experiencing not only a healthier public realm but also a strengthened connection to their shared environment, fostering ecological awareness and environmental sustainability.
What Are the Key Features of Biophilic Design in Urban Spaces?
.jpg_10.jpeg)
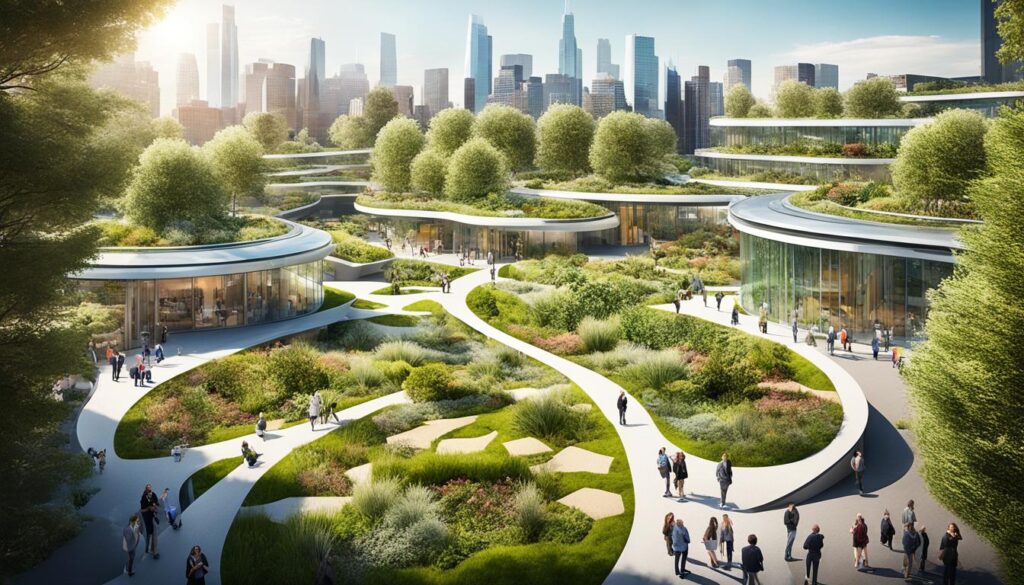
Key features of biophilic design in urban environments encompass the integration of green infrastructure, the promotion of nature connectivity, and the utilization of eco-friendly materials, all of which enhance the human-nature relationship. These elements not only improve the aesthetic appeal of urban spaces but also contribute to urban biodiversity and promote the overall health and wellness of the community.
For example, urban forests function as vital green lungs, purifying the air while providing habitats for a variety of species. Living walls, adorned with thriving plants, create visually appealing environments and assist in mitigating heat and regulating humidity levels in densely populated areas.
Additionally, innovative water management systems, such as rain gardens and permeable pavements, effectively manage stormwater, thereby reducing runoff and mitigating the risks of flooding, which is crucial for climate adaptation and resilience.
By adopting these principles, cities can cultivate a more sustainable and resilient ecosystem, encouraging residents to experience the myriad psychological and physical benefits derived from a closer interaction with nature and human-nature connections.
What is the Future of Biophilic Design in Extreme Urban Environments?
The future of biophilic design in extreme urban environments appears promising, as cities increasingly acknowledge the necessity for sustainable solutions to address climate change mitigation and enhance urban resilience through adaptive reuse and sustainable architecture.
Advances in design and technology are facilitating the more effective integration of natural elements into urban planning, thereby contributing to healthier and more sustainable living conditions for future generations.
How Can Biophilic Design be Used to Address Climate Change and Urbanization?
Biophilic design presents a viable approach to addressing the challenges posed by climate change and urbanization through the implementation of nature-based solutions. These solutions can mitigate urban heat islands, improve air quality, and promote environmental sustainability.
By integrating green infrastructure and sustainable practices into urban planning, cities can enhance their resilience and adaptive capacity in response to climate-related challenges, fostering restorative environments and sustainable urban design principles.
Such an approach fosters the creation of welcoming spaces that prioritize human well-being while concurrently restoring essential ecosystems. The integration of features such as green roofs, urban forests, and permeable surfaces not only alleviates flooding but also provides crucial habitats for diverse wildlife.
Furthermore, cities can harness renewable energy sources through innovative designs that facilitate passive solar heating and natural ventilation. These strategies not only address the adverse effects of climate change but also enrich the social fabric of communities by cultivating healthier, more livable environments that encourage active lifestyles and strengthen connections with nature.
What Are the Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Biophilic Design in the Future?
The future of biophilic design presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities, as urban planners and architects must effectively navigate complex urban dynamics while fostering community engagement and promoting environmental equity.
Emphasizing participatory design approaches can significantly enhance the effectiveness of biophilic solutions, leading to successful outcomes that benefit both communities and urban ecosystems through urban social equity and community engagement.
Integrating nature into urban environments necessitates addressing considerable hurdles, including funding constraints, regulatory frameworks, and the diverse needs of the population, ensuring environmental equity and inclusive design.
These challenges demand innovative urban planning strategies that prioritize sustainability, ecological footprint reduction, and inclusivity.
By actively engaging local communities in the design process, planners can identify specific environmental needs, encourage stewardship, and leverage local knowledge, fostering cultural significance and habitat restoration.
Consequently, urban landscapes can become more resilient and responsive, providing healing spaces that promote overall well-being and environmental equity, thus ensuring that the advantages of biophilic designs are accessible to all residents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Biophilic Design?
.jpg_11.jpeg)
Biophilic Design is a concept that focuses on incorporating elements of nature into the design of built environments. This can include natural materials, vegetation, and other elements that create a connection to the natural world.
Why is Biophilic Design important in extreme urban environments?
In extreme urban environments, there is often a lack of natural elements and green spaces. Biophilic Design aims to bring aspects of nature into these environments to improve the well-being and quality of life for those living there.
What are some examples of Biophilic Design in extreme urban environments?
Examples of Biophilic Design in extreme urban environments can include green roofs, vertical gardens, and the use of natural materials such as wood and stone in building design, promoting aesthetic harmony and place-making.
How does Biophilic Design benefit individuals in urban environments?
Biophilic Design has been shown to have numerous benefits for individuals living in urban environments, including improved mental and physical health, increased productivity and creativity, and reduced stress and anxiety, aligning with nature therapy and mindfulness in design.
Is Biophilic Design only for new buildings or can it be incorporated into existing structures?
Biophilic Design can be incorporated into both new and existing buildings through renovations and retrofits, emphasizing adaptive reuse. It is not limited to new constructions and can be applied to any built environment.
Are there any downsides to Biophilic Design in extreme urban environments?
One potential downside to Biophilic Design in extreme urban environments is the cost of implementing these designs. However, the long-term benefits for individuals and the environment may outweigh the initial costs.

I’m Bruno, an architect with a deep passion for Biophilic Design in Urban Architecture. Throughout my career, I’ve focused on integrating natural elements into urban planning, and I created this site to share my insights and foster a deeper understanding of how biophilic principles can significantly enhance urban living. Dedicated to sustainable development, I continually explore innovative design solutions that promote both environmental and human well-being in city landscapes.













Publicar comentário